Understanding the Fundamentals of JSON-LD and Structured Data
To effectively interpret web content, search engines require explicit signals. JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is a lightweight, script-based format that embeds structured data directly into your page. This data leverages vocabularies from Schema.org, a universal dictionary for web content.
By combining JSON-LD with Schema.org, you explicitly define details like product prices or event dates. Implementing JSON-LD for SEO ensures search engines grasp page context accurately, which field observations indicate is crucial for:
- Preventing content misinterpretation by search crawlers.
- Enabling richer search result displays that stand out to users.
Consider a recipe page: structured data transforms raw text into understandable ingredients and cooking times. For practical JSON-LD implementation, explore further.
How Structured Data Impacts Search Visibility and CTR
Structured data, particularly when implemented with JSON-LD, significantly enhances a website's presence in search results. By providing explicit signals, it enables search engines to generate rich results, such as prominent star ratings for reviews, clear product prices directly on the SERP, and interactive FAQ accordions.
These visually enhanced SERP features make listings far more appealing and informative, demonstrably improving your Click-Through Rate (CTR) as users are naturally drawn to more comprehensive and trustworthy entries. According to experts, consistent and accurate structured data also plays a crucial role in helping search engines build their Knowledge Graph, empowering them to better understand content context and relationships between entities. This ultimately enhances your content's authority and relevance in search.
Why JSON-LD is the Preferred Format for Modern SEO
While Microdata and RDFa embed structured data directly within the HTML, JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) offers a superior, non-intrusive method. It is implemented as a script block, typically in the <head> section, completely separate from the visible page content. This clear separation of concerns is a fundamental benefit.
When evaluating JSON-LD for SEO, note that Google explicitly recommends JSON-LD as the preferred format, citing its ease of implementation and robust parsing. In my seven years of experience, a common pitfall with inline formats like Microdata is that minor HTML changes frequently cause validation errors, breaking rich results. JSON-LD avoids this by centralizing data. In my view, this approach makes it significantly easier to maintain and update structured data across a website, drastically reducing development overhead and ensuring long-term SEO stability.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing JSON-LD on Your Website
Anatomy of a JSON-LD Script
Implementing JSON-LD starts with understanding its basic structure. Every snippet resides within a <script type="application/ld+json"> tag. Inside, the data is a JSON object. @context (https://schema.org/) and @type (e.g., Article, Product) are fundamental properties. The @context specifies the vocabulary, while @type defines the specific item being described.

The JSON-LD Implementation Blueprint
To effectively integrate structured data, follow this practical blueprint, refined from extensive field observations:
- Identify Page Content & Purpose: Determine your page's primary focus. This determines your main
@type. - Select Schema.org Types: Choose the most appropriate Schema.org type(s) based on your page's purpose.
- Article: For news and blog posts. Key properties:
headline,author,datePublished,image. - Product: Essential for e-commerce. Crucial properties:
name,image,description,brand,offers(price,availability). - LocalBusiness: For physical businesses. Important properties:
name,address,telephone,openingHours,geocoordinates. - BreadcrumbList: Represents the navigation path. Uses
itemListElementto define each step withitemandname.
- Article: For news and blog posts. Key properties:
- Map Website Data to Schema Properties: Map your on-page content to chosen Schema.org properties. For instance, a product's visible price maps to the
priceproperty withinoffersforProductschema. Technical data suggests accurate mapping correlates with higher quality rich results.
