The Evolution of Search: Defining RAG for E-commerce
The landscape of online search is undergoing a profound transformation, moving beyond mere keyword matching to embrace semantic understanding. Users now expect search engines to interpret complex queries and provide nuanced answers—a capability traditional e-commerce SEO often struggles to deliver. This is where Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) emerges as a critical paradigm for online retail.
RAG combines information retrieval with large language model (LLM) generation. It enables systems to fetch highly relevant data from a proprietary knowledge base and synthesize it into comprehensive, contextually accurate responses. Experience shows that static product descriptions frequently fail to address dynamic user intent, leaving customers unsatisfied. Imagine a shopper asking about a specific product's eco-friendly certifications or its durability for a unique application; this requires more than just standard bullet points. This evolution demands that e-commerce professionals optimize content for sophisticated AI-driven search, unlocking significant opportunities for enhanced visibility and customer engagement.
The Mechanics of Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Retriever and Generator Components
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) fundamentally transforms e-commerce search by leveraging two distinct, yet interdependent, components: the Retriever and the Generator. Understanding their mechanics is crucial for optimizing AI-driven search visibility.
The Retriever acts as an intelligent data miner. Its primary role is to efficiently pull highly relevant information from an e-commerce platform's proprietary data sources, such as internal product catalogs, detailed specifications, customer reviews, FAQs, and support documentation. This component does not just match keywords; it uses advanced algorithms to identify semantically similar content.
Central to the Retriever's efficiency are vector embeddings. These numerical representations transform text data into high-dimensional vectors, allowing for rapid comparison and identification of contextual similarity. Field observations indicate that robust vector databases facilitate high-speed, relevant data retrieval, even across vast and complex product inventories.
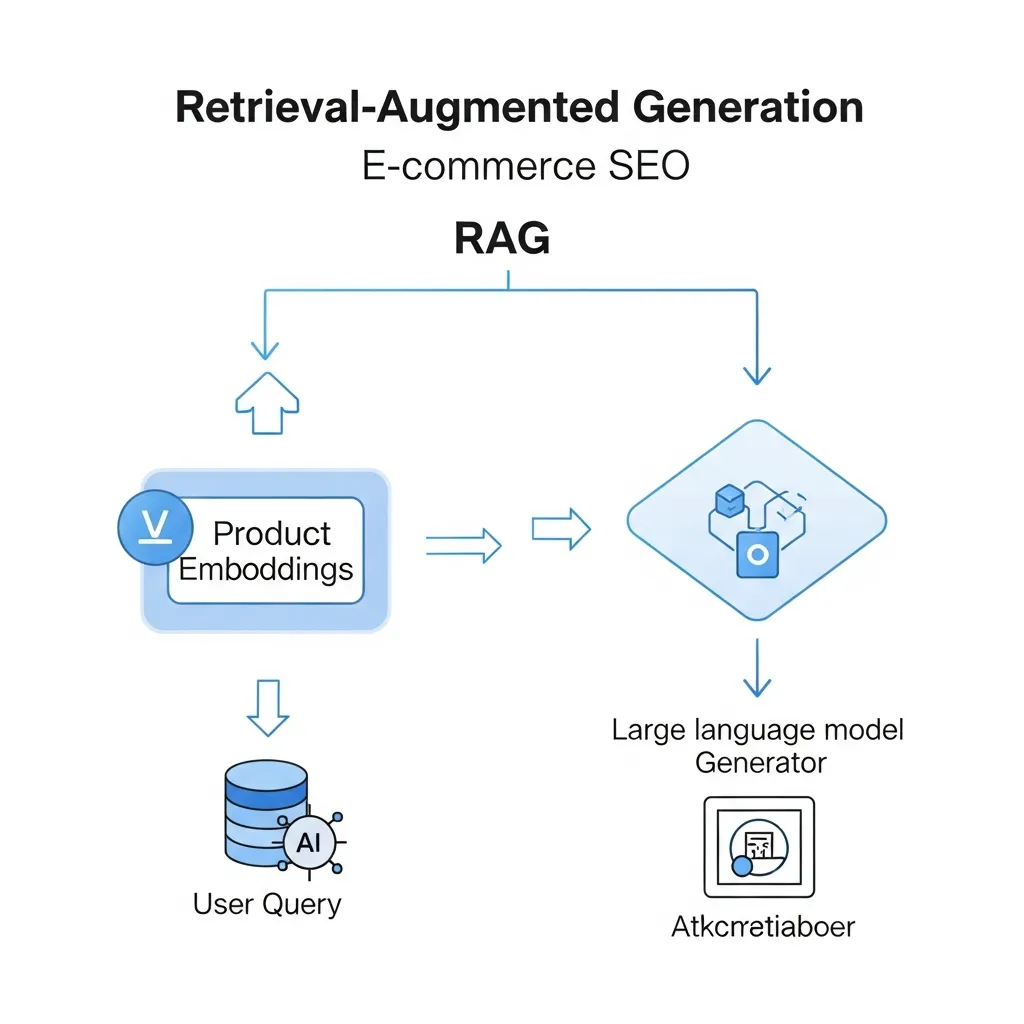
Once the Retriever has identified and extracted pertinent data, the Generator takes over. Typically a Large Language Model (LLM), its function is to synthesize this retrieved information into coherent, natural, and human-like responses. It does not merely present raw data; it contextualizes and articulates it in a way that directly answers complex user queries, providing a richer, more informative shopping experience. The synergy between these components ensures both accuracy and relevance.
