Introduction to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
The evolving search landscape presents a formidable challenge for SEO professionals and content marketers. Traditional keyword-centric strategies are increasingly insufficient as generative AI reshapes how users discover and consume information. This guide introduces Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), a crucial framework for maintaining and enhancing visibility in AI-powered search environments. It will equip practitioners with the knowledge to navigate this transformation effectively.
GEO fundamentally shifts focus from optimizing for algorithms to optimizing for the AI models that interpret user queries and generate responses. Its current relevance lies in adapting content for AI's comprehension and synthesis, ensuring brand presence in AI Overviews and conversational search. This approach is vital as AI-driven results increasingly dominate user journeys. For a comprehensive overview, see Zero-Click Search strategies. This article will detail the principles and actionable strategies for mastering GEO.
GEO vs. Traditional SEO: Navigating the Evolving Search Landscape
Traditional SEO primarily focused on keyword matching and ranking individual web pages for specific search queries, aiming to drive organic traffic through direct clicks on search engine results pages (SERPs). Its strategies revolved around optimizing for algorithms that assessed factors such as keyword density, backlinks, and technical elements. In contrast, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) represents a fundamental paradigm shift. It moves beyond mere keyword relevance to optimizing content specifically for AI-driven search models, such as Large Language Models (LLMs) and conversational AI. These advanced systems interpret queries with profound semantic understanding, discerning the true intent behind natural language questions rather than just surface-level keywords or phrases.
This evolution profoundly alters user interaction and content consumption. Users increasingly engage with search via natural, conversational queries, expecting synthesized, direct answers or AI Overviews, often bypassing traditional result listings entirely. For content to be visible and utilized by AI, it must excel at answer generation, providing comprehensive, authoritative, and contextually rich information that AI can readily extract, understand, and present. The emphasis shifts from simply ranking a page to ensuring content is structured and written in a way that AI can easily synthesize and present as a definitive answer. Therefore, GEO prioritizes deep context, user intent, and the delivery of comprehensive answers that anticipate and satisfy the full scope of a user's information need, often addressing potential follow-up questions within a single, well-articulated response.
The Core Principles Powering Effective Generative Engine Optimization
Generative AI engines, such as Google Gemini, ChatGPT, and Perplexity, process information by leveraging large language models (LLMs) to understand not just keywords, but the deep semantic meaning and underlying intent of a query. They analyze content for contextual relationships, nuanced language, and the overall completeness of the information presented. This enables them to synthesize answers, summarize complex topics, and engage in conversational interactions, moving far beyond traditional document retrieval.
Effective Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) hinges on several foundational principles. First is semantic relevance, ensuring content aligns precisely with user queries and related concepts, anticipating follow-up questions. Second, comprehensiveness is paramount; AI systems favor content that covers a topic thoroughly, addressing various facets and perspectives. Third, clarity and conciseness aid AI in extracting and presenting information accurately. Finally, authority remains critical.
The expanded framework of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) serves as a core pillar. AI models prioritize content authored by individuals or entities demonstrating genuine experience and proven expertise, backed by strong authority and trustworthiness. This signals to AI that the information is reliable and valuable. Ultimately, the goal is to satisfy complex user intent comprehensively, providing direct, insightful answers and solutions rather than merely matching keywords for a click. This holistic approach ensures content is truly optimized for AI-driven discovery.
Crafting Content for AI: Actionable Strategies for Generative Engine Optimization
Advanced Semantic Research and Content Structuring for AI
Optimizing for generative AI requires a shift from traditional keyword stuffing to a deeper understanding of semantic relationships and user intent. Generative engines excel at comprehending the nuances of language, making advanced research techniques paramount.
