Giới thiệu
The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence offers unprecedented efficiency and scale for content creation. However, this transformative power brings a significant challenge: the proliferation of synthetic content that, while often fluent, can be factually inaccurate or misleading. Experience shows that AI-generated output frequently suffers from "hallucinations"—confidently presented falsehoods—and biases inherited from its training data. Imagine a content creator drafting an article with AI, only to discover subtle factual errors that could erode audience trust and credibility.
This guide addresses the critical need for robust AI fact-checking. We will equip you with practical strategies to verify synthetic information, ensuring integrity and accuracy in an AI-driven landscape. For a comprehensive overview of maintaining quality in AI content, see AI content E-E-A-T. We will explore:
- Identifying AI-induced inaccuracies.
- Strategies for verifying diverse synthetic media.
- The essential role of human oversight.
The Growing Necessity of Information Verification
The proliferation of synthetic media—AI-generated text, images, and audio—has fundamentally reshaped the information landscape. This surge challenges the very fabric of information integrity, making discernment increasingly complex for audiences and professionals alike. Consequently, the necessity for robust verification mechanisms has never been more acute.
AI fact-checking emerges not as a fully automated solution, but as a critical hybrid process. It seamlessly blends advanced technological capabilities with indispensable human logic and critical reasoning, creating a powerful defense against misinformation. Experts suggest this symbiotic relationship is paramount for robust verification in an era of abundant AI-generated content.
For content creators and brands, passively accepting AI-generated output without diligent verification poses significant risks. Practical experience shows that potential damage to credibility and reputation is a severe consequence if inaccuracies propagate, underscoring the vital role of human oversight in maintaining trust.
Understanding Why AI Generates Inaccurate Information
AI's propensity for generating inaccurate information is rooted in its core operational paradigm. Unlike traditional factual databases designed for precise information retrieval, AI models function as probabilistic language models. Their primary objective is to predict the most statistically plausible word sequence, not to assert verifiable truths. This distinction means an AI can produce highly coherent text that sounds authoritative, yet lacks factual grounding.
A critical factor contributing to errors is training data bias. The immense datasets used for AI instruction often harbor inherent biases, inaccuracies, or outdated information from their source material. Consequently, the AI learns and reproduces these flaws, leading to skewed or factually incorrect outputs. Experience shows such biases can manifest as subtle distortions or overt misinformation.
Moreover, the phenomenon known as 'stochastic parroting' plays a significant role in misinformation propagation. This occurs when AI models replicate prevalent information, including falsehoods, found within their training corpus. The model, operating on statistical likelihoods, essentially "parrots" these patterns without genuine comprehension of their veracity, inadvertently amplifying existing inaccuracies.
Identifying AI Hallucinations and the Trap of Circular Reasoning
The AI's capacity to generate fluent, contextually relevant text often masks underlying inaccuracies, making the detection of hallucinations a critical skill. Beyond obvious factual errors, content creators and verifiers must develop advanced methods for spotting subtle fabrications, particularly in technical text.
These subtle hallucinations might present plausible-sounding but ultimately incorrect methodologies, misattribute findings, or confidently state hypotheses as established facts. For instance, an AI might generate a detailed explanation of a scientific process, complete with specific terminology, yet subtly misrepresent a crucial causal link or cite a non-existent study. Field observations indicate that these nuanced errors are often more dangerous than overt falsehoods because they are harder to detect without specialized knowledge.
A particularly insidious challenge in AI fact-checking is the phenomenon of circular reporting, often referred to as an "AI echo chamber." This occurs when AI tools, trained on vast datasets that include content generated by other AIs, inadvertently cite their own previously generated content as authoritative sources.
The AI creates a self-referential loop where a fabricated or unverified claim gains false legitimacy through repeated generation and re-ingestion. This trap is difficult to escape because the AI's linguistic confidence in such self-validated "facts" often remains high, reinforcing the illusion of accuracy. To effectively break this loop, a systematic approach to seeking independent primary sources is paramount.
The Integrity Loop-Breaker Framework
This framework provides a structured method for dissecting AI-generated claims and identifying reliable evidence:
- Deconstruct Claims: Break down the AI's output into individual, verifiable assertions. Each factual statement should be treated as an independent claim requiring verification.