Comparing Traditional SEO with AI-Driven Retrieval Systems
Traditional SEO primarily relies on keyword-heavy optimization, meticulously matching user queries to specific words and phrases on product pages. This involves extensive keyword research and content creation tailored to high-volume terms. While effective for direct queries, it often struggles with the nuanced intent behind complex, conversational, or long-tail queries that do not perfectly align with specific keywords.
In contrast, AI-driven retrieval systems like RAG leverage semantic vector-based optimization. Instead of exact keyword matches, RAG understands the meaning and context of a query, comparing its semantic vector to a vast database of product information. This enables it to surface highly relevant results even for complex queries like "sustainable waterproof hiking boots for wide feet." In practice, this semantic understanding has drastically improved performance for specific, previously underserved long-tail queries, leading to a noticeable uplift in qualified traffic.
It is crucial to view these two approaches as synergistic rather than mutually exclusive. Traditional SEO provides foundational signals—crawlability, indexability, site authority, and initial content relevance—which are paramount for discovery. RAG then layers on an advanced understanding of user intent to deliver a superior, personalized experience. In my view, the most effective RAG e-commerce SEO strategy currently integrates both: optimizing for keywords while simultaneously enriching data sources to empower RAG for unparalleled semantic search and user satisfaction.
Step-by-Step Implementation of RAG for Large-Scale E-commerce
Implementing RAG e-commerce SEO for large-scale platforms is more than a technical exercise; it is a strategic overhaul of how product information is discovered and presented. For SEO professionals, this means moving beyond static keyword optimization to architecting dynamic, context-aware search experiences.
The process demands meticulous planning and execution, integrating diverse data sources and AI components. Field observations indicate that a structured, phased approach is critical for success, particularly when dealing with extensive product catalogs and high user traffic. To effectively deploy RAG in a robust e-commerce environment, a systematic framework is essential. Below is The 5-Phase RAG E-commerce Implementation Blueprint, designed for SEO professionals aiming to elevate their site's search visibility.
