Understanding Structured Data for Local Search
Securing prime visibility in local search is paramount. Many businesses struggle with inconsistent online information, which often leads to missed opportunities in local queries.
- Challenge: Inconsistent online information.
- Outcome: Missed opportunities in local search.
Local Business Schema is a standardized data format, typically JSON-LD, that explicitly tells search engines about your business. It is fundamental to the semantic web, enabling machines to understand the meaning of your data rather than just identifying keywords.
Unlike general schema types (e.g., Product), local business schema provides specific properties like address, openingHours, and geo coordinates for precise categorization. Search engines currently leverage this detailed markup to populate crucial features such as the Knowledge Graph, local pack listings, and enhanced Google Maps profiles. This semantic understanding directly influences a business's discoverability. For a deeper dive into these foundational elements, see critical schema types.
The Strategic Benefits of Implementing Local Markup
Implementing local business schema offers profound strategic advantages for your online presence. Field observations indicate that accurately structured data directly contributes to enhancing click-through rates (CTR). By enabling search engines to display rich snippets—such as star ratings, operating hours, and contact information—businesses stand out in results, compelling users to click.
Schema implementation is also crucial for improving visibility in local map packs and voice search. Search engines leverage this precise data to present highly relevant results, making businesses more likely to appear in prominent local packs and as direct answers to voice queries.
Technical data suggests that providing verified, consistent business details through schema plays a pivotal role in establishing trust and authority. This consistency signals reliability to both search engines and prospective customers, fostering confidence and reducing user friction. Ultimately, robust local markup is indispensable for securing a competitive edge.
Choosing the Right Business Subtype for Maximum Impact
Relying solely on the generic LocalBusiness schema type is a significant missed opportunity for local search visibility. While foundational, it offers less precise context to search algorithms, which constantly seek to understand the specific nature of a business for optimal relevance.
Consider marking a business as Restaurant, LegalService, or MedicalBusiness instead. These industry-specific types allow for additional, highly relevant properties (e.g., servesCuisine for a restaurant, legalServiceType for a law firm, or medicalSpecialty for a clinic). This niche-specific markup provides search engines with a much richer context, enabling better categorization and matching with targeted user queries.
In my experience, a common mistake is underestimating this specificity. I once guided a client to switch their schema from LocalBusiness to Dentist, resulting in a measurable uplift in relevant local pack impressions within weeks. This granular detail signals exactly what you offer, leading to improved rankings for niche keywords. Maximizing this contextual relevance is the most effective approach to fully leverage local business schema.
Essential Properties for a Valid Schema Implementation
A robust local business schema implementation hinges on accurately defining its essential properties. While choosing a specific business subtype offers granular detail, several core fields are universally critical for search engine comprehension and rich result eligibility.
Foremost are the Name, Address, and Phone (NAP) details. These must precisely match the information presented on your website, Google Business Profile, and all other online directories. Field observations indicate that inconsistent NAP data is a primary contributor to local search ranking volatility, directly impacting how accurately search engines can connect your business to local queries. Ensuring this fundamental consistency builds trust and authority.
Beyond NAP, incorporating an image property is crucial for visual search results and enhancing your knowledge panel. Technical data suggests that businesses providing a high-quality, representative image are more likely to achieve prominent rich results, significantly enhancing click-through rates. Similarly, the priceRange property informs users about your service or product cost tier, managing expectations and qualifying leads even before a click.
Finally, strengthening your entity recognition and digital footprint involves leveraging the sameAs property. Practical experience shows that linking your official social media profiles (e.g., Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter) and other authoritative web presences via sameAs helps search engines consolidate your brand's online identity, reinforcing credibility and relevance in local search.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Local Business Schema
Implementing local business schema effectively transforms how search engines perceive and present your business. While previous sections covered the strategic benefits and essential properties, this guide delves into the practical execution, offering a robust framework for integrating this powerful markup into your website. The goal is to provide search engines with crystal-clear, machine-readable data, enhancing your visibility in local search results and enriching your Knowledge Panel presence.
The Local Schema Implementation Blueprint
Successfully deploying local business schema requires a systematic approach. The following blueprint outlines the key steps, from crafting the markup to its strategic placement and ongoing consistency.