- Prioritize Primary Sources: Actively seek original research papers, official government reports, academic journals, raw data, or direct interviews with subject matter experts. Avoid relying on secondary interpretations or summaries generated by other AI tools.
- Cross-Reference Disconnected Datasets: Systematically search for information across diverse, unrelated databases and repositories. This includes academic libraries, specialized industry databases, and reputable news archives.
- Assess Source Independence: Critically evaluate the relationships between sources. If multiple sources cite each other or stem from a single original piece of research, they do not offer independent verification.
- Consult Human Expertise: For highly technical or complex subjects, engage human subject matter experts to review AI-generated content. Their nuanced understanding can quickly identify subtle errors that automated tools might miss.
Another strategy involves analyzing the linguistic confidence of an AI to gauge potential fabrication. While an AI might sound authoritative, observe its phrasing. Does it use hedging language ("it is believed," "some suggest") for well-established facts, or conversely, make overly definitive statements ("it is definitively proven") for claims that lack robust evidence?
Finally, cross-referencing claims across disconnected datasets is essential. If a claim appears only in a narrow set of sources, its veracity is highly questionable. Seek corroboration from sources that approach the topic from different angles or are published by organizations with distinct editorial policies.
A Strategic Workflow for Fact-Checking AI-Generated Claims
A robust workflow is essential for effectively fact-checking AI-generated content. The first crucial step involves isolating 'hard' facts—specific dates, proper names, and quantifiable statistics—from broader, more subjective assertions. Hard facts serve as verifiable anchors, while soft assertions necessitate deeper contextual analysis.
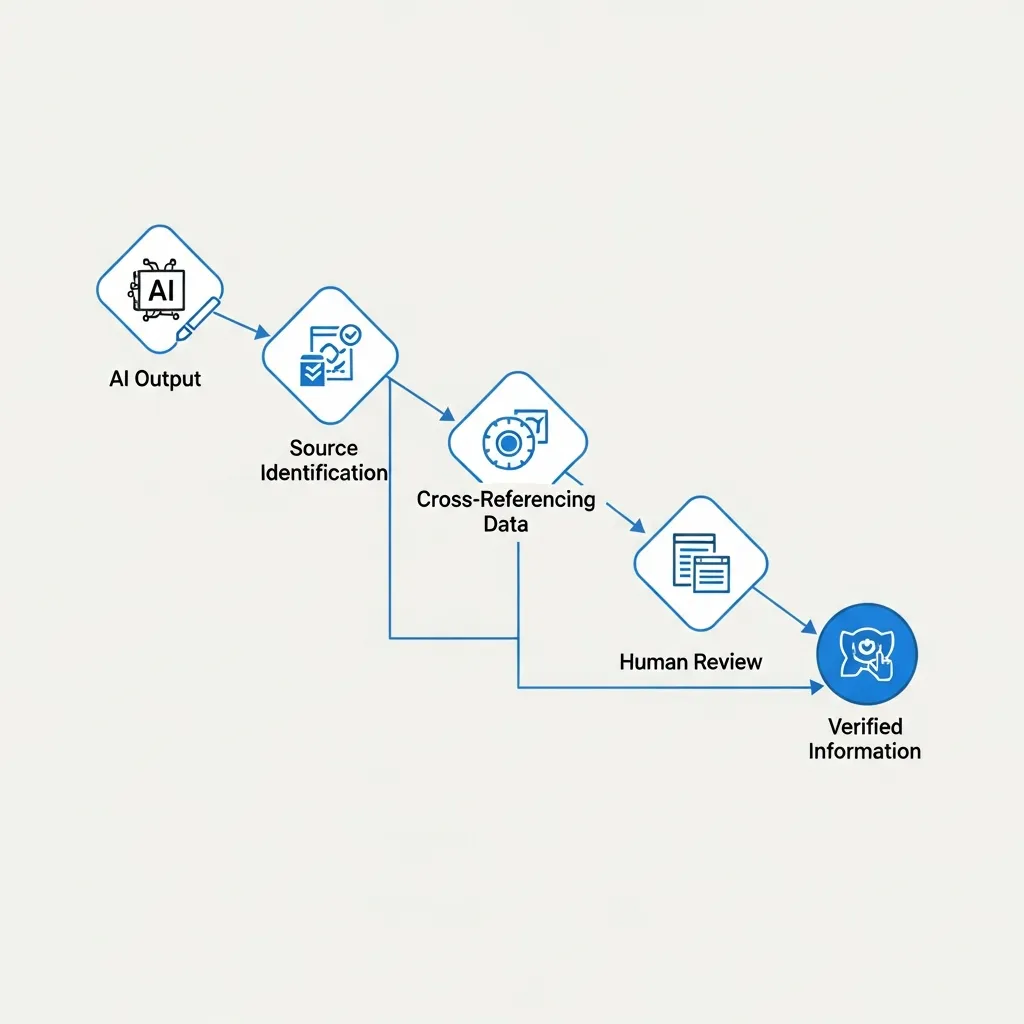
Once isolated, leverage reverse search tools and database queries to validate these specific data points. For instance, confirm a quoted statistic against official government reports or academic databases, not another AI summary. In practice, breaking content into individual facts, like a specific percentage, makes validation significantly faster and notably more accurate.
