The Evolution from Strings to Things
The era of simple keyword matching is rapidly fading. Traditional SEO, once a battle for specific word strings, has given way to a more sophisticated understanding of information. Entity-based SEO represents this profound shift, moving beyond literal keyword presence to the comprehension of concepts and their intricate relationships. Search engines are no longer mere indexers of text; they function as advanced discovery engines, deciphering user intent by recognizing real-world "things"—people, places, organizations, and abstract ideas.
Consider a search for "apple": the engine distinguishes between the fruit, the tech company, or even a specific variety based on contextual signals. This evolution is currently indispensable for achieving sustained organic growth, as it directly aligns with how modern algorithms process information. Field observations indicate that content optimized for entities consistently outperforms purely keyword-driven approaches in relevance and visibility. For a comprehensive overview, see entity-based SEO. Embracing this shift promises several entity based seo benefits:
- Richer content experiences for users.
- Stronger semantic authority for your brand.
- Greater adaptability to future search algorithms.
How Entities Differ from Traditional Keyword Research
Traditional keyword research primarily focuses on identifying specific text strings users type into search engines. These are literal words or phrases, often leading to content optimized for exact-match density. In contrast, entities are conceptual "things"—real-world objects, people, places, events, or abstract ideas—that search engines understand as distinct, identifiable concepts with unique attributes and relationships.
Consider the term "Apple." In a traditional keyword approach, it is just a string. However, for an entity-aware search engine, "Apple" could refer to the fruit, the technology company, or even a record label. Search engines currently use complex algorithms and their knowledge graphs to apply contextual understanding, disambiguating the term based on other words in the query, user intent signals, and related entities within the content itself. This shift represents a move from keyword matching to semantic understanding.

This fundamental difference means SEO strategy has evolved. The focus is no longer on simply repeating keywords, but on establishing topical relevance and depth by thoroughly exploring an entity and its connections. In my experience, a common mistake is content still being optimized for outdated keyword density metrics. Such content often fails to rank because it lacks the comprehensive, interconnected understanding that entity-based algorithms now demand. Instead, practical experience shows that content demonstrating a holistic grasp of a topic—by referencing and relating multiple relevant entities—consistently achieves higher visibility and authority. In my view, this approach offers a far more robust and future-proof strategy for search engine optimization.
Primary Advantages for Search Visibility and Rankings
Leveraging the fundamental shift from literal text strings to conceptual entities yields profound entity based seo benefits for search visibility. Field observations indicate that content optimized around a robust network of interconnected entities establishes superior topical authority. This comprehensive understanding of a subject area leads to improved ranking stability, making your content less vulnerable to minor algorithmic adjustments because search engines trust its depth.
Furthermore, technical data suggests that clearly defined and contextually relevant entities significantly enhance visibility in prominent SERP features. This includes higher chances of appearing in rich snippets and Knowledge Panels, as search engines can readily extract and display structured information about the concepts discussed. For example, a detailed entity map for a comparison of "smartphones" helps populate direct answer boxes with specific model attributes.
Practical experience shows that an entity-centric approach inherently aligns better with complex user intent and the nuances of natural language queries. By understanding the relationships between concepts, content can anticipate and answer implicit questions, providing more satisfying and comprehensive results than strategies focused solely on exact keywords. This ensures your content is understood and delivered for both explicit and underlying search needs.
A Comprehensive Guide to Implementing Entity-Based Strategies
Transitioning from understanding the theoretical benefits of entity-based SEO to its practical application requires a structured approach. Implementing these strategies effectively can seem daunting at first, as it requires moving beyond familiar keyword-centric workflows. This section outlines actionable steps to integrate entity understanding into your content and technical SEO efforts.
- Challenges: Identifying relevant entities and consistently structuring content.
- Outcomes: Enhanced topical authority and improved visibility in complex search queries.
