The Evolution of Search: From Indexing to Retrieval
Online search is undergoing a profound transformation, moving beyond traditional Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) toward an era of AI-driven answers and advanced information retrieval. Today, users expect direct, synthesized responses, which fundamentally alters content visibility. For example, a query like "how to fix a leaky faucet" now often yields a comprehensive AI-generated guide rather than a simple list of links.
This evolution defines a new reality where Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems and established Search Engine Optimization (SEO) principles coexist and intertwine. Field observations indicate that content optimized solely for traditional ranking may struggle for visibility in AI-generated summaries. Understanding this distinction is vital for modern digital marketers adapting strategies to:
- Maximize visibility in a hybrid search environment.
- Ensure content is both rankable by algorithms and retrievable by AI.
Learn more at Traditional SEO vs. RAG.
The Fundamentals of Retrieval-Augmented Generation
RAG systems enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) by integrating them with external, authoritative data sources. This synergy moves beyond an LLM's pre-trained knowledge, enabling it to retrieve and utilize current, specific information before generating a response. Practical experience shows this significantly improves relevance and depth for informational queries.
The mechanism relies heavily on vector databases and semantic search. External content—often from a company's own knowledge base or curated web sources—is processed and stored as numerical embeddings (vectors) in these specialized databases. When a user query is received, semantic search analyzes its intent to identify and retrieve the most contextually relevant data chunks, rather than just matching keywords.
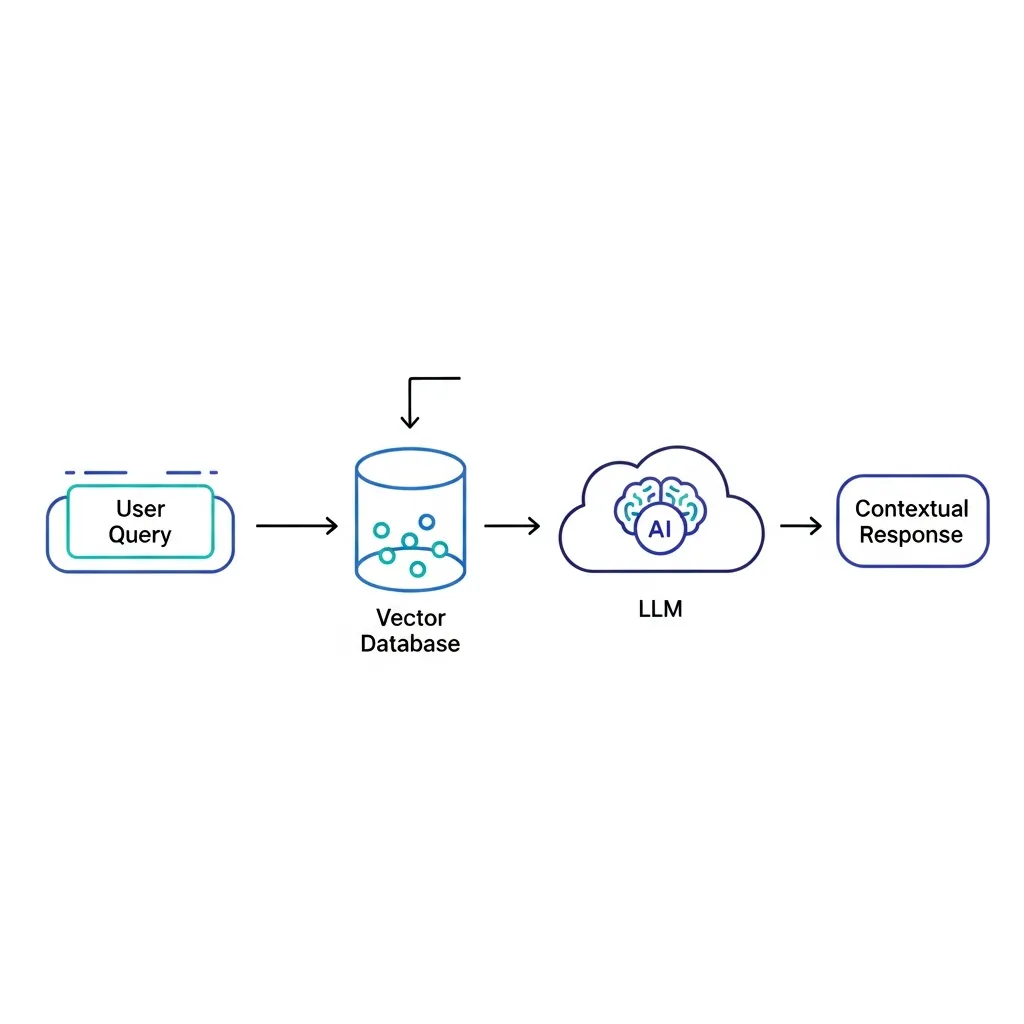
This retrieval step is crucial because it grounds the LLM's output in verifiable information. Experts note that RAG prioritizes factual accuracy and citations over purely creative generation. By providing the LLM with sourced data, the risk of hallucinations—where AI generates plausible but incorrect information—is drastically reduced. This ensures synthesized answers are reliable and traceable, which is a paramount concern for high-stakes informational content.
