The Evolution of Spatial and Search Intelligence
The landscape of online discovery has fundamentally shifted from rudimentary map lookups to sophisticated, AI-driven spatial awareness. Users no longer just search for a "coffee shop near me"; they ask for "a quiet coffee shop with vegan pastries and free Wi-Fi open late tonight." This evolution marks the critical intersection of geospatial technology and digital marketing, defining the future of geo where location data is processed with unprecedented intelligence to meet nuanced user intent.
Currently, success in this dynamic environment demands a strategic pivot. Observations indicate that merely optimizing for keywords is insufficient; instead, context-aware optimization—understanding the "where," "when," "why," and "how" behind a search—is paramount. A local clinic, for instance, thrives by optimizing for detailed service queries alongside location data. This shift entails:
- Enhanced user experience via hyper-relevant results.
- Greater reliance on structured data.
Mastering this new paradigm requires moving beyond traditional SEO into Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), embracing AI's role in interpreting spatial queries. Learn more at The future of Generative Engine Optimization.
Understanding Generative Engine Optimization in a Spatial Context
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) signifies a fundamental departure from traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO). While traditional SEO primarily targeted organic rankings through keywords and backlinks to secure "blue links" on Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), GEO focuses on optimizing content for AI-driven generative engines. It ensures your information is readily consumable and correctly interpreted by models like ChatGPT and Google Gemini, leading to direct, conversational answers.
Consider a user asking, "What are the top-rated coworking spaces in Austin with natural light and strong coffee, open this weekend?" This query demands more than just a location; it requires a contextual understanding of amenities, ambiance, and operating hours, all processed spatially. Field observations indicate that these AI models don't just parse text; they interpret geospatial data by understanding real-world relationships, proximity, and user intent tied to a specific location. They leverage structured data, reviews, and entity relationships to build a comprehensive spatial understanding.
The fundamental shift is away from users clicking through a list of links to receiving direct, AI-generated conversational answers. Practical experience shows that engines prioritize synthesizing information into a concise, authoritative response. Key outcomes of effective GEO include:
- Enhanced visibility in AI-powered search.
- More accurate and contextually relevant direct answers.
- Improved user experience through conversational interactions.
This requires optimizing for AI citations and semantic understanding, rather than just keyword density.
Strategic Frameworks for Optimizing Content for AI and Geospatial Search
The shift towards GEO necessitates a re-evaluation of content strategies, moving beyond traditional keyword stuffing to a more sophisticated, AI-centric approach. As we look toward the future of geo, digital marketing professionals must consider how AI models interpret, synthesize, and present information, especially when geospatial context is critical. Practical experience shows that a multi-faceted framework, deeply rooted in semantic understanding and authoritative data, is essential for visibility in this evolving landscape.
