The Landscape of Automated Content Generation
The digital landscape is currently witnessing an unprecedented surge in the adoption of AI in content workflows. AI-generated content, crafted by sophisticated algorithms, is no longer a futuristic concept but a prevalent tool transforming how businesses approach content strategy. Practical experience shows that while AI offers immense efficiency and scalability, it simultaneously introduces a critical tension: balancing this newfound speed with unwavering quality control.
Consider a scenario where a brand rapidly deploys AI to scale its blog posts, only to discover factual errors and a diluted brand voice impacting its authority. This highlights the inherent challenges of the medium. Understanding AI content risks is essential in this automated landscape, particularly regarding:
- Factual accuracy and potential hallucinations
- Legal and ethical compliance issues
- Maintaining brand voice and integrity
For a comprehensive overview of how authority is impacted, see E-E-A-T and AI content creation. This guide will delve into these critical areas, providing actionable strategies to protect your brand.
Legal and Ethical Liabilities in Machine-Generated Text
The integration of AI into content creation introduces significant legal and ethical liabilities. Navigating the "black box" of copyright ownership for AI output is a complex challenge. In my experience reviewing content strategies, many overlook this ambiguity, exposing brands to risks of unintentional plagiarism and intellectual property infringement if AI-generated text closely resembles existing copyrighted material.
A common mistake is assuming AI output is inherently neutral; without robust human oversight, biased training data can lead to content with significant legal ramifications. This is critical for defamatory or biased content in regulated industries like finance or healthcare, where strict compliance demands accuracy and fairness to avoid severe legal consequences.
Businesses must also continuously monitor the evolving global landscape of AI-specific regulations. Proactive legal counsel and continuous monitoring of these legislative shifts are indispensable for any brand leveraging AI to safeguard against unforeseen liabilities and maintain compliance.
The Threat of Hallucinations and Factual Inaccuracies
AI hallucinations represent a significant risk, occurring when Large Language Models (LLMs) generate information that is plausible-sounding but factually incorrect or entirely fabricated. This inherent challenge stems from their design to predict the most likely sequence of words rather than to verify truth, leading to convincing falsehoods that can severely undermine credibility.

Such inaccuracies swiftly erode brand trust, particularly when content feels generic or impersonal, failing to connect genuinely with the audience. Field observations indicate these errors manifest across diverse sectors: from misrepresenting product features in marketing to citing non-existent precedents in legal documents or fabricating historical events in educational materials.
Moreover, the default settings of many AI tools often produce standardized outputs, making it exceptionally difficult to cultivate and maintain a unique brand personality and voice that stands out in a crowded digital landscape.
A Strategic Framework for Mitigating Generative Risks
Navigating AI content risks requires a structured approach to safeguard brand integrity and ensure compliance. Field observations indicate that merely deploying AI tools without a robust oversight mechanism can expose organizations to significant reputational and operational risks. To counteract these challenges, businesses need a proactive and integrated framework that blends technological capabilities with essential human expertise.
The Brand Shield AI Content Framework
Implementing a comprehensive strategy is paramount for mitigating the inherent risks of generative AI. The following 5-step framework, "The Brand Shield AI Content Framework," provides actionable guidance for organizations looking to leverage AI responsibly while maintaining high standards of quality and trustworthiness.