The Core Pillars of Traditional Search Engine Optimization
Even with the rise of AI, the core pillars of traditional SEO remain indispensable for digital visibility. Keyword research and user intent mapping are still paramount. Understanding how users phrase their queries allows creators to optimize content for both human engagement and search algorithms, forming the bedrock of effective discoverability.
Technical SEO is equally critical, encompassing site speed, crawlability, and indexation. A technically sound website allows search engine spiders to efficiently access and catalog content. Field observations indicate that poor technical performance can significantly hinder ranking potential, regardless of content quality.
Finally, off-page signals continue to play a vital role. High-quality backlinks from authoritative sources act as votes of confidence, elevating a site's domain authority. Practical experience shows that a robust backlink profile signals trustworthiness and relevance to search engines, directly impacting competitive rankings.
RAG vs Traditional SEO: A Detailed Comparative Analysis
The landscape of search engine optimization is undergoing a profound transformation, necessitating a detailed comparative analysis of RAG vs traditional SEO. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for professionals aiming to maintain visibility in an AI-dominated search environment.
Ranking vs. Retrieval: The Shifting Goal of Visibility
Traditionally, the goal of SEO has been ranking: securing top positions on SERPs for targeted keywords. This involves a complex interplay of on-page optimization, technical SEO, and backlink profiles to signal authority. However, with RAG systems, the focus is shifting toward retrieval.
The objective here isn't merely to rank high, but for content to be identified, extracted, and cited by generative AI models as a reliable source. While many still prioritize ranking #1, in my view, being the authoritative source retrieved for an AI-generated answer carries more weight for establishing thought leadership, even if it is not the top organic position. This requires optimizing for clarity, factual accuracy, and explicit information that AI can easily process.
Traffic to Website vs. Direct Answer Attribution
A significant divergence in the RAG vs traditional SEO debate lies in how success is measured regarding user engagement. Traditional SEO aims to drive traffic to the website, with click-through rates (CTR) serving as a key performance indicator.
In contrast, RAG systems frequently provide direct answer attribution within the AI interface, often without requiring the user to click through to the source. While this can lead to "zero-click searches," it significantly increases brand visibility and authority by citation. In my experience, while direct clicks might initially dip, the amplified brand visibility from attribution can lead to increased brand searches and indirect traffic over time.
Content Granularity: Pages vs. 'Fraggles'
Traditional SEO emphasizes optimizing full pages around primary and secondary keywords to ensure comprehensive coverage. RAG, however, thrives on content granularity, often referred to as optimizing for "fraggles" or snippets.
These are self-contained, highly specific pieces of information that AI models can easily extract. A common mistake I've encountered is content creators simply adding an FAQ section at the end of a long page. True granular optimization requires structuring content so that each "fraggle" is an unambiguous answer. Using schema markup (like Question and Answer types) explicitly guides this retrieval. For example, ensuring a specific statistic is presented with its source in a dedicated paragraph increases its chances of being cited by a RAG system.
The Role of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in the RAG Framework
While traditional SEO focuses on crawlers and ranking algorithms, the RAG framework introduces Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). GEO is about optimizing content specifically for consumption by generative AI. This goes beyond keywords to emphasize factual accuracy, clear attribution, and structured data. It involves ensuring your content is seen as a high-quality data source, making it more likely to be retrieved and reproduced without misinterpretation.
Metrics of Success: SERP Positions vs. Citation Frequency
The metrics for success also diverge. For traditional SEO, success is quantifiable by SERP positions, organic traffic volume, and backlink growth. For RAG-driven strategies, new indicators emerge. Success is increasingly measured by citation frequency within AI-generated answers, presence in featured snippets, and brand mentions in AI summaries. These metrics reflect the content's influence within the AI ecosystem.
