The Role of On-Site Connectivity in Modern Search Optimization
Modern search optimization extends far beyond keywords; it hinges on a website's internal structure. Internal linking for SEO refers to the strategic web of hyperlinks connecting pages within the same domain, fundamentally defining its site architecture. Unlike external links, which point to different websites, internal links are entirely under your control, offering a powerful lever for search visibility.
Observations indicate that poorly structured internal links can leave valuable content undiscovered by both users and search engines. For instance, an expansive e-commerce platform with a weak internal link profile might find its product category pages struggling for visibility despite high-quality content. These on-site connections are crucial for:
- Guiding users seamlessly through related content.
- Facilitating efficient search engine crawling and indexing.
- Distributing PageRank and topical authority across your site.
Effectively, internal links act as digital breadcrumbs, directing both human visitors and bots through your site's hierarchy, ensuring no valuable content remains an isolated island. For a comprehensive overview, see internal linking.
How Internal Links Impact Crawlability and PageRank Distribution
Internal links serve as the circulatory system for search engine bots navigating your website. They are essential for distributing Link Equity, often referred to as PageRank, which flows from stronger, more authoritative pages to linked pages. A well-structured internal linking profile ensures this valuable equity is shared efficiently across your domain, bolstering the perceived authority of deeper content.
Furthermore, strategic internal linking significantly assists search engine bots in discovering new content efficiently. Every internal link acts as a clear signal, guiding crawlers to pages they might otherwise miss. By carefully linking to all important content, you reduce the crawl depth required for bots to reach crucial pages, ensuring they are indexed quickly and regularly. Technical data suggests that pages buried too deep within a site's architecture receive less attention and can struggle with indexing.
Crucially, internal links establish a clear information hierarchy for search engines. They communicate the relationships between different content, indicating which pages are most important and how various topics relate. This structural clarity helps algorithms understand your site's overall thematic organization, which is vital for effective topical authority distribution and improved visibility in search results.
Navigational vs. Contextual: Categorizing Your Link Profile