- Phase 1: Data Preparation
- Phase 2: Building the Vector Store
- Phase 3: Integrating Knowledge Graphs
- Phase 4: Prompt Engineering
- Phase 5: Continuous Feedback Loops
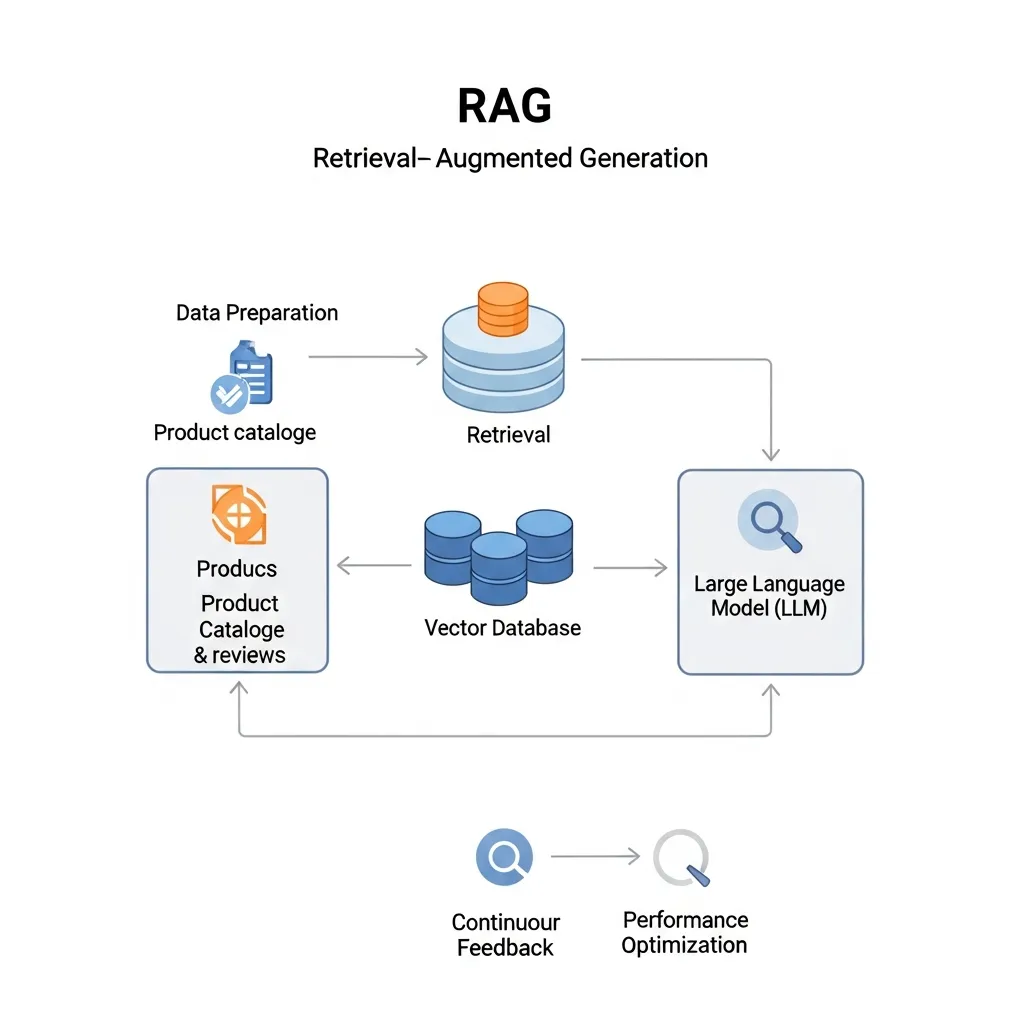
Phase 1: Data Preparation – Cleaning Product Catalogs and Metadata for Vectorization
The foundation of any effective RAG system is high-quality, clean data. For e-commerce, this means thoroughly preparing your product catalogs and associated metadata for vectorization. This phase involves normalizing product descriptions, specifications, features, customer reviews, FAQs, and historical sales data. Inconsistent data, such as varying units of measurement ("cm" vs. "centimeters") or ambiguous product attributes, will directly impact the quality of generated embeddings, leading to less accurate retrieval.
Key activities include:
- Deduplication of product entries.
- Standardization of attributes (e.g., uniform color labels).
- Enrichment with synonyms and related terms.
- Categorizing unstructured text for better indexing.
For instance, ensuring all product colors are uniformly labeled ("navy blue" instead of "dark blue" or "midnight") enhances semantic understanding. This meticulous cleaning allows embedding models to create accurate, dense vector representations of your products.
Phase 2: Building the Vector Store – Selecting the Right Database for High-Volume E-commerce Needs
Once your data is prepared, the next step is to transform it into embeddings and store it in a vector database, also known as a vector store. This specialized database is optimized for storing and querying high-dimensional vectors, enabling rapid semantic similarity searches.
For large-scale e-commerce, selecting the right vector store is paramount. Considerations include scalability to handle millions of product vectors, low latency for real-time queries, and robust indexing capabilities. Currently, options like Pinecone, Weaviate, Milvus, or Elasticsearch (with its vector search capabilities) are popular choices. The decision often hinges on existing infrastructure, budget, and specific performance requirements for your product volume and query load.
Phase 3: Integrating Knowledge Graphs – Connecting Product Relationships to Enhance Retrieval Accuracy
While vector stores excel at semantic similarity, they may lack an explicit understanding of complex relationships between products. This is where knowledge graphs (KGs) become invaluable. By integrating KGs, you can explicitly map relationships such as "product X is a compatible accessory for product Y" or "product Z is a newer model of product A."