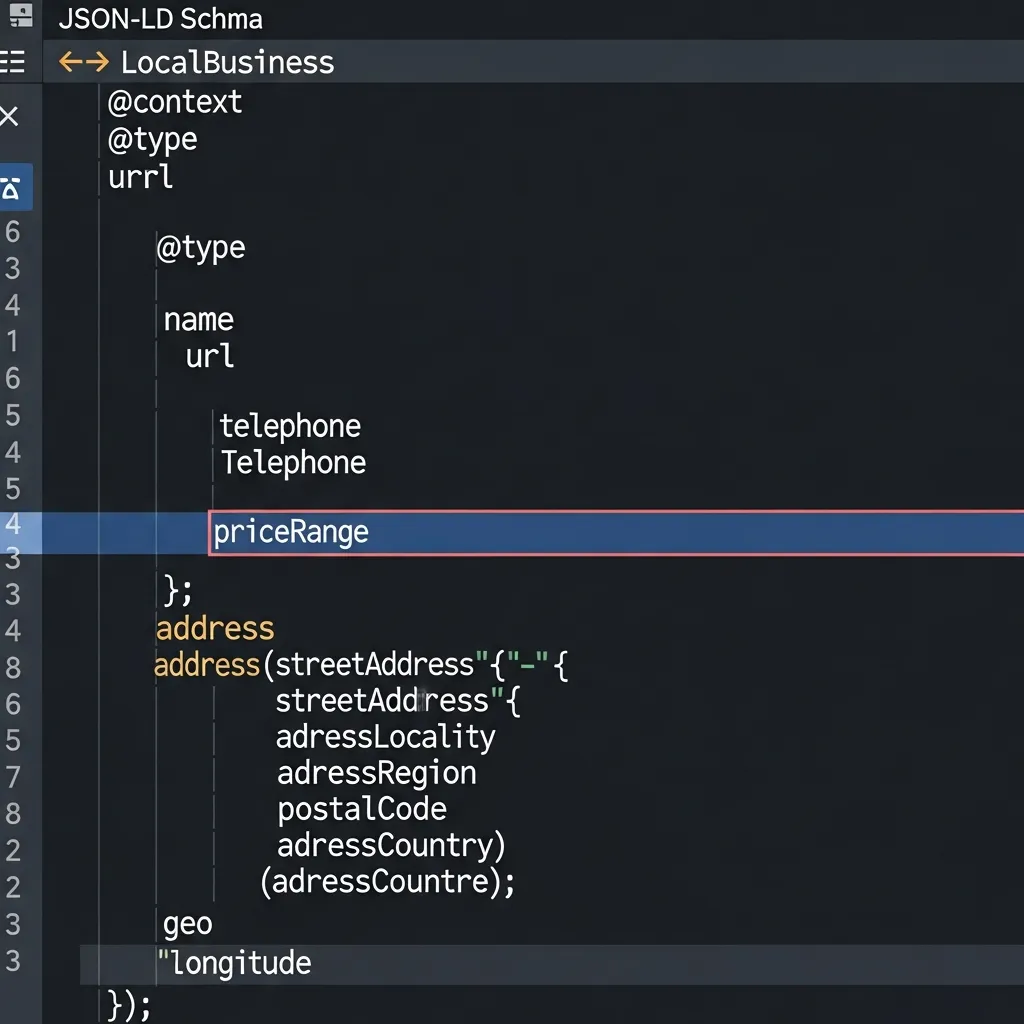
1. Crafting the JSON-LD Script for a Single Location
The preferred method for implementing structured data is JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data). It is easy to read, simple to maintain, and can be injected into the HTML without altering the visual presentation of your content. For a single-location business, the process involves creating a single script block containing all relevant properties.
Begin by defining the @context as https://schema.org and the @type as LocalBusiness (or its most specific subtype). You will then populate this object with the necessary properties. Field observations indicate that accurately nested properties significantly improve data interpretation by search engines.
In this example, address and geo (for latitude and longitude) are nested within the main LocalBusiness object. The openingHoursSpecification is also a critical nested property, allowing you to specify daily or weekly operating hours, including multiple time slots if applicable. This granular detail ensures search engines can accurately display your availability.
