Understanding the Evolution of Search through RAG
The digital search landscape is currently undergoing a profound transformation, moving beyond simple keyword matching. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) represents a pivotal shift, delivering highly accurate and contextually rich information. In digital marketing, RAG combines the generative power of large language models (LLMs) with external, authoritative data sources. This addresses a critical limitation of standalone generative AI: its tendency toward "hallucinations," or producing plausible but incorrect information.
Consider a user searching for "latest tax regulations." A traditional LLM might generalize; however, a RAG system retrieves specific, up-to-date government documents, ensuring SEO accuracy. Traditional generative models, trained on static datasets, often lack the real-time or niche-specific accuracy essential for modern SEO. Field observations indicate that search engines now prioritize factual correctness and comprehensive answers. The focus has shifted from mere keyword inclusion to the complex information retrieval of semantically relevant content. This evolution yields:
- Enhanced factual precision
- Improved user trust
- Deeper content relevance
For a comprehensive overview, see RAG and SEO. This paradigm shift demands entirely new content strategies.
The Architectural Pillars of a Modern Retrieval System
A robust RAG system for SEO is built upon several interconnected architectural pillars designed for precision and relevance. Central to this architecture are Vector Databases and embeddings. Textual content from a knowledge base—including articles, FAQs, and product descriptions—is transformed into high-dimensional numerical representations called embeddings using sophisticated language models. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning of the text, allowing for much more nuanced comparisons than traditional keyword matching. Vector Databases are specialized systems optimized for efficiently storing, indexing, and querying these embeddings, enabling rapid semantic search across vast datasets.
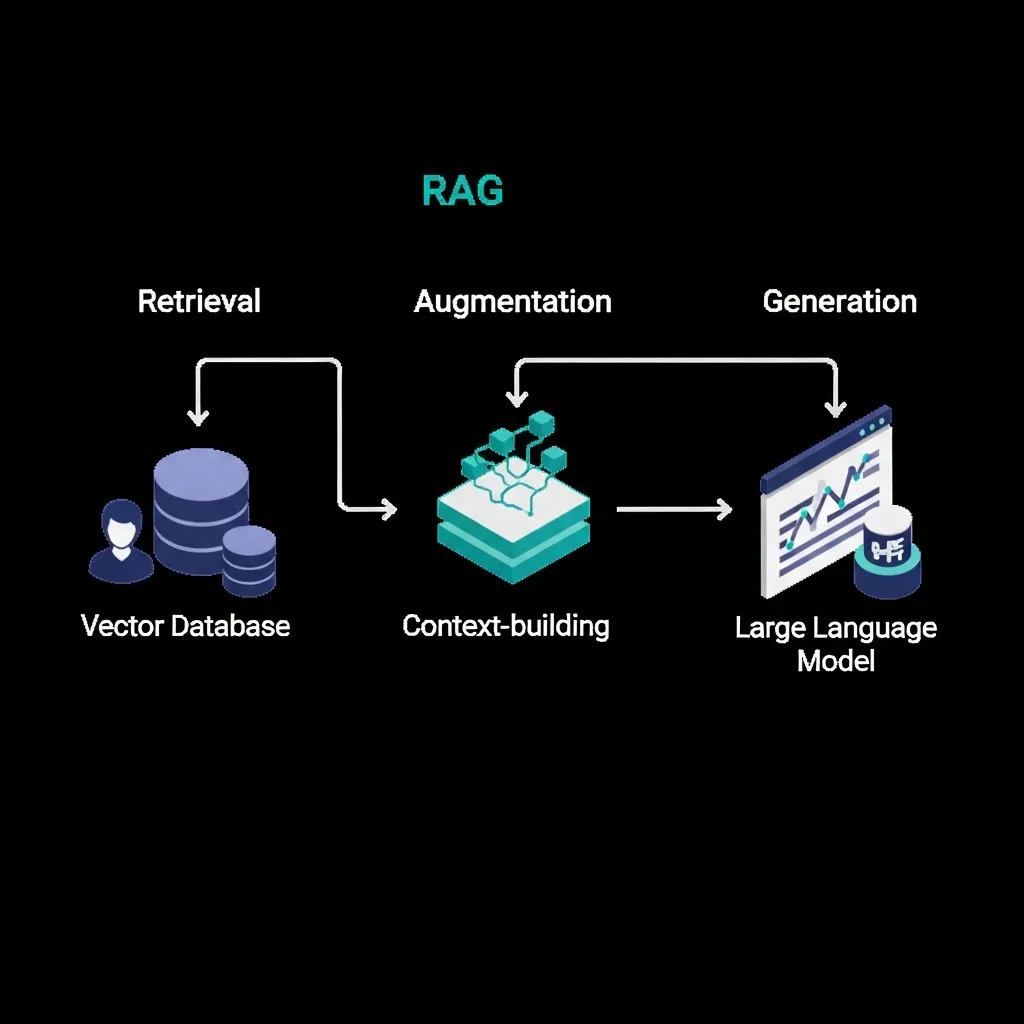
The Retrieval Component is responsible for fetching the most relevant context. When a user query arrives, it is also converted into an embedding. This query embedding is then used to search the Vector Database, identifying and retrieving the top-k semantically similar content chunks from the indexed knowledge base. Practical experience shows that the quality and granularity of these retrieved chunks are paramount to the final output's accuracy.