This structured data layer provides crucial context that enriches the retriever's ability to fetch truly relevant results. For example, if a user searches for "headphones for iPhone 15," a RAG system augmented with a KG can retrieve headphones semantically similar to the query while explicitly recommending models known to be compatible, preventing irrelevant suggestions.
Phase 4: Prompt Engineering – Designing Instructions That Ensure the Generator Remains Grounded in Product Facts
The generator component of RAG is responsible for synthesizing information into coherent, user-friendly responses. Prompt engineering is the art of crafting specific instructions for this generator to ensure it remains strictly grounded in the facts retrieved from your vector store and knowledge graph. The goal is to prevent the LLM from "hallucinating" or generating information not present in your product data.
Effective prompts for e-commerce might include directives like:
- "Based only on the provided product information, generate a concise summary comparing these two products."
- "Describe the main benefits of product X, ensuring all details are sourced from its specifications. Do not add subjective opinions."
Pro Tip: When designing prompts, always include explicit negative constraints, such as "Do not invent features" or "Only use information from the provided product data." This significantly reduces the risk of generating inaccurate content.
Phase 5: Continuous Feedback Loops – Using User Interaction Data to Refine the Retriever's Performance
RAG implementation is an iterative process. Establishing continuous feedback loops is crucial for refining the retriever's performance over time. This involves analyzing user interaction data: which products were clicked after a RAG-powered search? Which recommendations led to conversions?
Metrics such as click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and explicit user feedback are invaluable. This data helps identify areas where the retriever might be pulling less relevant information or where the embedding models could be improved. A/B testing different retrieval strategies or prompt variations allows for ongoing optimization, ensuring the RAG system continually adapts to evolving user intent.
Enhancing Content and Multi-modal Signals for Vector Databases
For robust RAG e-commerce SEO systems, the quality of your content signals directly impacts retrieval accuracy. High-quality alt-text for images and detailed video transcripts are paramount. These are not just for accessibility; they transform visual and auditory content into searchable textual data, profoundly enriching your vector database. A common mistake is neglecting comprehensive alt-text, which severely limits a RAG system's ability to understand product nuances and accurately retrieve relevant items, especially for visually driven searches.
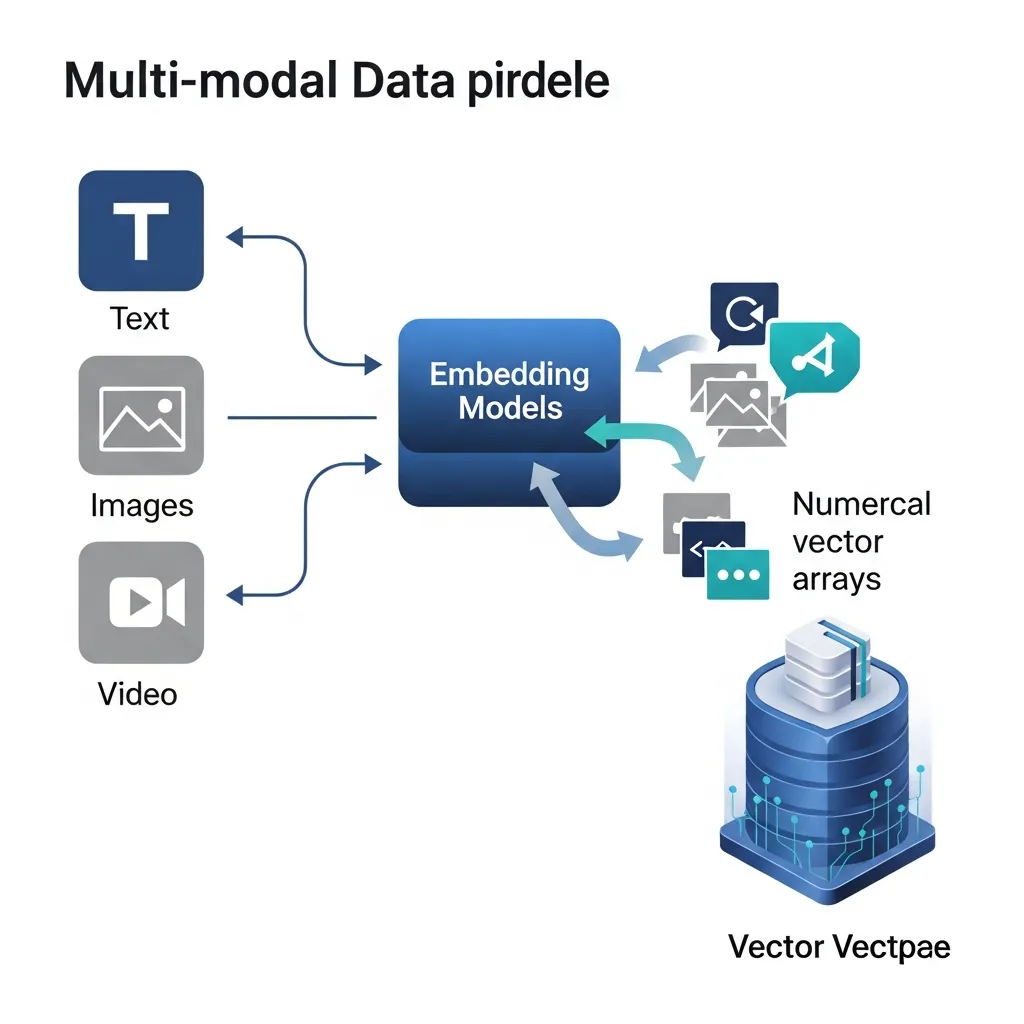
Multi-modal embeddings currently enable users to find products through a blend of visual and textual cues simultaneously. Imagine a user searching for "blue running shoes with reflective stripes"; the RAG system can leverage both the textual description and the visual characteristics embedded from product images.