-
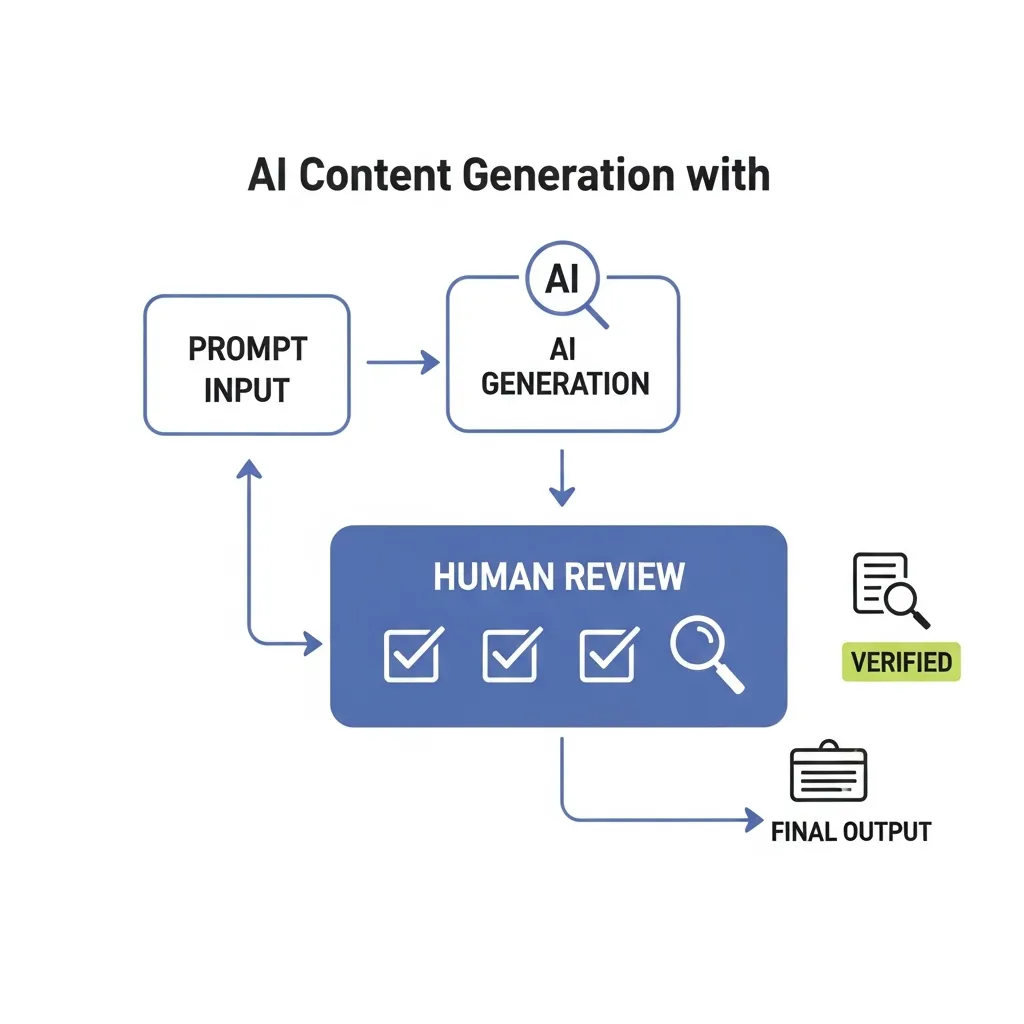
Implementing a Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Editing Workflow:
A HITL workflow is foundational, ensuring that human expertise remains central to content quality. This involves a multi-stage review process where AI generates initial drafts, but human editors are responsible for critical evaluation, refinement, and final approval. Practical experience shows that defining clear roles—such as an initial AI operator, a subject matter expert editor, and a final proofreader—significantly enhances accuracy and brand alignment. Collaborative editing platforms with robust version control are indispensable tools for tracking changes and ensuring accountability within this workflow.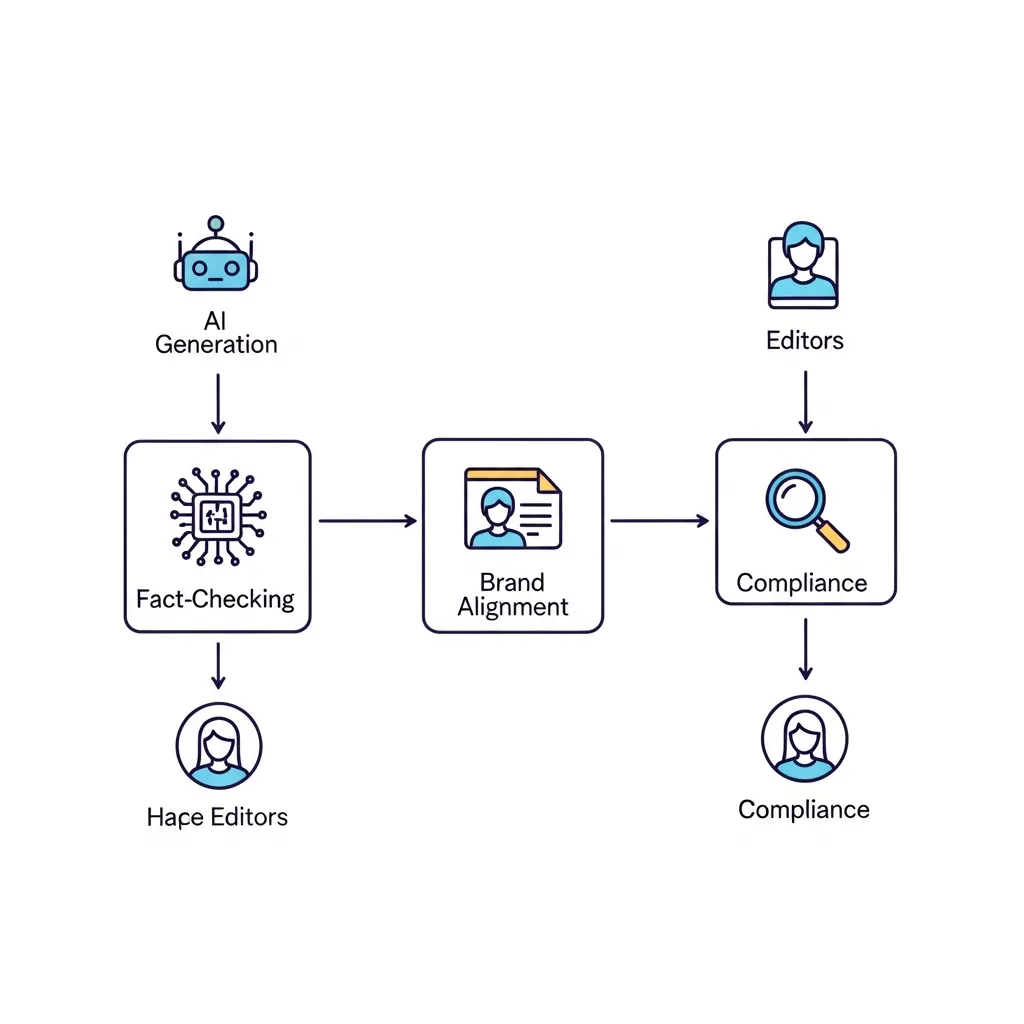
Diagram of a Human-in-the-Loop AI content workflow showing human review stages for brand integrity and compliance.
-
Factual Verification Using Primary Sources and Cross-Referencing:
Given the propensity for AI models to "hallucinate" or generate plausible but incorrect information, rigorous factual verification is non-negotiable. This step requires content teams to proactively cross-reference all critical data points, statistics, and claims against reliable primary sources. These include academic research papers, official government reports, industry surveys, and direct expert interviews. Supplementing this with verification against multiple reputable secondary sources further strengthens accuracy. Tools such as specialized academic databases and internal knowledge repositories can streamline this essential fact-checking phase. -
Bias Detection and Correction Through Diverse Prompt Engineering:
AI models, trained on vast datasets, can inadvertently perpetuate or amplify existing societal biases. Detecting these biases requires a critical eye during content review, often benefiting from a diverse team of human editors who can identify subtle linguistic or representational imbalances. For correction, diverse prompt engineering is key. Instead of single, narrow prompts, employ varied and inclusive prompts designed to challenge assumptions (e.g., "Describe X from multiple cultural perspectives," "Ensure representation across various demographics"). Iterative prompting and A/B testing different prompt variations can help refine outputs for neutrality and inclusivity. -
Maintaining a Brand Voice Repository for Stylistic Alignment:
AI-generated content often defaults to a generic tone, diluting a brand's unique identity. To counteract this, organizations must establish and maintain a comprehensive brand voice repository. This repository should include a detailed style guide, tone guidelines, approved terminology, specific persona examples, and a list of "do's and don'ts" for language use. This resource serves as a training ground for both human editors and, increasingly, as custom instructions for advanced AI models. Regularly updating this repository ensures the brand voice remains consistent and adaptable across all AI-assisted content initiatives. -
Documenting the AI Usage Process for Legal and Ethical Transparency:
Establishing clear documentation protocols for AI content generation is crucial for legal defense and ethical accountability. This involves meticulously recording which AI tools were used, the specific prompts provided, the extent of human modification applied, and the chain of internal approvals. Technical data suggests that maintaining a comprehensive audit trail offers transparency, demonstrates due diligence in compliance with evolving regulations (such as AI disclosure requirements), and provides a robust defense against potential copyright claims or allegations of misinformation. Content management systems with strong version control and activity logging features are vital for this purpose.