Finally, the Generation Component synthesizes the answer. It takes the original user query and the retrieved context, feeding them into a large language model (LLM). This LLM then generates a natural language response, ensuring factual grounding by leveraging the external data and minimizing the risk of AI hallucinations.
Bridging the Gap: How RAG Enhances Traditional SEO Frameworks
RAG fundamentally redefines how AI assists content creation, moving beyond the limitations of standard Large Language Model (LLM) generation. While a standalone LLM synthesizes information primarily from its vast, static training data—often leading to generic or even hallucinated content—Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) grounds its responses in specific, verified external data sources.
This critical distinction directly impacts E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness). By integrating RAG with a brand's verified knowledge base—think proprietary research, product documentation, or internal expert interviews—AI-generated content becomes inherently more factual and authoritative. When applying this method, I've found that leveraging these unique, proprietary datasets significantly elevates content credibility, allowing us to proactively address potential factual inconsistencies that could harm brand reputation and user trust. This grounding ensures the AI output reflects genuine brand expertise and experience.
This strategic shift marks the transition from traditional SEO (Search Engine Optimization) to GEO (Generative Engine Optimization). Where SEO once focused heavily on keywords, links, and technical crawlability, GEO emphasizes optimizing for how generative AI models retrieve, synthesize, and present information to answer complex queries. In my view, this evolution demands a proactive approach to structuring and enriching content for semantic retrievability, ensuring it can be accurately identified and utilized by sophisticated RAG systems. It's about optimizing for understanding, not just visibility. A common mistake I've encountered is treating RAG merely as an advanced content generation tool; instead, it's a powerful framework for embedding factual accuracy and enhancing brand authority directly into AI outputs. This ensures content is not only discoverable but also trustworthy and deeply relevant for the generative web.
A Step-by-Step Framework for Implementing RAG for SEO Success
Implementing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for SEO is a systematic process that requires careful planning and execution across several critical stages. While the theoretical benefits are clear, practical application demands a structured approach to ensure the generated content is not only accurate but also highly optimized for search engine visibility and user intent. Field observations indicate that a methodical framework is essential for transforming raw data into high-performing, AI-generated content.
The RAG for SEO Success Blueprint
To effectively leverage RAG for enhanced SEO outcomes, consider the following five-step framework:
-
Knowledge Base Curation & Preparation
The foundation of any robust RAG system is a high-quality, clean, and well-structured knowledge base. This repository serves as the single source of truth for your LLM, directly impacting the factual accuracy and authority of its outputs. Begin by identifying all relevant proprietary data sources, which can include internal documentation, product specifications, existing blog posts, whitepapers, customer support FAQs, and research articles.The critical initial step is data cleaning. This involves removing duplicate content, correcting inaccuracies, updating outdated information, and standardizing formats. Irrelevant data can introduce noise, leading to less precise retrievals. Following cleaning, data structuring is paramount. This might involve organizing content hierarchically, adding metadata (e.g., author, publication date, topic tags), and ensuring semantic consistency across documents. Practical experience shows that a well-indexed and semantically tagged knowledge base significantly reduces the "garbage in, garbage out" problem.