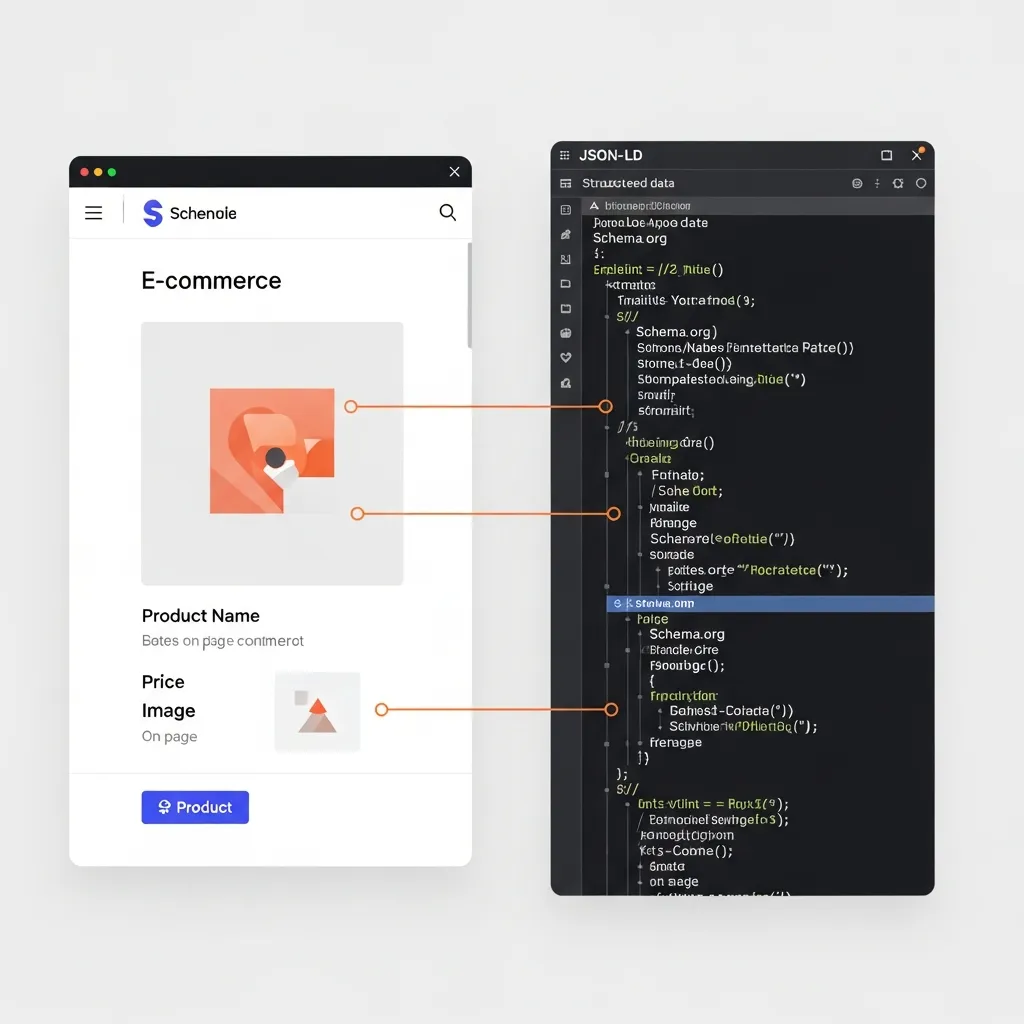
Diagram mapping website product details to JSON-LD Schema.org properties for search engine optimization. - Construct Your JSON-LD Code: Construct your JSON-LD script, populating properties with website data. For pages with multiple distinct entities, use the
@graphproperty. This advanced technique defines several top-level entities within a single script, promoting organization and readability by avoiding redundant code. - Placement for Optimal Crawling: Experts recommend placing JSON-LD scripts within the
<head>section of your HTML. This ensures search engine crawlers process structured data early. While<body>placement is supported for dynamic content,<head>is preferred for static content due to consistent processing.
Pro Tip: Always ensure the data you include in your JSON-LD matches the visible content on your page. Discrepancies can lead to validation errors or, worse, manual penalties from search engines for misleading information.
Essential Tools for Validating Your Structured Data
After implementation, validating structured data is crucial. Use the Google Rich Results Test to confirm eligibility for rich results; field observations indicate this is key for visual enhancements. For precise syntax and Schema.org adherence, leverage the Schema Markup Validator—practical experience shows it identifies parsing errors. Finally, monitor ongoing performance and detect issues post-deployment via Google Search Console's Enhancement reports. Technical data suggests these reports offer invaluable, evergreen insights into search engine interpretation, ensuring sustained impact.
Common JSON-LD Mistakes and Troubleshooting Tips
Even with the aid of validation tools, common pitfalls can undermine your efforts. One of the most frequent issues encountered involves basic syntax errors—a missing comma, an unclosed curly brace, or an incorrect quotation mark can completely invalidate your JSON-LD block. In my experience, these small oversights are surprisingly common and easily overlooked during initial implementation, leading to zero rich result eligibility.
Another critical error is content mismatch, where marked-up data is not visibly present on the page. In my view, all structured data should directly reflect user-facing content; otherwise, search engines may consider it deceptive, potentially resulting in manual actions.