Key Insight: Proactive, continuous training of human teams on the nuances of AI output and the specific brand guidelines is as critical as the AI's own training data. This human-centric investment ensures the framework remains adaptive and effective against emerging AI content risks.
Search Visibility and the Technical Pitfalls of Automation
Search engines currently distinguish helpful, human-centric content from scaled, low-quality output, with algorithms prioritizing E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Relying solely on unedited AI text leads to volatile rankings and a high risk of de-indexing. In my experience, content lacking unique insights quickly loses visibility. To counter this, brands must implement robust human editing, fact-checking, and value addition, ensuring content resonates genuinely with audiences and search intent.
Beyond SEO, automated content introduces security vulnerabilities, such as AI-generated deepfakes and sophisticated phishing campaigns that can severely damage brand reputation. Practical experience shows that strong internal verification protocols and considering digital watermarking for sensitive AI-generated assets are crucial.
Furthermore, the limitations of current AI detection software for quality assurance are significant; these tools are imperfect and can misclassify content. In my view, relying on them exclusively is a critical mistake. Instead, a multi-stage human review remains the ultimate arbiter of content quality and brand safety.
Expert Strategies for Balancing Automation and Human Oversight
True success in leveraging AI for content lies in viewing it as a collaborator, augmenting human creativity rather than replacing it. A common mistake I've encountered is organizations treating AI as a complete content solution, rather than a valuable assistant that streamlines workflows.
In my view, the most effective approach is to empower internal teams with specialized training in AI ethics and responsible content generation. This foundation enables setting clear internal policies for AI disclosure and transparency, ensuring every piece of content meets brand standards and maintains authenticity.
Beyond initial creation, regularly auditing content performance and audience sentiment is crucial. Practical experience shows that failing to consistently monitor can lead to a gradual decline in brand trust and engagement. Implementing systematic checks and feedback loops helps maintain content quality and audience resonance, proactively addressing any shifts in perception.
Ensuring Long-Term Content Resilience
Achieving long-term content resilience requires proactive management of AI content risks. In my experience, neglecting a robust governance framework often leads to costly content overhauls. True resilience hinges on human intuition guiding AI, not replacing it. Start now by implementing a comprehensive AI content governance framework to protect your brand's integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary AI content risks for businesses?
The main risks include factual inaccuracies (hallucinations), legal liabilities regarding copyright, and the potential for biased or non-compliant content that damages brand reputation.
How do AI hallucinations affect brand authority?
AI hallucinations occur when models generate false information that sounds plausible. If published, these errors can erode audience trust and undermine your brand's perceived expertise.
Can AI-generated content negatively impact SEO?
Yes. Search engines prioritize E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Low-quality, unedited AI content may be flagged as unhelpful, leading to lower rankings or de-indexing.
What is a Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) workflow?
A HITL workflow is a process where human editors oversee AI generation, performing critical reviews and factual verification to ensure the final output meets quality and brand standards.