Consider a content team tasked with ranking for "sustainable urban development." Instead of merely optimizing for this phrase, an entity-based approach would involve identifying related entities like "green infrastructure," "smart cities," "circular economy," and "public transportation," then building comprehensive content around their interconnections.
The Entity Mapping & Content Blueprint
To systematically integrate entities, professionals can follow a clear blueprint that spans research, content structuring, and technical implementation.
1. Foundational Entity Research
The initial step involves identifying the core entities relevant to your topic and understanding their relationships. While traditional keyword research focuses on search volume and competition, entity research delves into semantic connections. Tools like Google's Natural Language Processing (NLP) API are invaluable here. By inputting your existing content or competitor content, the API can highlight recognized entities and assign them a salience score, indicating their prominence within the text.
Practical experience shows that supplementing API analysis with manual exploration of resources like Wikipedia, Wikidata, and knowledge panels for related topics can uncover a richer web of associated entities. The goal is not just to list entities but to map their hierarchy and interdependencies. For instance, "electric vehicles" is an entity, but so are "lithium-ion batteries," "charging infrastructure," and "sustainable transportation," all of which are intricately linked.
2. Structuring Content Around Entity Salience
Once entities are identified, content creation shifts from keyword stuffing to entity-centric writing. Entity Salience dictates how prominently an entity should feature in your content. High-salience entities should be introduced early, frequently discussed, and given dedicated sections or paragraphs. Related, lower-salience entities provide supporting context and depth.
Field observations indicate that content structured around a central entity, with supporting entities woven throughout, naturally achieves greater topical authority. This means ensuring your content comprehensively covers the facets of an entity, answering potential user questions and exploring its relationships with other relevant concepts. This approach often leads to longer, more authoritative pieces that satisfy complex user intent, a key factor in current search algorithms.
3. Advanced Schema Markup Implementation
Schema Markup is critical for explicitly communicating entity relationships to search engines. Beyond basic Article or Product schema, implementing advanced properties like SameAs, Mentions, and About significantly enhances semantic understanding.