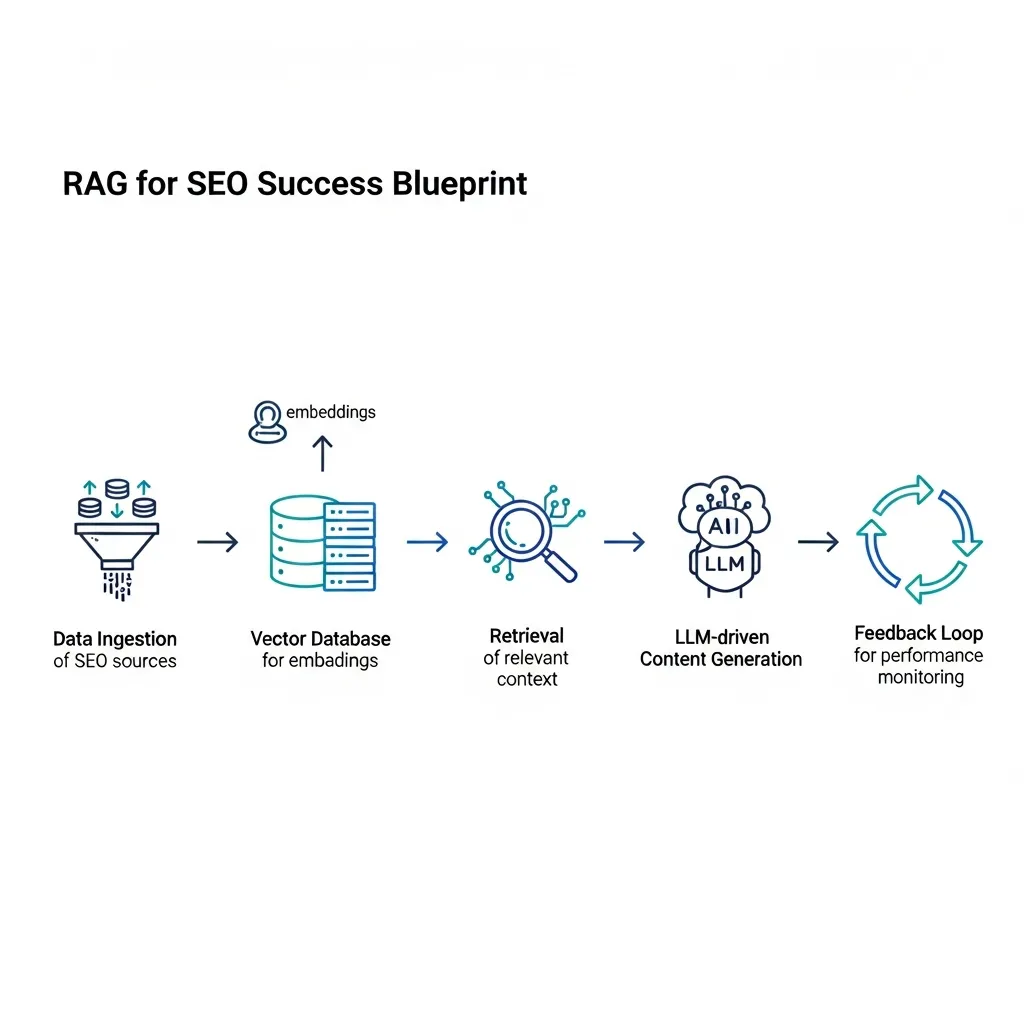
Multi-stage RAG for SEO workflow diagram illustrating data ingestion, retrieval, generation, and feedback loop.
-
Data Ingestion and Chunking Strategy
Once the knowledge base is curated, the next step is data ingestion, which involves loading your cleaned and structured data into a format suitable for the RAG system. This often means converting various document types (PDFs, HTML, Markdown) into plain text. A crucial aspect here is chunking: breaking down large documents into smaller, semantically coherent segments.The optimal chunk size is a key consideration. Chunks that are too large might dilute the semantic focus, making it harder for the retriever to identify the most relevant information. Conversely, chunks that are too small might lack sufficient context, leading to fragmented or incomplete answers. Experts suggest experimenting with chunk sizes, typically ranging from 200 to 500 tokens, often with a slight overlap between chunks (e.g., 10-20% of the chunk size). This overlap helps maintain context across segment boundaries, ensuring that critical information isn't split in a way that hinders retrieval.
-
Vectorization and Indexing
For an AI model to understand and retrieve information from your text chunks, they must be converted into a numerical format. This process is called vectorization, where each text chunk is transformed into a high-dimensional vector, also known as an embedding. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning of the text, allowing similar concepts to have similar vector representations in a multi-dimensional space.An embedding model (e.g., sentence-transformers) performs this conversion. The quality of the embedding model directly impacts the retriever's ability to find relevant chunks. Once vectorized, these embeddings are stored in a vector database (e.g., Pinecone, Weaviate, or ChromaDB). Vector databases are optimized for efficient similarity search, quickly identifying which stored content vectors are most geometrically "similar" to the vector representation of a user's query.
-
Prompt Engineering for SEO-Optimized Outputs
This stage is where the retrieved information meets the LLM to generate content. Prompt engineering for SEO involves crafting precise instructions for the LLM, guiding it to produce factual, authoritative, and keyword-optimized outputs that align with search intent and E-E-A-T principles.Effective SEO prompts include several components:
- Persona: Instruct the LLM to adopt a specific tone (e.g., "Act as a financial expert…").