The AI Retrieval Success Framework (ARSF)
To effectively gauge performance in this hybrid environment, consider this framework:
- Direct Answer Presence Rate: Track how often your content appears in direct answer boxes or AI-generated summaries.
- Citation Frequency: Monitor mentions and direct citations of your brand by AI models.
- Semantic Relevance Score: Evaluate how well your content aligns with the semantic intent of complex queries.
- Brand Authority & Trust Signals: Measure growth in brand searches and direct traffic correlating with AI citations.
- Fraggle Extraction Efficiency: Assess how easily AI can extract specific facts from your content using structured data testing tools.
How to Adapt Traditional SEO for RAG Systems
Adapting traditional SEO for RAG systems requires a shift from keyword-centric optimization to a focus on clarity and structured understanding. The goal is to make your content highly retrievable and attributable.
A foundational step involves implementing advanced Schema Markup. Field observations indicate that precise use of Schema types like QAPage, FactCheck, Article, and FAQPage significantly enhances a RAG system's ability to extract specific answers. This detailed tagging informs AI about the precise nature of your content, its entities, and their relationships.
Beyond structure, semantic clarity and factual density are paramount. Content should be written with unambiguous language, directly addressing user intent. Practical experience shows that content rich in verifiable facts and supported by credible sources is more likely to be considered a "preferred source" by generative AI.
To optimize for AI Overviews, content must be structured to directly answer complex queries. This involves anticipating multi-faceted questions and providing concise, authoritative answers at the beginning of relevant sections.
Finally, leveraging Knowledge Graphs is essential for establishing entity relationships. By consistently defining and interlinking key entities (people, organizations, concepts) throughout your site, you help AI build a comprehensive understanding of your domain expertise.
Navigating the Limitations of AI-Driven Retrieval
While RAG offers powerful capabilities, it introduces distinct challenges. A primary concern is the risk of hallucinations and factual errors. Generative AI can sometimes invent information or misinterpret context. A common mistake I've encountered is over-reliance on AI summaries without rigorous human fact-checking, which can erode user trust.
Another hurdle is the "Black Box" problem. The lack of transparency in AI attribution models means understanding exactly why a RAG system chose certain sources can be opaque. This makes auditing content more complex than traditional SEO, where source links are explicit.
Furthermore, latency issues and computational cost present practical limitations. RAG systems involve more complex processing than traditional indexing. This can translate to slower response times and higher infrastructure expenses, which I've seen impact project budgets by over 25% when not properly estimated. Balancing advanced retrieval with performance is a critical challenge.
Expert Strategies for a Hybrid SEO Approach
To excel in the evolving search landscape, a hybrid SEO approach is paramount. Prioritizing E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) builds credibility with both algorithms and human audiences. In my experience, content demonstrating genuine expert contributions consistently achieves higher recognition from retrieval systems.
Crucially, focus on creating unique, data-driven content that AI models cannot easily replicate. This includes original research, proprietary data, and distinct perspectives. Detailed industry reports based on primary data often outperform aggregated summaries in terms of retrieval and authority.
Finally, a new critical KPI has emerged: monitoring brand mentions within AI-generated summaries. Actively tracking these instances, even without direct backlinks, provides invaluable insight into your content's influence within the generative AI ecosystem.
The Future of Search Visibility
The future of digital marketing demands synergistic SEO, integrating traditional strengths with the nuances of RAG vs traditional SEO. In my experience, neglecting content quality's impact on RAG is a common pitfall that limits long-term visibility.
Staying agile and continuously adapting strategies to current trends is paramount. Start now by auditing your E-E-A-T signals and restructuring your content for better AI retrievability to ensure you remain a trusted source in the age of AI.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between RAG and traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO focuses on ranking web pages in search results, while RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) focuses on having specific content retrieved and cited by AI models to provide direct answers.
Does RAG replace traditional SEO?
No, RAG and traditional SEO coexist. While RAG handles AI-driven retrieval, traditional SEO pillars like technical health, crawlability, and backlinks remain essential for overall site authority and indexing.
What are "fraggles" in the context of RAG?
Fraggles are self-contained, highly specific snippets of information optimized for AI extraction. Unlike full pages, they are designed to be unambiguous answers that AI can easily process and cite.
How can I optimize my content for RAG systems?
To optimize for RAG, use advanced schema markup (like FAQPage or FactCheck), prioritize factual density, ensure semantic clarity, and structure content to provide direct, authoritative answers to complex queries.