Advanced Keyword Research and Semantic Analysis
Moving beyond head terms and long-tail keywords, GEO demands an exploration of the entire semantic landscape surrounding a topic. This involves:
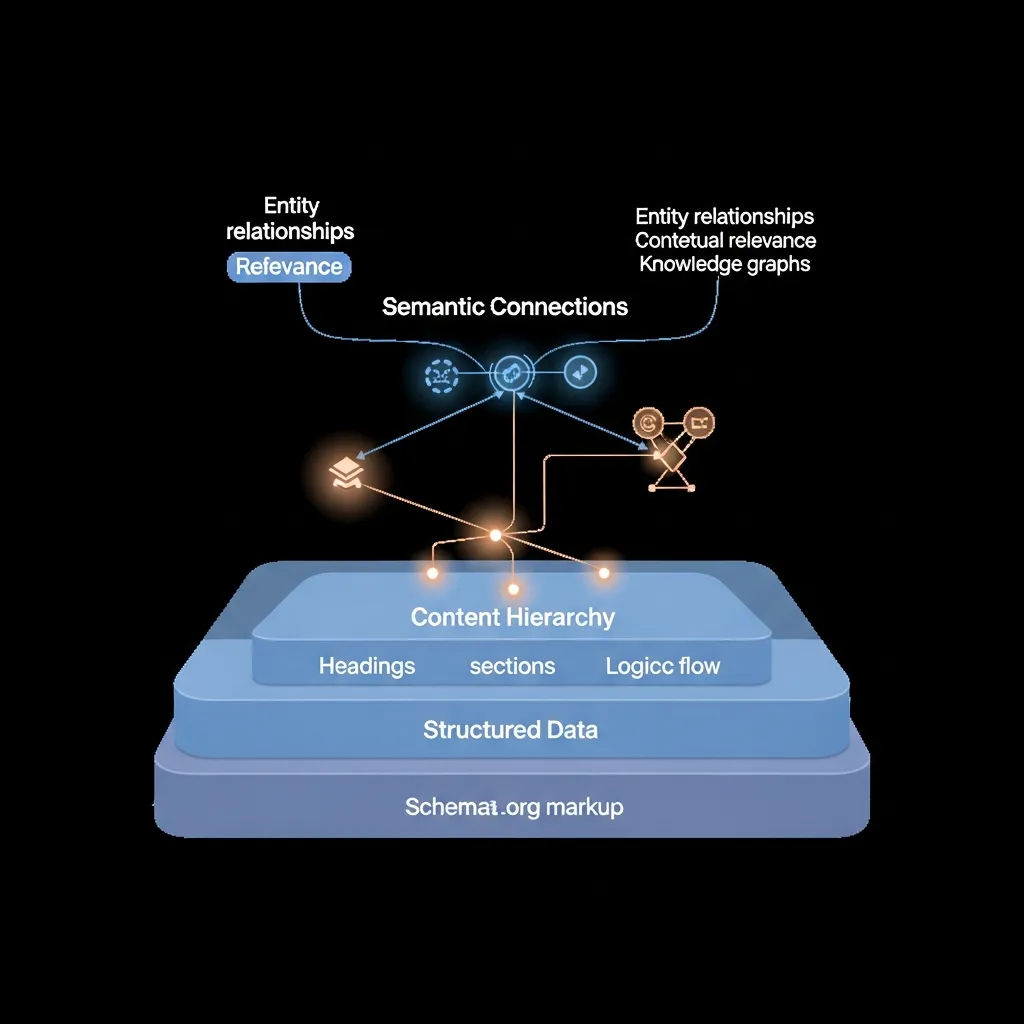
- Entity Recognition and Salience: Identify key entities (people, places, things, concepts) relevant to your topic and understand their relationships. AI algorithms recognize these entities and their connections, helping them build a comprehensive knowledge graph. Tools leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP) can help uncover these entities and their prominence within a topic.
- Topical Authority Mapping: Instead of focusing on individual keywords, aim to cover topics exhaustively and authoritatively. This means creating content clusters that address every facet of a broad subject, establishing your domain as a go-to resource. Analyze competitor content and "People Also Ask" sections to identify gaps in topical coverage.
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) Keywords: While traditional LSI isn't a direct ranking factor, the concept of using semantically related terms to provide context remains vital. Generative AI uses these co-occurring terms to better understand the true meaning and depth of your content.
- Intent-Based Query Analysis: Categorize queries not just by keywords, but by the underlying intent (informational, navigational, transactional, commercial investigation). Craft content that directly and comprehensively addresses each intent type.
Enhancing E-E-A-T for Generative AI
The E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is amplified in the age of generative AI. To concretely improve these signals:
- Experience: Showcase direct, first-hand knowledge. Include case studies, personal anecdotes (where appropriate for the content type), user-generated content, or detailed "how-to" guides that demonstrate practical application. Author bios should highlight relevant professional experience.