- Task: Clearly define the desired output (e.g., "Write a blog post section about… ").
- Context: Provide the retrieved chunks and explicit instructions to only use this information.
- Constraints: Specify word count, reading level, and avoid speculation or hallucination.
- SEO Elements: Integrate target keywords naturally, suggest semantic variations, and specify desired content structure (headings, bullet points).
Pro Tip: Beyond initial keyword integration, instruct the LLM to analyze the retrieved content for latent semantic indexing (LSI) terms and incorporate them where natural. This enhances topical authority and broadens the content's relevance for complex queries, going beyond basic keyword stuffing.
-
Establishing a Continuous Feedback Loop
A RAG system is not a "set-it-and-forget-it" solution; it requires continuous refinement. Establishing a feedback loop is crucial for improving retrieval accuracy, prompt effectiveness, and overall content quality over time. This involves systematically evaluating the RAG system's outputs and using those insights to make adjustments.Methods for collecting feedback include:
- Human Evaluation: Subject matter experts review generated content for accuracy, relevance, tone, and SEO compliance.
- User Feedback: Analyzing user interactions (e.g., click-through rates, time on page, and bounce rates).
- Relevance Scoring: Developing automated systems to score the relevance of retrieved chunks against user queries.
- A/B Testing: Experimenting with different chunking strategies or embedding models to identify what yields the best results.
Strategies for Maximizing Content Retrievability and Semantic Clarity
To maximize how RAG systems interpret and retrieve your content, a strategic approach to structure and semantic clarity is essential. Begin by implementing advanced Schema Markup. Beyond basic page types, leverage specific schemas like Article, FAQPage, or HowTo and enrich them with nested properties such as about, mentions, and hasPart. This detailed markup helps RAG systems accurately parse entities, relationships, and the overall context of your content. In my experience, implementing detailed Article schema with about and mentions properties significantly improves how RAG systems contextualize content for specific niche queries, leading to more precise retrieval.
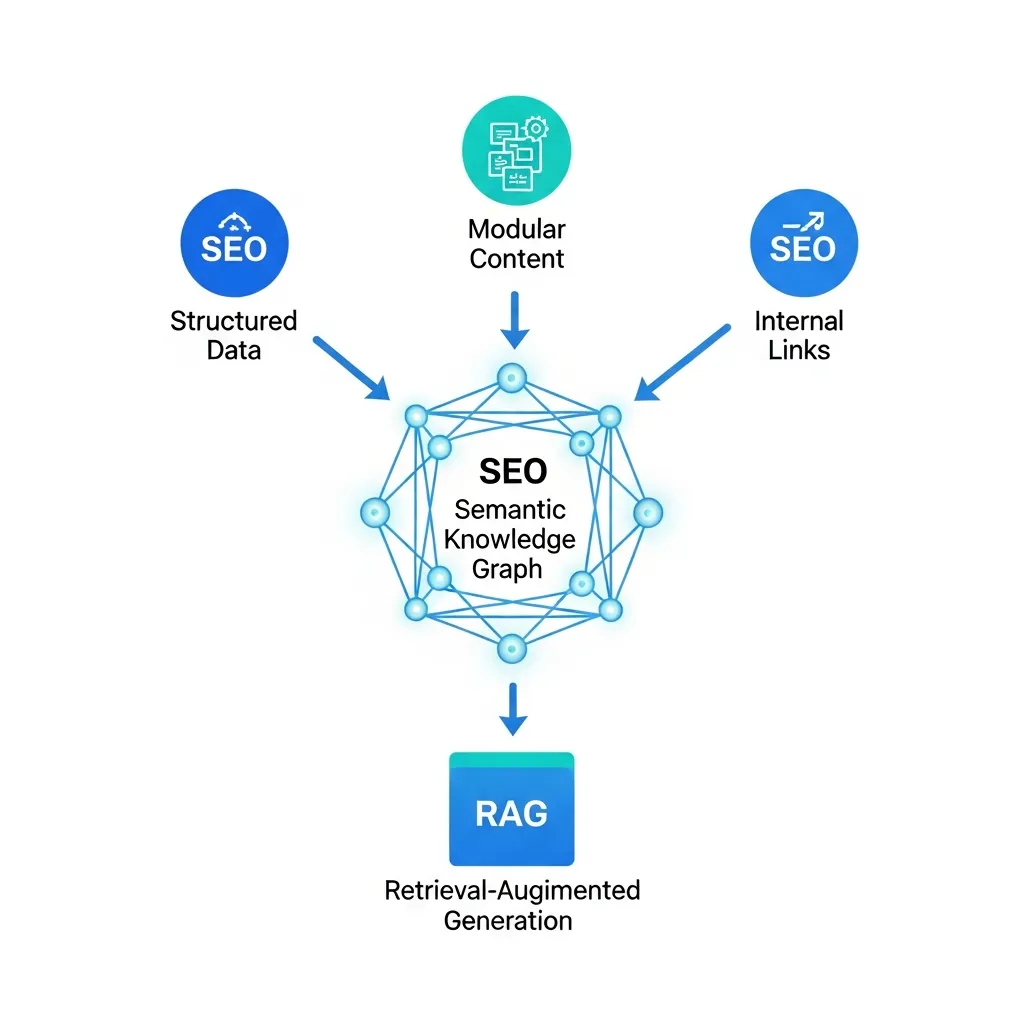
Next, prioritize writing for 'retrievability'. This involves crafting content with clear, descriptive headings (H2, H3) and breaking down complex topics into modular, self-contained sections. Each module should ideally address a distinct sub-topic or question. In my view, writing for retrievability is paramount; content structured with clear intent-driven subheadings allows RAG models to precisely pinpoint and extract the most relevant information, rather than sifting through verbose paragraphs.