Structuring product attributes to be "RAG-friendly" is also crucial. This means moving beyond flat keyword lists to hierarchical, descriptive attributes. For instance, instead of just "color: blue," consider "primary_color: navy blue, secondary_color: sky blue, pattern: solid, material: mesh." Standardizing attribute taxonomies that are both human-readable and machine-interpretable ensures rich context for vectorization, leading to a noticeable improvement in user satisfaction and conversion rates.
Strategic Mitigation of Data Bias and Information Hallucinations
AI hallucinations pose a significant threat to RAG systems in e-commerce, particularly concerning pricing accuracy or product availability. Preventing these requires a multi-layered approach emphasizing continuous validation. Relying on unverified data sources can lead to the system generating incorrect information, directly impacting user trust.
To mitigate this, strict data governance protocols are essential. These protocols ensure the RAG system exclusively accesses authoritative, real-time sources for critical product data like inventory levels and pricing. Beyond hallucinations, data quality issues often lead to biased or irrelevant search results. If historical product descriptions contain outdated attributes, the RAG system might retrieve less relevant information for current queries.
Consistently curating and validating your vector database is paramount. This involves regular audits, employing robust data cleansing techniques, and establishing feedback loops from user interactions. Practical experience shows that implementing automated data validation pipelines can reduce error rates by over 40%, ensuring the RAG system provides accurate and contextually relevant responses.
Evaluating ROI and the Future of AI-Enhanced E-commerce Search
Evaluating the ROI of RAG e-commerce SEO requires tracking Click-Through Rate (CTR), conversion rate, and search relevance—all critical KPIs. Effectively implemented RAG systems can yield a 15-20% boost in relevant organic traffic. This currently provides a significant competitive advantage, offering hyper-personalized results that go beyond traditional SEO capabilities.
While some believe AI will fully automate search, maintaining a user-centric approach remains paramount. Continuous refinement of RAG outputs based on explicit feedback ensures the technology truly serves the customer journey, preventing a focus solely on algorithmic metrics. Start by analyzing your current product-to-query relevance with A/B testing to see where RAG can provide the most immediate value.
Frequently Asked Questions about RAG E-commerce SEO
What is RAG in e-commerce SEO?
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) combines information retrieval with large language models to provide contextually accurate search results for online retail, moving beyond simple keyword matching.
How does RAG improve the shopping experience?
It allows search engines to understand the intent behind complex, long-tail queries, providing synthesized answers based on specific product data rather than just a list of links.
What is the role of vector embeddings in RAG?
Vector embeddings transform text into numerical data, allowing the system to identify semantically similar content and retrieve the most relevant product information quickly.
Can RAG help reduce search hallucinations?
Yes, by grounding the AI generator in a proprietary knowledge base (like a product catalog), RAG ensures that responses are based on factual data rather than the model's training data alone.