Understanding the distinct roles of internal link types is crucial for strategic SEO. Navigational links establish site architecture and user pathways, commonly found in headers, footers, and sidebar menus. They guide users across key sections and help search engines grasp your site's hierarchy.
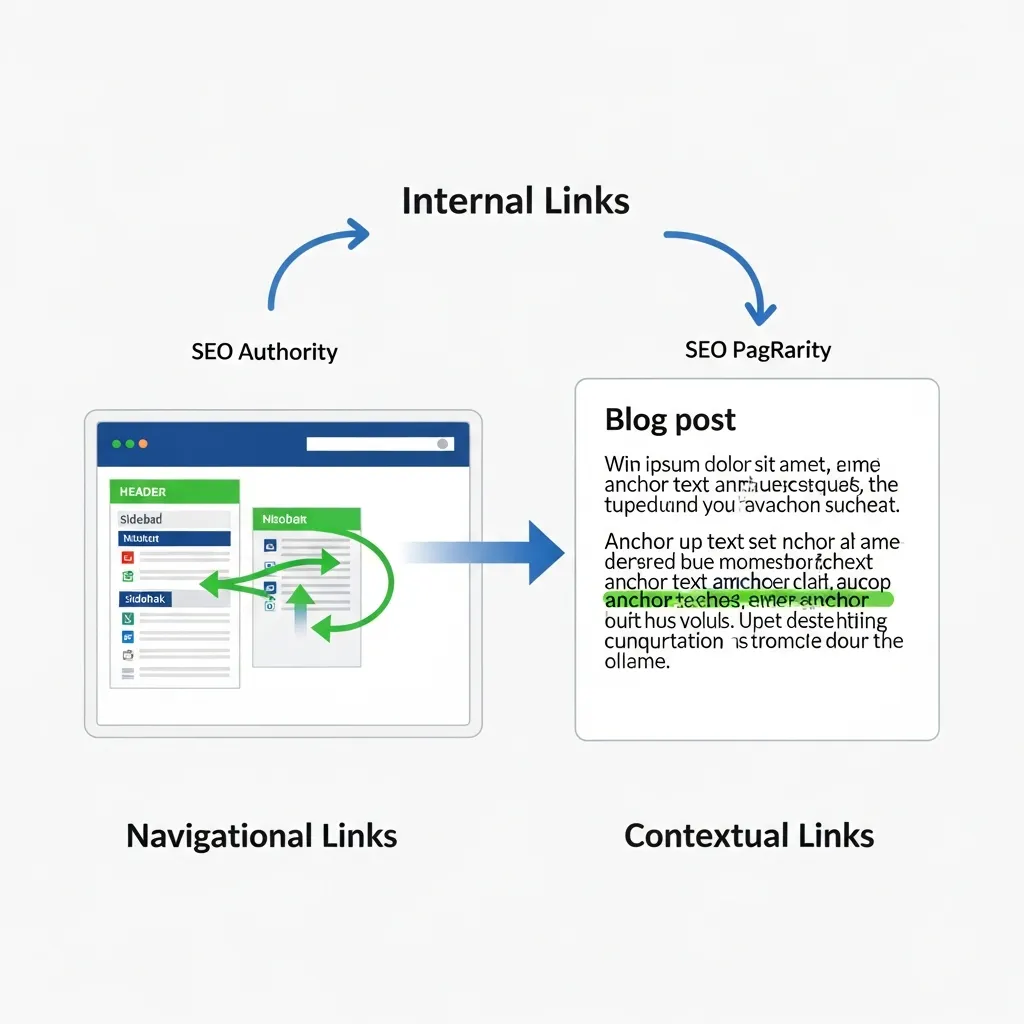
In contrast, contextual links are editorial, embedded within content bodies. These powerful links pass topical authority and relevance between related articles, driving deeper user engagement and signaling semantic connections.
Breadcrumbs serve a dual purpose, enhancing user experience by showing location within the site hierarchy and providing clear crawl paths. Finally, image links leverage their alt text as anchor text, making it critical to optimize these descriptions for both accessibility and SEO value, ensuring search engines understand the linked content.
A Step-by-Step Framework for Building a High-Performance Internal Linking Strategy
Building an effective internal linking for SEO strategy is less about adding links randomly and more about architecting a cohesive, interconnected web that guides both users and search engine crawlers. This requires a systematic approach, moving beyond ad-hoc linking to a deliberate framework. Websites implementing a structured internal linking methodology consistently outperform those with a chaotic link profile.
Here is the Strategic Link Architecture (SLA) Process, a step-by-step framework designed to build a high-performance internal linking strategy:
1. Conduct a Content Audit to Identify Power Pages
The foundation of any robust strategy begins with understanding your existing assets. Perform a comprehensive content audit to catalog all pages on your site. During this audit, specifically identify your 'Power Pages'—those URLs that have accumulated significant backlink authority from external sources.
These pages are invaluable because they act as reservoirs of link equity. Strategically linking from these high-authority pages to less authoritative, yet relevant, content can significantly boost the latter's ranking potential. Tools that analyze backlink profiles can help pinpoint these pages efficiently.
2. Create Topic Clusters and Content Silos
To establish strong topical authority, organize your content into topic clusters and content silos. A topic cluster consists of a central 'pillar page' (a broad, comprehensive overview of a topic) surrounded by multiple 'cluster content' pages (more specific articles that delve into sub-topics).
All cluster content links back to the pillar page, and the pillar page links out to all cluster content. This structure clearly signals to search engines the depth of your expertise on a subject.
