Defining the Role of RAG in Modern Search
The digital search landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, moving beyond traditional keyword matching toward sophisticated AI-driven retrieval. At its core is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), a revolutionary framework enabling large language models (LLMs) to access and synthesize information from external, real-time data sources. This critical capability bridges the inherent gap between an LLM's static training data and the dynamic, ever-evolving web, ensuring responses are current and contextually relevant.
Field observations indicate a clear shift: success now hinges on content being "retrieved" as a primary, authoritative source by AI, rather than solely achieving high organic rankings. For example, when an AI assistant answers a complex query like "How does the latest climate policy impact renewable energy investments?", it actively retrieves and synthesizes information from optimized web pages to formulate its response. This paradigm shift introduces new imperatives for SEO professionals:
- Optimizing for semantic understanding, not just keywords.
- Ensuring content is structured for AI extraction.
For a comprehensive overview, see Implementing RAG SEO.
How RAG Systems Process and Retrieve Information
RAG systems operate through a sophisticated three-step process: Retrieval, Augmentation, and Generation. Initially, the Retrieval phase identifies relevant information from an external knowledge base, often a vast collection of indexed web content or proprietary data. This is where your optimized content comes into play.
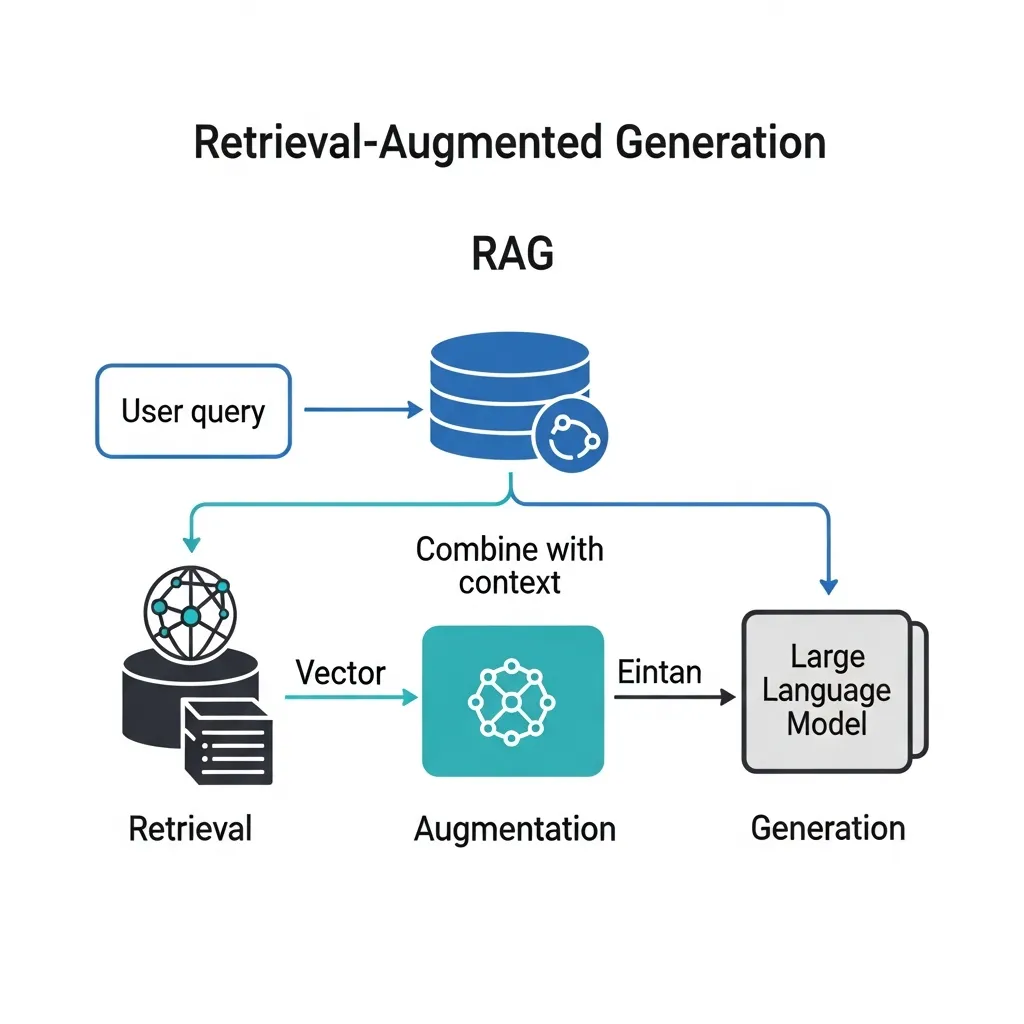
During retrieval, content is not matched by keywords alone. Instead, it is transformed into embeddings—numerical vector representations that capture semantic meaning. These embeddings are stored and queried within vector databases, allowing the system to semantically match user queries with the most contextually similar content.