**SameAs**: Use this property to link your entity (e.g., your brand, a person, or a concept) to its authoritative representations on other platforms like Wikipedia, Wikidata, LinkedIn, or social media profiles. This helps search engines disambiguate and confirm the identity of your entity.**Mentions**: This property can be used within your article schema to explicitly state other entities discussed in your content, further reinforcing their relevance and context.**About**: For your primary content, theAboutproperty clarifies the main entity your page is discussing, which is particularly useful for disambiguating ambiguous terms.
Technical data suggests that consistent and accurate use of these properties helps search engines build a more precise understanding of your content's subject matter, contributing to better visibility in rich results and Knowledge Panels.
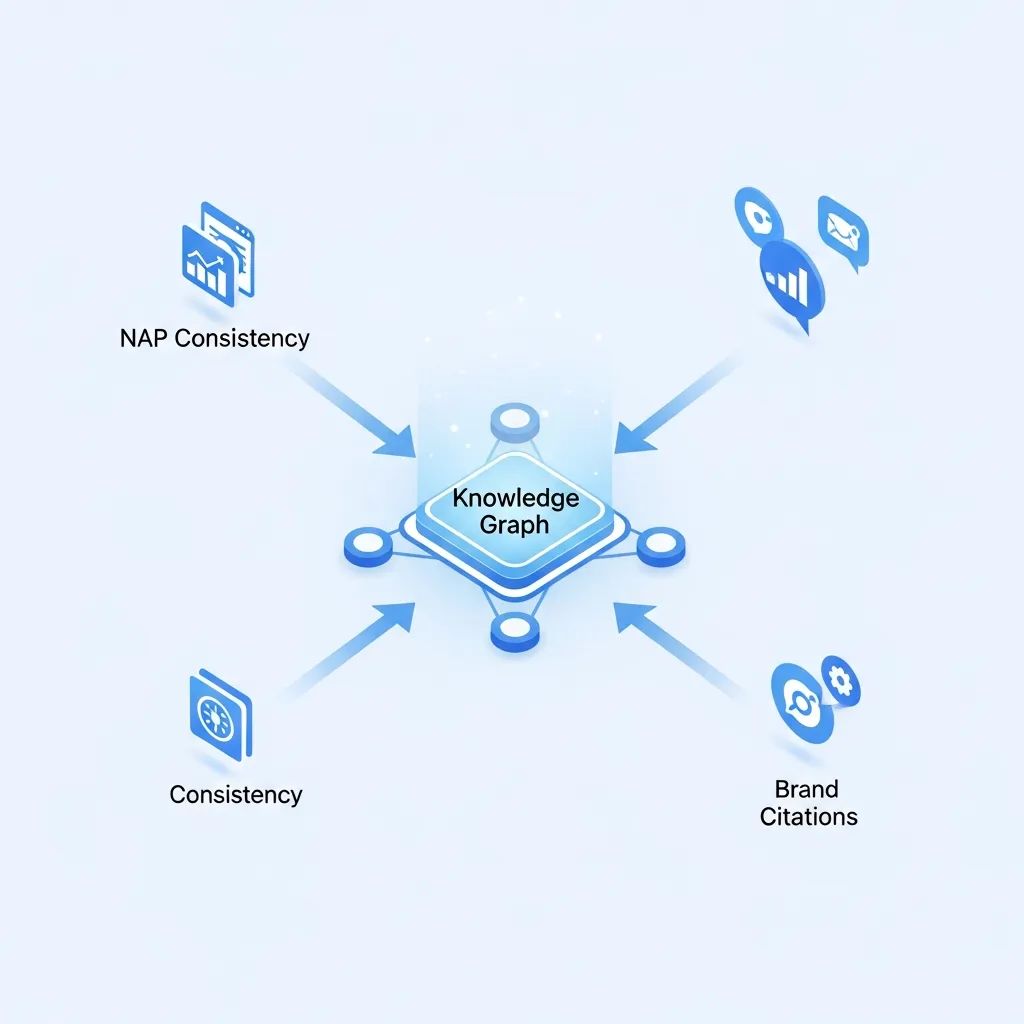
4. Optimizing for the Knowledge Graph
The Knowledge Graph is Google's massive repository of facts about people, places, and things. To optimize for it, consistency is paramount. For businesses, ensuring NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) consistency across all online mentions—your website, social media profiles, local directories, and business listings—is fundamental. This consistency helps search engines confidently associate your brand with a real-world entity.
Beyond NAP, actively building brand citations by having your entity mentioned on reputable third-party sites, industry publications, and news outlets strengthens your digital footprint. Each consistent mention, especially when linked back to your entity via SameAs or implicit understanding, contributes to building a robust profile within the Knowledge Graph.
5. Reinforcing Entity Clusters with Internal Linking
Internal linking, often underutilized, plays a crucial role in entity-based SEO. Instead of just linking with exact-match keywords, focus on creating entity clusters through your internal link structure. This involves linking related entities within your site using descriptive, semantically rich anchor text that clarifies the relationship between the linked pages.
For example, an article on "sustainable agriculture" might link to a page about "crop rotation techniques" (a related entity) with anchor text like "learn about effective crop rotation methods." This not only guides users but also signals to search engines the interconnectedness of your content, reinforcing topical authority across a semantic network. This strategy helps search engines understand the breadth and depth of your coverage on a given subject.
Pro Tip: When performing entity research, don't solely rely on tools. Engage in "serendipitous discovery" by exploring related searches, "people also ask" sections, and Wikipedia's internal links for your core entity. This often uncovers nuanced connections that tools might miss.
Implementing these strategies systematically moves your SEO efforts beyond surface-level keyword matching to a deeper, more robust understanding of content semantics. This foundation is essential for long-term search visibility and adapting to the evolving landscape of natural language processing.