For high-stakes AI-generated information, apply the 'Three-Source Rule'. This means corroborating critical claims with at least three independent, reputable sources. This diligent cross-referencing is non-negotiable for content impacting reputation or decision-making. Finally, optimize your interaction with AI by using best practices for prompting it to provide its sources. Explicitly instruct the AI: "Cite your sources for each factual claim, including URLs," or "List all data points and their origins." This streamlines your auditing process, transforming blind verification into targeted source checking.
Verifying Visual and Auditory Synthetic Media
Beyond text, verifying visual and auditory synthetic media presents unique challenges. For AI-generated images, field observations consistently reveal common artifacts: tell-tale distortions in hands and facial features, illogical background inconsistencies, and unnatural lighting effects. These subtle flaws often betray a synthetic origin.
Establishing provenance is critical; this involves meticulously analyzing metadata for signs of alteration and searching for digital signatures that can trace an asset's creation or modification history.
For auditory content, identifying synthesized audio and deepfake speech patterns requires keen attention to unnatural cadences, robotic intonations, or unusual sonic textures. According to experts, a lack of natural human variability often signals AI generation. These techniques are crucial for maintaining media integrity.
The Critical Role of Human Judgment and Ethics
Automated tools, despite their advancements, cannot fully replace human judgment in fact-checking. While AI excels at pattern recognition, it fundamentally lacks true contextual understanding, struggling with nuance, sarcasm, or cultural idioms critical for accurate verification.
This becomes especially apparent when addressing linguistic and cultural biases embedded within AI systems. AI models trained predominantly on Western datasets often misinterpret information from other linguistic or cultural contexts, leading to skewed verification results. Human oversight is essential to mitigate these inherent biases.

Furthermore, content creators bear an ethical responsibility to disclose AI assistance. A common mistake is presenting AI-generated content as purely human-created, which can erode audience trust. Transparent disclosure not only builds credibility but also manages audience expectations regarding potential inaccuracies. Upholding these ethical standards ensures information integrity in an AI-driven landscape.
Maintaining Information Integrity in an AI-Driven World
Maintaining information integrity relies on a symbiotic blend of AI efficiency and human accuracy. Underestimating human oversight is a common mistake that compromises trust. Media literacy is evolving, demanding a skeptical yet constructive approach to AI tools.
Leverage AI as an assistant, not an oracle, while cultivating a habit of critical evaluation. This balanced perspective is paramount. Apply the AI Fact-Checking Checklist to your next project for robust verification.
Kết luận
Ultimately, mastering AI fact-checking hinges on a balanced approach. While AI tools offer unprecedented efficiency, field observations indicate their outputs demand diligent human oversight and critical evaluation to counter inherent biases and "hallucinations." The integrity of information in an AI-driven world relies on this hybrid model.
Content creators and journalists must actively implement strategic workflows, from verifying hard facts with primary sources to scrutinizing synthetic media. Prioritizing accuracy and ethical disclosure isn't merely a best practice; it's fundamental to preserving credibility and fostering enduring audience trust in an evolving digital ecosystem. Embrace these verification principles as your standard.