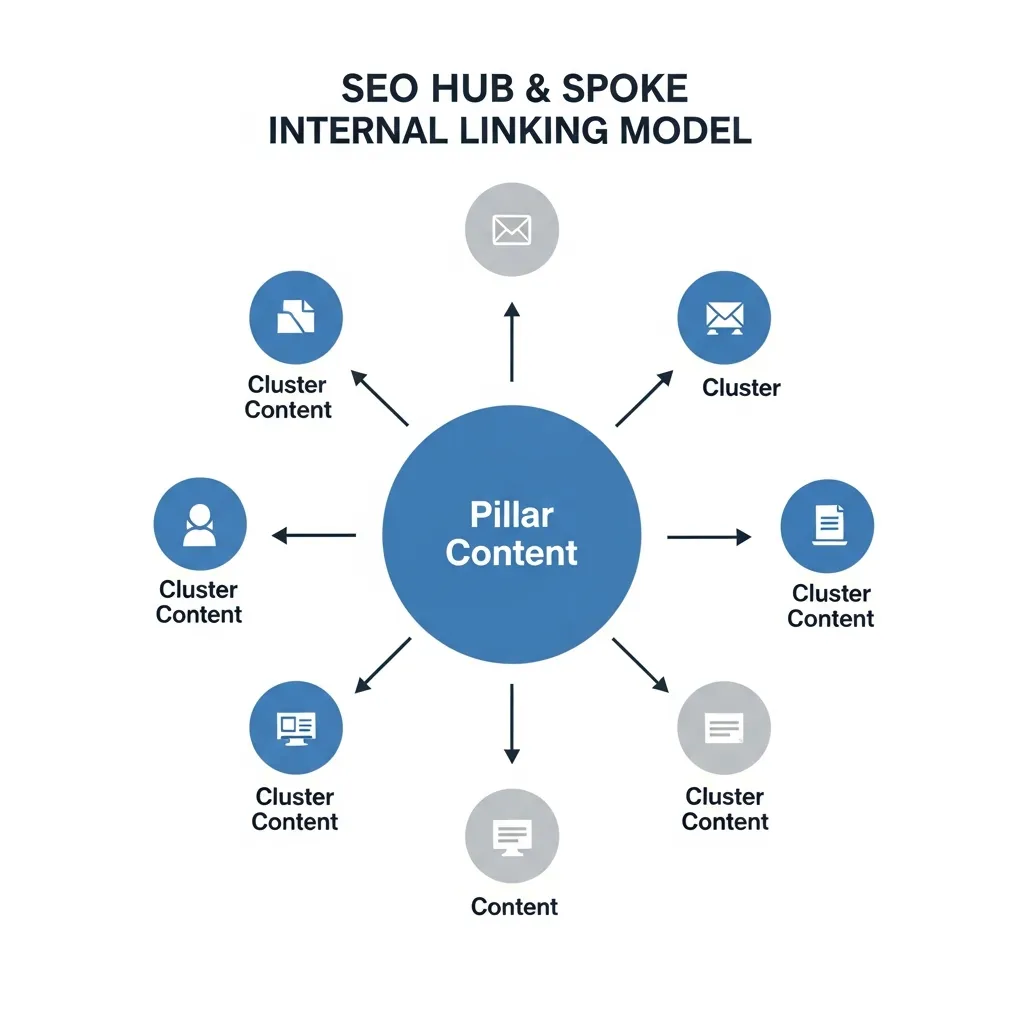
This approach is essentially the 'Hub and Spoke' model in action. The pillar page acts as the hub, distributing relevance and authority to its spokes (cluster content). For instance, a pillar page on "Advanced SEO Techniques" might link to spokes like "Technical SEO Audits," "Schema Markup Implementation," and "Voice Search Optimization." This hierarchical organization builds robust topical authority and makes your site easier to navigate.
3. Map Keywords to Specific URLs to Prevent Keyword Cannibalization
A critical step is to meticulously map your target keywords to specific URLs. This ensures that each piece of content is optimized for a distinct set of keywords, preventing keyword cannibalization.
Cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on your site compete for the same keywords, confusing search engines about which page is most authoritative for a given query. By clearly defining which URL owns which keyword, you can direct internal links with precision, reinforcing the relevance of the target page for its intended search terms.
4. Identify and Integrate Orphan Pages
Orphan Pages are pages on your website that receive no internal links from other pages within your site's structure. These pages are virtually invisible to search engine crawlers, making them difficult to discover and index, regardless of their content quality.
Utilize site crawl tools to identify these isolated pages. Once identified, integrate them into your site's internal linking structure by finding relevant existing content (especially Power Pages or pillar content) to link from. This ensures that no valuable content remains hidden, distributing link equity more effectively across your entire site.
5. Establish a Practical Workflow for Adding Links
Implementing internal linking should be an ongoing process, not a one-time fix.
- For New Content: When publishing a new article, identify 3-5 relevant existing pages on your site to link to from the new content. Simultaneously, revisit 3-5 older, relevant pages and add internal links from them to your newly published content. This ensures new content quickly gains visibility.
- For Existing Content: Regularly audit your older content. As new relevant articles are published, update older posts to include links to these newer resources. Conversely, identify opportunities within new content to link back to evergreen, high-performing older articles. Consistent maintenance can significantly improve the longevity and performance of content over time.