- Expertise: Ensure content is written or reviewed by recognized experts. Provide detailed author profiles with credentials, affiliations, and links to other authoritative works. Cite academic research, industry reports, and reputable sources within the content.
- Authoritativeness: Build a robust backlink profile from highly reputable and relevant domains. Seek mentions and citations from industry leaders. Develop a strong brand presence online that positions your organization as an authority in its niche.
- Trustworthiness: Maintain factual accuracy, provide clear sources for data and claims, and regularly update content to reflect the latest information. Implement strong editorial guidelines, transparency about content creation processes, and clear contact information.
Structuring Content for AI Consumption
Generative AI consumes and processes information differently than human readers or traditional search algorithms. Optimizing content structure is crucial:
- Clear Hierarchical Structure: Utilize HTML heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) logically to outline your content. This helps AI understand the main topics and sub-topics, making it easier to extract key information and generate summaries.
- "Answer-First" Approach: For informational queries, provide a direct, concise answer at the beginning of your content or section, followed by detailed explanations and supporting evidence. This caters to AI's preference for quick, factual extraction.
- Structured Data (Schema.org Markup): Implement relevant Schema.org markup (e.g., Article, FAQPage, HowTo, Product) to explicitly tell AI what your content is about and what specific information it contains. This enhances machine readability and interpretation.
- Semantic Interlinking: Build topic clusters by creating a strong internal linking structure that connects related pieces of content. This demonstrates comprehensive coverage of a subject to AI and improves crawlability.
- Summaries and Key Takeaways: Include executive summaries, bulleted lists of main points, or "key takeaways" sections. These elements act as signposts for AI, guiding it to the most critical information.
Pro Tip: Think of your content as a well-indexed library. Generative AI isn't just reading a book; it's looking for specific passages, summaries, and cross-references. Make it easy for AI to navigate, comprehend, and synthesize your information.
Ethical Considerations and Best Practices for AI-Assisted Content Creation
While AI tools offer immense potential, their use in content creation comes with ethical responsibilities:
- Human Oversight and Fact-Checking: AI-generated content, especially large language models, can "hallucinate" or present inaccurate information. Human editors must rigorously fact-check, verify sources, and ensure accuracy before publication.
- Transparency (When Necessary): While not always required, consider transparency about AI's role in content creation, especially if the content relies heavily on AI generation. This builds trust with your audience.
- Originality and Value Addition: AI should augment human creativity, not replace it. Focus on using AI to streamline research, generate ideas, or draft initial outlines, but ensure the final content offers unique insights, original perspectives, and genuine value that only human expertise can provide. Avoid producing generic, low-value content simply for the sake of quantity.
- Bias Mitigation: Be aware that AI models can inherit biases from their training data. Review AI-generated content for fairness, inclusivity, and neutrality, actively correcting any biased language or perspectives.
- Copyright and Plagiarism: Ensure that AI-assisted content creation adheres to copyright laws and avoids unintentional plagiarism. Always review AI outputs for uniqueness and proper attribution.
The GEO Content Opportunity Blueprint: A Step-by-Step Method
Identifying content opportunities for generative AI involves a systematic approach that looks beyond traditional keyword gaps.
- Map Core User Intent Clusters:
- Action: Group related queries and topics that share an overarching user need or question. Use tools to analyze "People Also Ask," forum discussions, and related searches.
- Goal: Understand the complete spectrum of intent within a subject area, moving from individual keywords to thematic clusters.
- Uncover Knowledge Gaps and Unanswered Questions:
- Action: Analyze existing content (both yours and competitors') for areas where information is incomplete, outdated, or poorly explained. Look for questions users frequently ask but struggle to find clear answers for.
- Goal: Identify content opportunities where you can provide genuinely novel or superior information.
- Assess Semantic Breadth and Depth:
- Action: Evaluate how comprehensively current content covers a topic's entities, sub-topics, and related concepts. Use NLP tools to identify missing semantic relationships.
- Goal: Pinpoint areas where your content can establish greater topical authority by offering a more thorough and interconnected body of knowledge.
- Evaluate E-E-A-T Signal Strength:
- Action: For each identified content opportunity, determine if your organization or contributing authors possess the requisite experience, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
- Goal: Prioritize opportunities where you can credibly assert E-E-A-T, or develop a plan to build those signals if they are currently lacking.