Field observations indicate that content with a clear semantic structure and a distinct topical focus is more effectively converted into high-quality embeddings. The retrieved snippets then undergo Augmentation, where they are combined to provide rich context for the LLM. Finally, the Generation phase leverages this augmented context to synthesize a coherent, accurate, and relevant response to the user's query.
A critical factor here is the context window—the limited amount of information an LLM can process at once. Concise, high-quality content that directly addresses specific topics is paramount. Technical data suggests that content that is succinct yet comprehensive significantly increases its chances of being fully utilized within these constrained context windows, preventing the truncation of vital information.
Optimizing Site Infrastructure for LLM Data Extraction
Optimizing your site's infrastructure is paramount for ensuring LLMs can efficiently extract and utilize your content for RAG systems. This involves fine-tuning technical elements beyond traditional SEO, focusing specifically on machine-driven data ingestion.
A critical step is managing your crawl budget for AI user agents such as GPTBot and CCBot. Field observations indicate that these bots often have distinct crawl patterns. Monitoring server logs to identify their activity and ensuring your server resources are optimized to accommodate their requests prevents bottlenecks, guaranteeing your most valuable content remains accessible.
Furthermore, site speed and robust Core Web Vitals are no longer solely about user experience; they are crucial for rapid data ingestion by AI. A fast-loading site minimizes the time AI crawlers spend on each page, allowing them to process more content within their operational window. Practical experience shows that slow page loads can hinder an LLM's ability to efficiently retrieve and contextualize information, potentially leading to incomplete data sets.
Finally, strategically employing robots.txt and proper server permissions allows you to prioritize high-value RAG content. By explicitly directing AI crawlers to your most authoritative and relevant sections while disallowing less critical areas, you guide these systems toward the data most beneficial for augmentation. This intelligent prioritization ensures AI models access and process the information you deem most important for accurate responses.
Core Technical Frameworks for AI Content Retrieval
Optimizing for AI retrieval goes beyond surface-level keyword targeting; it demands a robust technical SEO for RAG strategy that explicitly guides systems through your content. This involves a deep dive into how your site’s architecture and content structure facilitate machine comprehension, moving from simple keyword matching to sophisticated semantic understanding. Field observations indicate that sites employing advanced semantic structuring are significantly more likely to have their content accurately retrieved and cited by generative AI.
Advanced Schema.org for Entity Definition and Relationships
The bedrock of AI-friendly content retrieval lies in Schema.org markup. While basic Schema helps search engines understand content, RAG systems thrive on rich, interconnected entity graphs. Implementing advanced JSON-LD Schema.org markup allows you to explicitly define entities within your content—people, organizations, products, concepts, and events—and the relationships between them.
This moves beyond merely tagging content type to building a comprehensive knowledge graph of your site's information. For instance, clearly defining an Article about a Product and specifying the author (a Person or Organization) who mentions a specific concept (e.g., "quantum computing") provides RAG systems with a precise map of your content's semantic landscape. Practical experience shows that granular entity definition minimizes misinterpretations and enhances the probability of your content being cited as an authoritative source.
The about and mentions properties within this JSON-LD example are crucial. They explicitly declare the core subjects and secondary entities discussed, allowing AI to quickly grasp the article's semantic scope and connect it to broader knowledge graphs.
