The Evolution of Site Structure and Semantic Search
Internal linking is a foundational strategy that has moved beyond simple navigation to build topical authority and demonstrate complex content relationships. Search engine algorithms have evolved, shifting from basic keyword matching to understanding entities—real-world concepts and their contexts. This paradigm shift necessitates a robust internal linking entity approach, constructing a cohesive knowledge graph within your website.
This interconnectedness signals deeper topical relevance to search engines. For a comprehensive overview, see Linking in Entity SEO.
- Outcomes: Enhanced content discoverability and improved user journeys.
- Example: Imagine a recipe blog where linking "pasta" to "spaghetti carbonara" and "Italian cuisine" builds a rich network of related dishes and concepts.
Defining the Relationship Between Entities and Internal Links
An entity is a distinct, well-defined concept or "thing" that search algorithms recognize beyond mere keyword strings. This could be a person, place, event, idea, or product, each possessing unique attributes and relationships. Current trends indicate that search engines process content by identifying these entities to form a rich, interconnected web of information.
Within this web, internal links serve as the crucial edges connecting various nodes (your content entities) in a site's internal knowledge graph. Unlike traditional linking, which primarily focused on distributing PageRank or optimizing for specific keywords, entity-based linking strategically maps semantic relationships. This approach goes beyond simple relevance, explicitly signaling to search engines how different concepts on your site interrelate. Experience shows this creates a more robust, authoritative representation of your topical expertise, enhancing discoverability and guiding users through related concepts.
How to Build a Semantic Content Architecture Using Topic Clusters
Building a robust semantic content architecture is paramount for establishing topical authority and enhancing discoverability. This strategy moves beyond keyword stuffing, focusing instead on connecting related informational entities across your website. It structures your content to mirror how search engines categorize information.
Identifying Pillars and Supporting Sub-Topics
The foundation of a semantic architecture lies in identifying your core "Pillar" entities. These are broad, foundational topics central to your niche, typically represented by comprehensive, long-form content. For instance, if your business focuses on digital marketing, a pillar might be "SEO Strategy" or "Content Marketing Best Practices."
Once pillars are established, you identify supporting sub-topics, also known as cluster content. These are specific articles that delve into particular aspects of the pillar entity. For "Content Marketing Best Practices," cluster content could include articles like "Crafting Engaging Blog Posts," "Optimizing Headlines for Clicks," or "Utilizing Video in Content Marketing." Each cluster piece should thoroughly cover a specific entity related to the pillar, offering depth and unique value.