Pro Tip: Consider creating an internal linking spreadsheet or database. This "template" can track your pillar pages, cluster content, target keywords, and identified Power Pages, making it easier to manage and execute your strategy consistently.
Expert Insights on Anchor Text Optimization and Keyword Mapping
Effective internal linking for SEO extends beyond mere connectivity; the anchor text you use critically informs search engines about the linked page's content and relevance. A balanced approach is paramount, skillfully integrating exact-match, partial-match, and descriptive anchor text. While exact-match anchors provide strong signals for specific keywords, they should be used judiciously to avoid over-optimization.
Anchors like "click here" or "read more" offer zero SEO value, as they convey no topical context. Instead, focus on rich, descriptive phrases that enhance user experience and provide clear topical relevance.
Maintaining a natural link profile is crucial to avoid potential over-optimization penalties. Aggressively optimizing anchors with too many exact matches often results in a less natural link profile, which search engines can interpret negatively. The most effective approach prioritizes user-centric, descriptive anchors that naturally build a robust and trustworthy link profile. For descriptive anchors, aim for an ideal length of 3-7 words to provide context without becoming unwieldy.
Pro Tip: To truly optimize, consider the user's intent when crafting anchors. What question does the linked page answer? Use that answer as your descriptive anchor.
Enhancing User Experience and Engagement Through Strategic Linking
Strategic internal linking profoundly transforms the user journey. By providing relevant 'next steps,' you effectively reduce bounce rates, encouraging readers to delve deeper into your content. This directly increases average session duration and pages per visit, metrics that signal high user engagement and content value to search engines.
From a psychological standpoint, well-placed internal links are perceived as helpful resources, guiding users seamlessly through related topics and reinforcing your site's comprehensive authority.
A common oversight is neglecting visual distinctiveness and accessibility for links. Links must be clearly identifiable—often through color contrast or underlining—and easily clickable for all users, including those using assistive technologies. This prevents frustration and ensures a smooth, inclusive navigation path. Ultimately, internal linking should be approached as a user-first strategy, where every link genuinely enhances the reader's understanding.
Critical Internal Linking Pitfalls That Can Sabotage Your Rankings
Even well-intentioned internal linking can backfire. Broken internal links and 404 errors severely degrade user experience and waste crawl budget, signaling poor site health to search engines. Another common mistake is excessive linking—link stuffing—on a single page, which dilutes relevance and appears spammy.

Furthermore, redirect chains unnecessarily consume crawl budget and weaken link equity flow, hindering page authority. Neglecting these issues often results in significant drops in organic visibility. It is also crucial to avoid using 'nofollow' tags on internal links, as this prevents valuable link equity from distributing throughout your site, directly impacting ranking potential.
Tracking and Measuring the Success of Your Linking Efforts
To measure success, monitor crawl frequency in Google Search Console and track keyword ranking improvements for linked pages. Analytics tools can reveal user flow and click-through rates for internal links. Experience shows that even a 5% rise in crawl frequency often signals a positive impact from structural changes. This continuous, data-driven approach is paramount for long-term growth.
Future-Proofing Your Website with Sustainable Linking Habits
Sustainable internal linking for SEO is the bedrock of a robust, future-proof website, directly enhancing crawlability and user experience. Neglecting this continuous process often leads to stagnant organic visibility, where once-strong pages gradually lose their equity.
Consistent maintenance is not just beneficial but essential; dedicated, ongoing linking efforts can improve discoverability metrics by upwards of 20%. Don't let your efforts decay—conduct a comprehensive site-wide internal link audit now to secure lasting SEO gains.
Frequently Asked Questions about Internal Linking for SEO
What is internal linking for SEO?
Internal linking for SEO refers to the strategic use of hyperlinks to connect pages within the same domain. This helps search engines understand site architecture, discover new content, and distribute PageRank effectively.
How many internal links should a page have?
While there is no strict limit, links should be added naturally and provide value to the user. Excessive linking (link stuffing) can dilute the authority of a page and appear spammy to search engines.
What is the best anchor text for internal links?
The best anchor text is descriptive and relevant to the target page. Aim for a mix of exact-match and partial-match keywords, typically 3-7 words long, to provide clear context for both users and bots.
What are orphan pages?
Orphan pages are URLs on your website that have no internal links pointing to them. Because search engine crawlers follow links to find content, orphan pages are often difficult to index and rank.