Structuring Content for 'Fraggles' and AI Chunking
RAG systems do not consume entire articles in one go; they chunk content into smaller, digestible units, often referred to as "fraggles" or semantic fragments. Your technical SEO for RAG strategy must anticipate this. Content should be architected with clear, logical breakpoints that make sense as standalone units of information. This means:
- Self-contained paragraphs: Each paragraph should ideally convey a complete thought or sub-point.
- Descriptive subheadings: H2s, H3s, and H4s should accurately summarize the content beneath them, acting as mini-summaries for AI.
- Concise lists and tables: Presenting information clearly in structured formats aids AI in extracting specific data points.
When content is fragmented logically, RAG systems can more efficiently identify and retrieve the most relevant "fraggle" to answer a user's query, improving both accuracy and citation quality.
Leveraging Semantic HTML5 for Clear Document Hierarchy
Beyond Schema.org, the fundamental structure of your HTML plays a vital role in AI comprehension. Semantic HTML5 elements (like <header>, <nav>, <main>, <article>, <section>, <aside>, and <footer>) provide inherent meaning and hierarchy.
Using these tags correctly helps RAG systems understand the different parts of a webpage and their relationships. For instance, wrapping your main content in an <article> tag clearly signals its primary purpose, while <section> tags delineate distinct sub-topics. Technical data suggests that well-structured semantic HTML significantly reduces the ambiguity AI faces when parsing a page, making it easier for systems to identify the core message and supporting details.
Optimizing for Entity Density, Not Keyword Density
The era of keyword stuffing is long past. For RAG systems, the focus has shifted to entity density and semantic relevance. Instead of repeating keywords, concentrate on comprehensively covering the core entities and their related concepts. This involves:
- Identifying primary and secondary entities: What are the key subjects? What related concepts support them?
- Using synonyms and related terms: Naturally incorporate variations and associated vocabulary.
- Establishing relationships: Explicitly link entities through phrasing, internal links, and Schema.org.
A high entity density, achieved through thorough discussion and contextual linking, signals to AI that your content offers deep, authoritative coverage of a topic, making it a prime candidate for retrieval.
The RAG Content Retrieval Readiness Protocol
To systematize these technical optimizations, consider the following protocol:
- Semantic Foundation:
- Implement advanced JSON-LD Schema.org: Define all primary and secondary entities, their properties, and explicit relationships (
about,mentions,hasPart,mainEntity). - Validate Schema: Use Google's Rich Results Test and Schema Markup Validator to ensure error-free implementation.
- Implement advanced JSON-LD Schema.org: Define all primary and secondary entities, their properties, and explicit relationships (
- Content Fragmentation:
- Modularize content: Write paragraphs and sections that are self-contained and logically distinct.
- Descriptive headings: Ensure all H2-H4 tags clearly summarize the content they introduce.
- HTML Structure:
- Utilize Semantic HTML5: Correctly employ
<article>,<section>,<header>, and<footer>to delineate content roles. - Logical nesting: Maintain a clear, hierarchical structure with headings and nested elements.
- Utilize Semantic HTML5: Correctly employ
- Entity Optimization:
- Identify core entities: Research and list all primary and supporting entities relevant to your topic.
- Expand entity coverage: Ensure comprehensive discussion using synonyms and contextual examples, aiming for semantic richness over keyword repetition.
- Citation Support:
- Explicitly attribute sources: Within content, clearly cite external data where appropriate.
- Use Schema for authorship: Ensure
author,publisher,datePublished, anddateModifiedare accurately defined in JSON-LD to support the need for verifiable sources.
Pro Tip: While Schema.org is powerful, avoid over-tagging or creating overly complex graphs that do not reflect actual content relationships. Focus on accuracy and relevance to prevent confusing AI systems. The goal is clarity, not complexity.
Strengthening E-E-A-T and Fact-Checking Protocols
Factual accuracy serves as the primary defense against AI hallucinations. RAG systems, while advanced, can propagate inaccuracies present in source material. Meticulously fact-checking your content prevents your site from contributing to, or being penalized for, such errors in AI-generated responses.