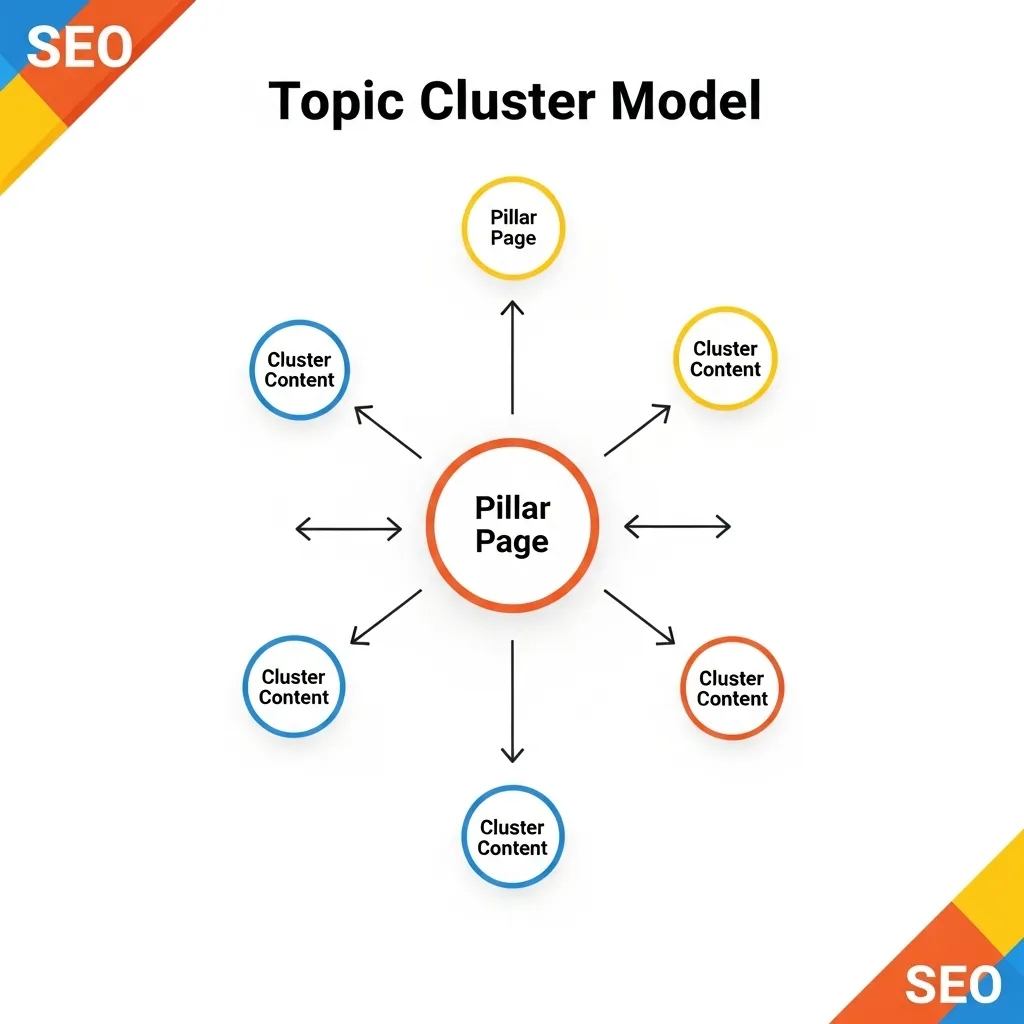
Mapping the Internal Linking Entity Flow
With your pillars and clusters defined, the next step is to map the internal linking entity flow. This involves creating intentional connections that demonstrate the semantic relationship between your content pieces. The goal is to build a tightly knit web of information that reinforces the authority of your pillar content while ensuring all supporting entities are easily discoverable.
Experience shows that a well-executed strategy employs three primary types of links:
- Downward Linking: From the pillar page to its relevant cluster pages. Anchor text should be descriptive, using specific keywords and synonyms related to the cluster topic (e.g., from "Content Marketing Strategy" to "developing effective content plans").
- Upward Linking: Crucially, each cluster page must link back to its central pillar page. This signals to search engines that the cluster content supports the broader pillar entity, consolidating topical relevance.
- Lateral Linking: Between related cluster pages within the same or different topic clusters where a clear semantic connection exists. This helps users and crawlers navigate related sub-entities, enriching the overall user journey.
Maintaining Shallow Click Depth
For optimal entity discovery and crawlability, maintaining a shallow click depth is essential. Ideally, your most important pillar content and key cluster pages should be reachable within 2-3 clicks from your homepage. This ensures that search engine spiders can easily find and index your valuable content. A well-structured topic cluster inherently helps achieve this by creating direct pathways between related content.
Pro Tip: Regularly review your site's navigation to ensure critical pillar pages are never more than a few clicks away. This directly impacts how efficiently search engines discover and attribute authority to your core entities.
The Semantic Architecture Audit Framework
Auditing existing content for entity gaps and linking opportunities is a continuous process. A systematic approach is often the most effective:
- Identify Core Pillar Candidates: Review your highest-performing or most comprehensive content to see which can serve as foundational pillars.
- Map Existing Content to Pillars: Group relevant articles under potential pillar topics, looking for natural relationships.
- Perform Entity Gap Analysis: Identify missing sub-topics or entities that should be covered to make your pillar truly comprehensive.
- Implement Strategic Linking: For each piece of content, identify opportunities for upward, downward, and lateral links using descriptive and varied anchor text.
- Assess Click Depth: Use tools to determine the click depth of your pillar and cluster pages, restructuring navigation if critical pages are buried too deep.
- Monitor and Refine: Track organic traffic, user engagement, and keyword rankings, adjusting your strategy based on performance data.