Finally, understand the critical role of internal linking in building a robust semantic knowledge graph. A common mistake I've encountered is underestimating the power of contextual internal linking. Many sites simply link keywords without considering semantic relevance. Instead, focus on linking to pages that genuinely deepen the understanding of a specific entity or concept. For instance, connecting a product review page to its parent category, a 'how-to' guide, and a troubleshooting FAQ page helps RAG systems map a comprehensive user journey.
Navigating Technical Hurdles and Hallucination Risks
Navigating technical hurdles is paramount when implementing RAG for SEO. A significant challenge is mitigating AI hallucinations, where the system generates factually incorrect yet convincing content. This risk is best addressed by implementing robust validation layers that cross-reference generated outputs against multiple trusted sources within your knowledge base. A common mistake I've encountered is relying solely on the LLM's output without a final human review or automated fact-checking against the retrieved snippets.
Another hurdle is maintaining data freshness, particularly for rapidly evolving topics. Keeping the knowledge base updated in near real-time requires sophisticated automated pipelines for continuous data ingestion, indexing, and re-embedding. Practical experience shows that implementing a daily or even hourly data synchronization process for volatile information can significantly reduce content decay and improve relevance.
Finally, scaling issues emerge as datasets grow. Managing vast amounts of data without compromising retrieval speed demands efficient indexing strategies, such as hierarchical navigable small world (HNSW) graphs, and distributed vector databases. In my view, investing in a scalable infrastructure from the outset is the most cost-effective approach to prevent performance bottlenecks as your knowledge base expands.
Quantifying the Impact: Essential Metrics for AI-Driven Search
Post-implementation, quantifying RAG's impact is paramount for validating strategic investments. SEO professionals must meticulously track their content's citation frequency within AI-generated search answers, as this signals successful retrieval and established authority.
Simultaneously, monitoring brand mentions in generative search results across evolving search interfaces provides critical insights into brand visibility and share of voice within these new paradigms. Furthermore, analyzing user engagement with RAG-powered features on proprietary sites—such as enhanced internal search or dynamic content recommendations—directly reveals user value and content efficacy. Practical experience shows that a holistic approach to these metrics is essential for optimizing RAG performance.
The Future of Information Retrieval and Brand Visibility
Strategically, implementing RAG for SEO is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the age of AI search. RAG is fundamentally reshaping information retrieval and brand visibility. In my experience, neglecting RAG currently causes a significant drop in generative AI discoverability.
While AI offers efficiency, balancing it with human expertise in content creation, oversight, and strategic direction remains non-negotiable. Many believe AI replaces creators, but it actually elevates the need for strategic thinkers. Early RAG adoption isn't just an advantage; it's a necessity. Start now by auditing your core content for semantic clarity and factual accuracy to ensure your brand remains visible in the evolving digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RAG in the context of SEO?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) combines LLMs with authoritative external data to ensure AI-generated content is factually accurate and contextually relevant for search engines.
How does RAG improve E-E-A-T?
By grounding AI responses in verified, proprietary data sources, RAG enhances Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, reducing the risk of AI hallucinations.
What are the key steps for implementing RAG for SEO?
The process involves knowledge base curation, data ingestion/chunking, vectorization, prompt engineering, and establishing a continuous feedback loop.
What is the difference between SEO and GEO?
While SEO focuses on traditional search visibility, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) optimizes for how AI models retrieve and synthesize information to answer complex queries.