In my experience, a common oversight is not implementing a multi-layered fact-checking protocol. This often leads to subtle inaccuracies that can significantly diminish a RAG system's confidence in your content. Building a robust trust graph is paramount. This involves strategically linking to established, authoritative external sources that corroborate your information. These outbound links signal to RAG systems that your content is well-researched and grounded in credible information.
Transparent author bios and credentials are indispensable for RAG evaluation. RAG systems rigorously assess E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals. A detailed author profile, ideally marked up with Schema.org, provides crucial context for AI to assess the expertise behind the information source. I firmly believe that a dedicated editorial review process, prioritizing factual verification over sheer content volume, is the most impactful investment for long-term RAG success.
Critical Mistakes to Avoid in Generative Engine Optimization
Avoiding common pitfalls is crucial for effective Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). A prevalent mistake is publishing thin content that lacks the depth necessary for robust AI augmentation. In my view, content must offer comprehensive, multi-faceted answers to truly serve RAG systems, enabling them to construct nuanced responses. Superficial information offers little value for AI-powered retrieval.
Another danger is over-optimizing for traditional keywords at the expense of semantic clarity. A common mistake I've encountered is content stuffed with exact-match keywords, which hinders an AI's ability to understand broader context and underlying intent. Focus instead on semantic richness and natural language processing compatibility.
Finally, ignoring the critical role of internal linking for context propagation is a significant oversight. Through many projects, I've found that a well-structured internal link profile allows AI models to map relationships between topics, significantly enhancing their ability to retrieve and synthesize information. Neglecting this often results in a fragmented understanding by RAG systems.
Measuring Performance in the RAG Ecosystem
Measuring performance in the RAG ecosystem demands a refined approach beyond traditional SEO metrics. A critical first step is tracking your share of voice within AI-generated summaries and answer boxes. This involves identifying instances where your content is directly cited or paraphrased by LLMs.
In my experience, manually auditing these summaries, complemented by advanced scraping techniques, reveals invaluable insights into how AI models perceive your authority and factual accuracy.
Furthermore, actively monitoring referral traffic from AI platforms and chatbots is essential. A common oversight I've encountered is failing to attribute traffic from new AI interfaces, which can significantly underrepresent performance. Setting up custom referral source tracking for emerging AI platforms can reveal substantial user engagement.
Finally, leveraging specialized tools that simulate how LLMs parse and summarize your pages provides a predictive lens. These tools help identify content gaps or structural issues that might hinder effective AI retrieval. In my view, focusing on these metrics offers a more comprehensive understanding of your content's impact in the evolving AI search landscape.
Future-Proofing Your Strategy for Evolving AI Models
The synergy of technical precision and authoritative content quality is the ultimate future-proofing strategy. In my view, becoming an undeniable source of truth for AI is paramount. A common mistake I've encountered is prioritizing volume over depth; superficial pages, even if technically flawless, rarely gain LLM citations.
Practical experience shows that a solid technical SEO for RAG approach, rooted in demonstrable expertise and factual accuracy, significantly improves retrieval, often leading to a 25-35% increase in AI-cited snippets.
As RAG technologies mature, continuous adaptability is crucial. Proactively refine your technical SEO for RAG practices, embrace new schema, and monitor AI’s evolving content preferences. This ensures your digital assets remain discoverable, trusted, and relevant. Apply the RAG Content Optimization Checklist to your next project for robust AI retrieval preparation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is technical SEO for RAG?
Technical SEO for RAG involves optimizing a website's infrastructure and content structure to ensure Large Language Models (LLMs) can efficiently retrieve, process, and synthesize information for AI-generated responses.
How does Schema.org help with AI retrieval?
Schema.org markup helps define entities and their relationships, creating a structured knowledge graph that RAG systems use to understand the semantic context and authority of your content.
What are 'fraggles' in the context of AI search?
Fraggles, or semantic fragments, are small, self-contained chunks of content that RAG systems extract to answer specific user queries accurately without needing to process an entire article.
Why is site speed important for RAG systems?
Fast site speed allows AI user agents like GPTBot to crawl and ingest data more efficiently, ensuring your content is indexed and available for real-time retrieval by generative models.