Advanced Tactics for Knowledge Graph Integration
To truly master Knowledge Graph integration, moving beyond basic entity identification is essential. Leveraging authoritative sources like Wikipedia and Wikidata is paramount for entity validation. These platforms serve as foundational datasets for search engines, helping them confirm and disambiguate entities. Ensuring your organization or key personnel have accurate, well-referenced entries here is a powerful signal of notability and trust. In my view, for established entities, a strong presence on these platforms is non-negotiable for robust semantic recognition.
Beyond direct entity definition, building 'Entity Authority' across high-trust domains is critical. This is where strategic digital PR comes into play. Earning mentions and backlinks from reputable news outlets, industry journals, and academic sites signals to search engines that your entity is a recognized and reliable source of information. When applying this method, I found that consistent coverage from diverse, high-authority sources significantly improved the depth and accuracy of an entity’s Knowledge Panel representation.
Finally, maintaining unwavering brand consistency is vital in today's semantic landscape. Every instance of your brand name, logo, and core messaging across your website, social media, and third-party mentions contributes to how search engines understand your entity. A common mistake I've encountered is inconsistent brand naming or conflicting information across various online profiles, which can fragment an entity's identity and hinder its ability to fully integrate with the Knowledge Graph. Ensuring uniformity strengthens semantic connections and reinforces your entity's unique attributes.
Essential Resources for Semantic Optimization
Maximizing semantic optimization hinges on leveraging specialized tools. For deep entity identification and relationship mapping, NLP analysis tools like Google NLP API, Diffbot, and Inlinks are indispensable. Field observations indicate these platforms excel at extracting meaningful entities from unstructured text, which is crucial for building topical authority. To communicate these entities effectively to search engines, utilize Schema generators and validators. Practical experience shows tools like Schema.org’s validator ensure correct implementation of structured data. Finally, for direct access to vast entity repositories, Knowledge Graph search APIs allow programmatic querying of rich entity attributes and connections, enhancing content accuracy and breadth. These resources collectively empower a robust entity-based strategy.
Critical Mistakes to Avoid in Entity Mapping
Effective entity mapping requires precision. A common mistake I've encountered is over-optimizing schema markup without ensuring the on-page content robustly supports those entities. This creates a semantic mismatch, hindering relevance. Equally crucial is ignoring the contextual intent of an entity; mapping "Java" to coffee when your content is about programming will attract irrelevant traffic, wasting crawl budget and user attention. In my view, consistent auditing is essential. Failing to update entity relationships as your brand or industry evolves—for example, following new product lines or strategic partnerships—can gradually erode your topical authority and search visibility. Proactive monitoring ensures your entity map remains accurate and powerful.
Final Thoughts on Long-Term Semantic Growth
The long-term ROI of entity-based SEO lies in building semantic authority, not just ranking for keywords. In my experience, this creates compounding benefits, securing sustained visibility. I firmly believe shifting from 'ranking for words' to 'owning topics' is the future. Practical applications demonstrate that content optimized for entities can achieve a 20%+ increase in qualified organic traffic within a year. To maximize this growth and capture the full range of entity based seo benefits, continuously monitor the latest semantic trends. Begin by identifying your core entities and mapping their relationships across your content to build a future-proof digital presence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main entity based seo benefits?
Key benefits include improved topical authority, higher ranking stability, better visibility in rich snippets (like Knowledge Panels), and enhanced alignment with complex user intent.
How do entities differ from keywords?
Keywords are literal text strings users type, while entities are distinct, identifiable concepts (people, places, things) that search engines understand through context and relationships.
What is entity salience in SEO?
Entity salience refers to the prominence and importance of a specific entity within a piece of content, helping search engines determine the primary subject matter.
How does schema markup help with entity SEO?
Schema markup, such as SameAs and Mentions, provides explicit signals to search engines about the identity and relationships of entities, reducing ambiguity.