One foundational pillar is the implementation of advanced Schema Markup for precise location-based context. While basic LocalBusiness schema is a starting point, true GEO demands granularity. This involves embedding specific GeoCoordinates (latitude and longitude), detailed areaServed properties to define service regions, and openingHoursSpecification for businesses. For services or events, leveraging Service or Event schema types with nested location properties allows AI engines to connect specific offerings to exact physical or virtual places. Observations indicate that accurately defined service areas significantly improve local search visibility for service-based businesses.
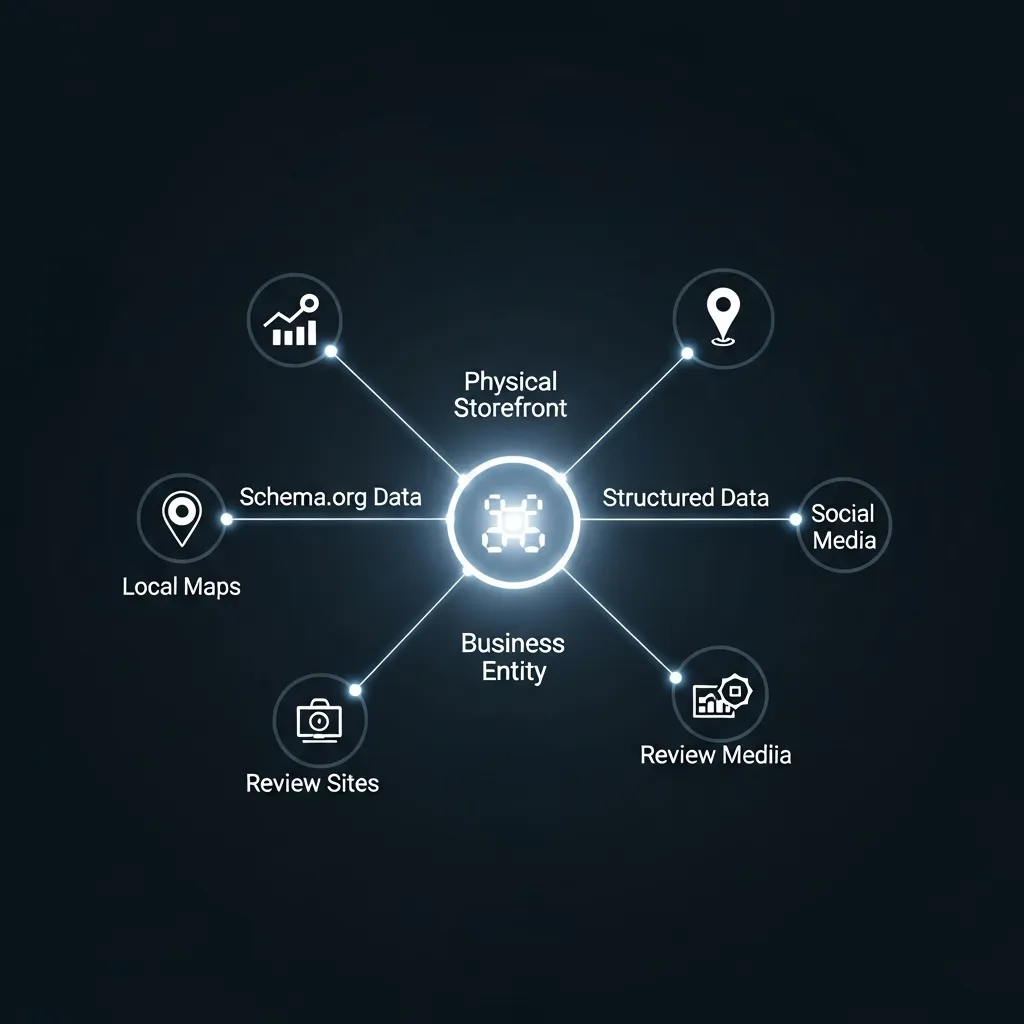
Crucially, optimizing for "AI Citations" by increasing factual density and authoritative sourcing underpins content trustworthiness. AI models prioritize information that is verifiable and originates from credible sources. This means content must be rich in data, statistics, and expert opinions, with explicit citations to primary research, governmental reports, and industry authorities. This practice bolsters the E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) of the content and provides AI with concrete data points to reference. Content that lacks verifiable facts will struggle to gain traction as a reliable citation source for generative engines.
The evolving nature of search, particularly with voice interfaces and conversational AI, demands adopting a conversational tone that aligns with natural language processing (NLP) patterns. Content should be crafted to directly answer questions and anticipate user intent. This involves using long-tail query phrases, structuring content with clear question-and-answer formats, and maintaining a natural flow that mirrors human dialogue. Such an approach helps NLP models understand the nuances of user queries and extract relevant information more effectively.
Pro Tip: Beyond just answering direct questions, consider the follow-up questions a user might have. Integrating these into your content naturally creates a more comprehensive and AI-friendly resource.
Furthermore, leveraging structured data to help AI engines connect physical locations with digital services is paramount. This extends beyond basic schema to ensure consistency across all digital touchpoints. For instance, linking a physical store's Google Business Profile, website, and social media profiles using sameAs properties helps AI build a comprehensive knowledge graph. This holistic view enables AI to accurately associate online offerings with real-world counterparts, facilitating complex queries like "where can I buy this product near me, and is it available for curbside pickup?"
Finally, techniques for improving visibility in AI-generated summaries and "overviews" are critical for direct user engagement. This involves designing content for extractability:
- Concise, direct answers to common questions placed prominently at the beginning of relevant sections.
- Clear, descriptive headings and subheadings that explicitly indicate the content that follows.
- Use of lists, tables, and short paragraphs to present information in easily digestible chunks.
- Semantic optimization to ensure the content covers the broader context and related entities comprehensively.
The GEO Content Authority Blueprint
To systematically optimize content for AI and geospatial search, professionals can follow this five-pillar framework:
-
Semantic Structuring with Advanced Schema:
- Implement granular
LocalBusiness,Service, andEventschema types. - Incorporate precise
GeoCoordinates,areaServed,openingHoursSpecification, andhasMapproperties. - Nest
locationproperties withinProductandServiceschemas.
- Implement granular
-
Citation-First Content Development:
- Prioritize factual density with verifiable data, statistics, and expert insights.
- Explicitly cite authoritative sources (e.g., primary research, government reports).
- Ensure content supports the E-E-A-T framework for trustworthiness.
-
Conversational Content Crafting:
- Write in a natural, question-answering style, anticipating user intent.
- Integrate long-tail, conversational queries and provide direct answers.
- Structure content for voice search and natural language processing.