Strategic Anchor Text Optimization for Entity Relevance
Moving beyond basic keyword stuffing, strategic anchor text optimization is pivotal for reinforcing entity relevance. Currently, search engines prioritize semantic understanding, making it crucial to evolve past exact-match anchors. Instead, focus on descriptive, user-centric language that accurately reflects the linked content's topic, leveraging synonyms and Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) terms. This enriches contextual signals without over-optimization.
In my experience, solely relying on exact-match anchors often leads to penalties rather than improved rankings. A common mistake is neglecting the variety of related terms; for instance, linking "SEO audit" exclusively when "website analysis" or "technical site review" are equally relevant. The most effective approach prioritizes user intent and semantic relevance over rigid targets, ensuring a natural, authoritative linking profile.
Technical Considerations for Crawlability and Indexation
After establishing a semantic content architecture, technical execution ensures search engines fully comprehend your site. Internal links are the conduits for distributing PageRank, or link equity, across your domain. This strategic flow from authoritative pages to supporting content bolsters the ranking potential of critical resources. Observations indicate that deliberate equity distribution significantly enhances target page importance.
For discoverability, links must be readily accessible within the Document Object Model (DOM). Avoid relying solely on JavaScript-only links that may not be fully rendered during initial crawls. Experience shows traditional <a> tags within HTML are the most reliable for consistent crawler access.
An optimized internal linking structure directly impacts crawl budget efficiency. By guiding search engine bots along clear pathways to your most valuable content and entity relationships, you prevent wasted crawl efforts on irrelevant or orphaned pages. This ensures your crawl budget is utilized effectively, leading to more thorough and timely indexation.
Critical Internal Linking Mistakes to Avoid
A critical misstep in building topical authority is neglecting orphan pages. These valuable content assets lack internal links, making them virtually invisible to search engine crawlers and users. Identifying these forgotten pages through site audits is crucial; without proper connections, their entity signals remain isolated, hindering ranking potential.
Another common mistake is link hoarding, where sites indiscriminately add excessive outbound internal links from a single page. This dilutes link equity and can appear overly aggressive. Always prioritize contextual relevance and quality over sheer quantity. Furthermore, broken links and long redirect chains actively erode internal linking efficacy. Regular link integrity checks are vital to preserve the flow of authority and ensure search engines accurately interpret your site's semantic structure.
The Role of AI in Automating Internal Linking Efforts
AI is currently revolutionizing internal linking by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) to identify intricate semantic relationships across content. These sophisticated algorithms analyze text to suggest highly relevant internal link opportunities, connecting related entities far more efficiently than manual methods.
While manual auditing is painstaking and time-consuming, AI-assisted tools dramatically accelerate the process, identifying gaps and potential improvements at scale. However, human oversight remains absolutely critical. Blindly automating link placements without review can lead to suboptimal user journeys. A balanced approach ensures links are not just semantically correct but also contextually appropriate, prioritizing user experience and reinforcing topical authority.
Future-Proofing Your SEO with Entity-Based Linking
The internal linking entity framework establishes robust semantic connections across your content, building undeniable topical authority. It is crucial to balance algorithmic signals with an intuitive user experience. In my experience, prioritizing user flow when designing these links significantly amplifies their SEO impact, as Google increasingly values helpful content.
I believe consistent auditing is non-negotiable for sustaining authority; a common mistake is neglecting link health, which leads to outdated connections. Future-proof your strategy by regularly reviewing and refining your internal link architecture, ensuring every connection remains relevant and valuable. Start mastering the internal linking entity strategy now with a comprehensive internal link audit to identify and close your entity gaps.
FAQ
What is an internal linking entity strategy?
It is an SEO approach that focuses on connecting distinct, well-defined concepts (entities) within a website to build a semantic knowledge graph and topical authority.
How does entity-based linking differ from traditional linking?
Traditional linking focuses primarily on PageRank and keyword matching, while entity-based linking maps semantic relationships between concepts to help search engines understand context.
What are the benefits of maintaining a shallow click depth?
Shallow click depth ensures that important pillar and cluster pages are reachable within 2-3 clicks from the homepage, improving crawlability and entity discovery.
Can AI help with internal linking for entities?
Yes, AI uses Large Language Models to identify complex semantic relationships and suggest relevant linking opportunities across large volumes of content efficiently.