2. Advanced Implementation: Handling Multiple Physical Locations
For businesses with multiple physical locations, the implementation strategy requires careful planning to avoid ambiguity. The recommended approach is to create a dedicated, unique page for each physical location on your website. Each of these individual location pages should then contain its own specific JSON-LD LocalBusiness schema markup.
This ensures that each location's unique name, address, telephone, geo-coordinates, and operating hours are distinctly communicated to search engines. While it is possible to use Organization schema on a main corporate page with hasPart or containsPlace properties linking to individual LocalBusiness entities, practical experience shows that placing specific schema directly on each location's dedicated page yields the most direct and impactful results. Consistency across all location data is paramount.
3. Connecting Schema Markup to Your Google Business Profile for Consistency
One of the most powerful aspects of local business schema is its ability to reinforce and validate the information provided in your Google Business Profile (GBP). Search engines prioritize consistent data across all digital touchpoints.
Technical data suggests that when your website's schema markup mirrors the name, address, phone number (NAP), website URL, opening hours, and service areas listed in your GBP, it significantly boosts search engine confidence. This consistency can positively influence your appearance in the Local Pack, Google Maps, and the Knowledge Panel. Regularly audit both your schema and GBP to ensure they remain perfectly synchronized.
4. Best Practices for Placing the Code within the HTML Structure
Once your JSON-LD script is ready, its placement within your HTML is straightforward. The <script type="application/ld+json"> block can be placed either in the <head> section or at the end of the <body> section of your HTML document.
- In the
<head>: Placing it here allows search engines to discover and process the structured data early in the page loading process. This is often the preferred method according to experts. - At the end of the
<body>: This ensures the HTML content loads first, which can sometimes be beneficial for perceived page speed, although modern search engine crawlers are highly efficient regardless of placement.
The crucial point is that the schema markup must be present on the relevant page it describes. For a single business, it belongs on the homepage or primary "About Us" page. For multiple locations, each location's schema belongs on its respective location page.
Pro Tip: While JSON-LD is the standard, avoid using multiple, conflicting JSON-LD scripts on the same page. If you have multiple services or products on a local business page, consolidate them into a single comprehensive JSON-LD block to prevent potential parsing errors or confusion for search engines.
By meticulously following these steps, you lay a robust foundation for enhanced local search visibility. The next critical step involves validating your markup to catch and correct any errors before deployment.
Validating Your Markup and Fixing Common Errors