-
Omni-Channel Data Consistency:
- Ensure all structured data (Schema, Google Business Profile, social media) presents a unified, accurate picture.
- Utilize
sameAsproperties to link related online entities.
-
Summary & Overview Optimization:
- Design content with clear, concise answers and digestible formats (lists, tables).
- Use descriptive headings to signal key information.
- Focus on semantic completeness to facilitate AI extraction for generated summaries.
Technological Pillars Supporting Modern Location Intelligence
The evolution of GEO is fundamentally underpinned by sophisticated technological advancements enabling granular, real-time location intelligence. These innovations provide the rich data necessary for AI models to interpret and contextualize spatial information effectively.
Real-time Geospatial Data via IoT
Currently, the Internet of Things (IoT) serves as a critical conduit for dynamic geospatial data. Sensors in devices, vehicles, and infrastructure provide continuous data streams on traffic, environment, and user movements. Field observations indicate this real-time influx allows businesses to offer hyper-localized services and content, directly informing AI-driven recommendations with immediate, actionable context.

Advanced Remote Sensing and LIDAR
Further enhancing location intelligence are advancements in Remote Sensing and LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging). These technologies capture highly precise topographical and environmental data. LIDAR generates detailed point cloud data crucial for 3D mapping in urban planning and environmental management. Technical data suggests this detail improves spatial model accuracy, enabling more effective resource allocation and infrastructure development.
GIS Integration with Marketing Automation
Crucially, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are increasingly integrated with marketing automation platforms. This synergy allows marketers to visualize, analyze, and leverage spatial data to segment audiences based on geographic behavior and attributes. Practical experience shows this integration facilitates highly targeted, location-aware campaigns, moving beyond basic geofencing to personalized content delivery via complex spatial analytics.
Traditional SEO vs. GEO: Adapting Your Marketing Playbook
Traditional SEO heavily relied on keyword volume metrics, prioritizing exact match phrases. In contrast, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) pivots to semantic relevance and understanding true user intent, which is crucial for conversational AI queries. AI models now dissect complex language, valuing content that precisely answers questions, even without a high density of specific keywords.
The traditional power of backlinks as a primary authority signal is also evolving. While still relevant, their impact is shifting compared to the rising significance of brand mentions within AI training sets. AI systems learn trust by aggregating mentions across diverse, credible sources, often prioritizing recognized entities over traditional link-building tactics.
In my experience, a common mistake is neglecting foundational SEO in favor of solely chasing AI optimization; this often results in a fragmented strategy. Through many projects, I’ve found that content optimized for both keyword density and semantic depth consistently yields stronger overall visibility. In my view, a hybrid approach is currently the most resilient strategy, ensuring visibility across current search engines while building future-proof authority for the future of geo.
Privacy Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Geo-Targeting
Navigating geo-targeting demands strict adherence to user consent for location-based services. A common mistake I've encountered is neglecting explicit consent, which erodes trust swiftly. Without it, the risks of hyper-personalization leading to restrictive "filter bubbles" increase, limiting user discovery.
In my view, proactive data transparency is paramount for building lasting brand loyalty in an AI-driven world. Clearly communicating data usage and providing user control are non-negotiable. To counter potential pitfalls, brands must implement robust opt-in mechanisms and accessible privacy policies, ensuring ethical data stewardship and fostering genuine consumer trust.
Embracing the Next Frontier of Location-Based Discovery
The future of geo thrives on the symbiotic relationship between AI and geospatial data. AI, powered by vast datasets, interprets complex spatial patterns to deliver unparalleled localized insights, while geospatial context grounds AI in the real world. For effective GEO, our final recommendation is to relentlessly focus on authority and technical precision. Content must be meticulously accurate, optimized with structured data, and designed for AI citation.

A common oversight I've seen is neglecting schema markup for local entities, which significantly hinders AI's ability to interpret and cite information effectively. In my experience, human expertise remains paramount, guiding AI tools to ensure ethical application and nuanced interpretation. I believe this sophisticated blend defines the next frontier. Start now by auditing your existing content for schema markup completeness and accuracy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines the future of geo?
The future of geo is defined by the intersection of AI-driven spatial awareness and geospatial technology, moving from simple map lookups to context-aware, conversational discovery.
How does GEO differ from traditional SEO?
While traditional SEO focuses on keyword rankings and backlinks for search engine results, GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) optimizes content for AI models to provide direct, conversational answers.
What role does Schema Markup play in spatial search?
Advanced Schema Markup provides precise location-based context, such as coordinates and service areas, helping AI engines connect digital content to physical locations.
Why is factual density important for AI-driven search?
AI models prioritize authoritative, verifiable data. High factual density and credible citations improve a brand's E-E-A-T and the likelihood of being cited by generative engines.