- Prioritize for AI Summarization and Direct Answers:
- Action: Identify questions or topics where generative AI is likely to pull a direct answer or concise summary. Look for opportunities to provide definitive, well-structured answers.
- Goal: Optimize content for rich snippets, featured snippets, and direct responses within AI search interfaces.
- Plan for Multi-Modal Content Integration:
- Action: Consider how the content could be enhanced with images, videos, interactive elements, or audio to satisfy diverse user preferences and provide richer context for AI.
- Goal: Create a holistic content experience that maximizes engagement and information transfer across various formats.
By meticulously applying these strategies, content creators and SEO professionals can adapt their approach to not only rank higher but also to be genuinely utilized and trusted by generative AI systems, ultimately serving user intent more effectively.
Measuring the Impact of Your Generative Engine Optimization Efforts
Measuring the impact of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) requires a refined approach that extends beyond traditional SEO metrics. Success in the AI-powered search landscape hinges on understanding how your content contributes to generative AI responses and influences user behavior. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for GEO focus on AI-sourced visibility, content attribution, and the quality of generative summaries.
Tracking visibility in AI-generated answers and featured snippets involves diligent monitoring of Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). This includes identifying instances where your content is directly referenced or paraphrased in answer boxes, generative AI summaries, or rich snippets. Specialized SERP tracking tools are evolving to highlight these specific AI-driven features, allowing professionals to measure their presence for targeted queries.
Measuring user engagement with AI-sourced content is critical. While direct clicks from AI answers can be lower, it’s essential to analyze click-through rates (CTR) from expanded AI responses that offer source links. Furthermore, examine time on page, bounce rate, and conversion rates for users who arrive via these AI-influenced pathways. This helps gauge the value and relevance of your content after initial AI exposure.
Analyzing brand mentions and sentiment in generative responses provides direct feedback on your brand's authority and perception. Utilize brand monitoring tools equipped with natural language processing (NLP) capabilities to detect when your brand or products are cited within AI summaries. Assess the sentiment – positive, neutral, or negative – to understand how AI models are interpreting and representing your brand identity.
Methodologies for monitoring GEO effectiveness include a combination of automated tracking and manual review for crucial queries. Connecting these GEO metrics to overall business objectives is paramount. Translate improved AI visibility and positive brand attribution into quantifiable business outcomes like increased organic traffic, enhanced brand reputation, higher lead generation, and ultimately, return on investment (ROI) for your content strategies.
Conclusion: Adapting to the Evolving Search Landscape with GEO
The emergence of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is no longer optional; it is critical for ensuring sustained visibility and brand authority within the rapidly evolving AI-powered search landscape. As search interfaces increasingly rely on generative AI to synthesize information and provide direct answers, content creators must proactively adapt their strategies to meet these new demands. This dynamic environment necessitates continuous learning and a commitment to iterating content approaches, moving beyond traditional SEO paradigms. Marketers are encouraged to view AI not as a competitor, but as an indispensable partner, leveraging its capabilities to enhance content creation, distribution, and overall audience engagement. By meticulously optimizing for AI understanding and generative output, organizations can effectively future-proof their content, ensuring it remains discoverable, trusted, and impactful in the age of generative search. The proactive embrace of GEO principles is paramount for navigating this new era of digital discovery. Start now with step 1: Auditing your existing content for generative AI compatibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is a crucial framework for optimizing content specifically for AI models that interpret user queries and generate responses, ensuring visibility in AI-powered search environments like AI Overviews.
How does Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) differ from traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO focuses on keyword matching and ranking pages for algorithms. GEO fundamentally shifts to optimizing content for AI-driven search models' semantic understanding, aiming for comprehensive answers and presence in AI Overviews, often bypassing traditional result listings.
What are the core principles of effective Generative Engine Optimization?
Effective GEO hinges on semantic relevance, comprehensiveness, clarity, and authority (E-E-A-T). It prioritizes deep context, user intent, and delivering comprehensive, insightful answers that AI can easily synthesize and present.
Why is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) crucial today?
GEO is vital because generative AI is reshaping how users discover and consume information. AI-driven results increasingly dominate user journeys, making it essential to adapt content for AI's comprehension and synthesis to maintain brand presence.