After implementing your local business schema, validation is crucial to ensure search engines correctly interpret your data. Start by utilizing Google’s Rich Results Test to preview how your markup might appear in search results, and use the Schema Markup Validator for a comprehensive technical check. These tools will highlight two primary issues: critical errors that prevent schema from being parsed, and warnings indicating missing but recommended fields. Prioritize resolving critical errors immediately, as they directly hinder visibility.
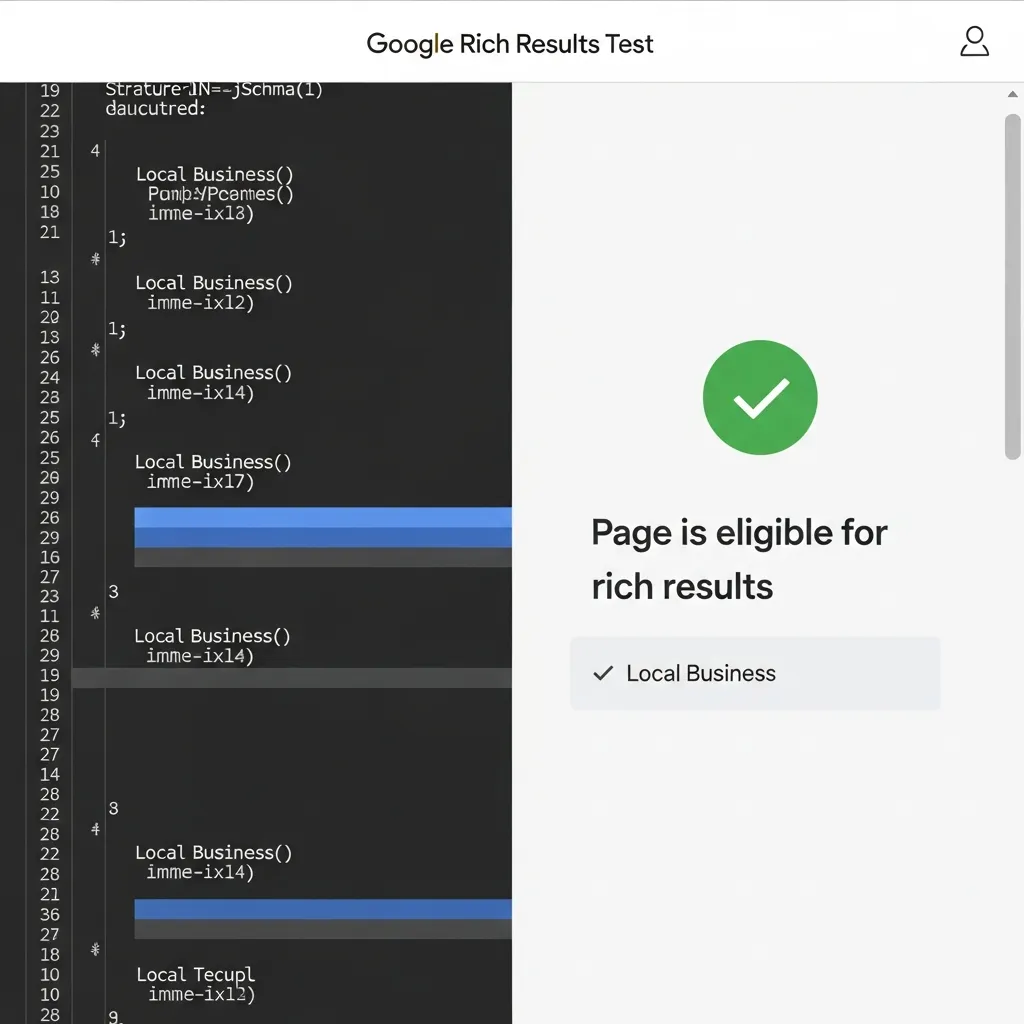
A common mistake I've encountered is mismatched NAP data (Name, Address, Phone) between the schema and the visible website content or external directories. This inconsistency can severely impact your local rankings. In my view, ensuring absolute consistency across all online mentions is paramount. Another pitfall is referencing hidden content within your schema, which search engines may penalize. Diligent validation ensures your schema provides accurate, consistent signals, reinforcing your local search presence.
Advanced Best Practices for Evergreen SEO Success
For evergreen local SEO success, schema consistency is paramount. A common mistake I've encountered during business rebrands is neglecting to update schema markup across all digital properties, which can confuse search engines and dilute authority. In my view, implementing dynamic JSON-LD schema, perhaps via a CMS or API integration, is the most effective approach for businesses with frequently changing details like hours or special events. This ensures real-time accuracy.
Regularly monitoring Google Search Console's Structured Data reports is also crucial. Through many projects, I've found that addressing warnings and errors promptly often leads to improved visibility and better interpretation by search engines, safeguarding your local presence against data discrepancies.
Future-Proofing Your Local Online Presence
The long-term value of robust structured data future-proofs your local online presence. In my experience, prioritizing this technical local SEO is paramount for sustained visibility. Neglecting schema updates is a common mistake that can erode rich results over time. I believe consistent, accurate markup is non-negotiable. Start now with step one: validating your existing markup.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is local business schema?
Local business schema is a standardized data format, usually written in JSON-LD, that provides search engines with specific details about a business, such as its name, address, phone number, and operating hours.
Why is local business schema important for SEO?
It helps search engines understand the context of your business, enabling rich snippets, improving visibility in local map packs, and increasing click-through rates by providing users with immediate, relevant information.
Should I use the generic LocalBusiness schema type?
It is better to use a more specific subtype if available, such as Restaurant, LegalService, or Dentist. This provides search engines with niche-specific details that improve categorization and relevance.
How do I check if my schema markup is correct?
You can use Google’s Rich Results Test to see how your data appears in search results and the Schema Markup Validator to identify technical errors or missing properties in your code.