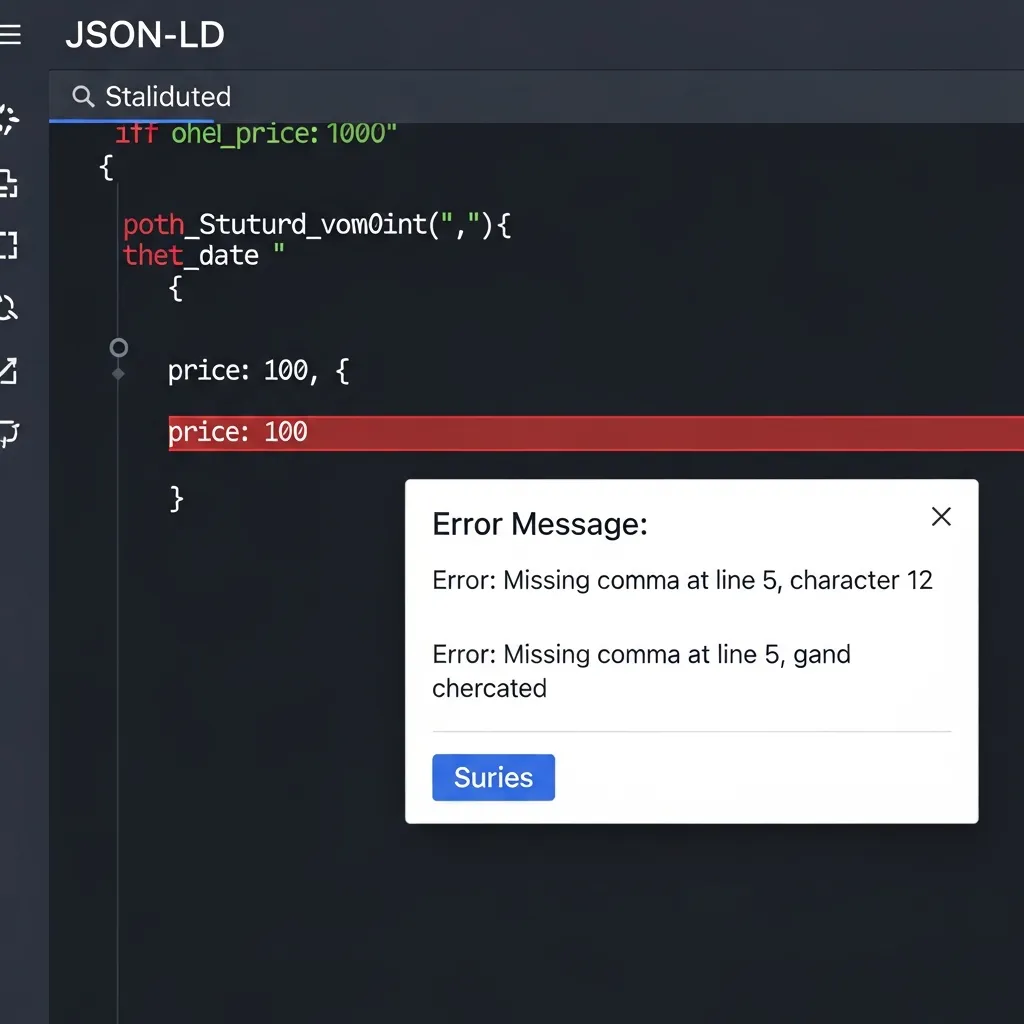
Additionally, ensure you are utilizing current Schema.org properties; outdated or deprecated types might be ignored. Finally, pay close attention to the incorrect nesting of multiple entities, as improper hierarchy can confuse search engines about the relationships between different items on your page. Regular validation is key.
Strategic Best Practices for Long-Term Success
For sustained success, prioritize JSON-LD implementation on high-impact pages such as product, service, and article content. In my view, the most effective approach is to start where rich results offer the greatest visibility boost.
Crucially, keep dynamic data, like prices and stock levels, meticulously synchronized with your markup. A common mistake I have encountered is neglecting this, leading to Google potentially deprecating rich results due to data inconsistency. Finally, avoid the 'over-optimization' trap; only mark up information visibly present and directly relevant to the page's core content. Irrelevant schema can confuse search engines and offers no real SEO benefit.
Future-Proofing Your SEO Strategy with Structured Data
Mastering JSON-LD for SEO is pivotal for constructing the semantic web, allowing search engines to profoundly grasp content context. In my experience, even deploying basic schema types like Article or Product consistently delivers noticeable improvements in visibility and CTR.
I firmly believe that proactive engagement with JSON-LD for SEO isn't merely an optimization, but a fundamental shift towards a future-ready search strategy. Staying abreast of the latest Google guidelines is paramount for sustained impact. Start now by implementing Article schema on your most critical blog posts to secure your place in the evolving search landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions About JSON-LD for SEO
What is JSON-LD for SEO?
JSON-LD for SEO is a script-based format used to implement structured data on a website. It helps search engines understand page content, enabling rich results like star ratings and product prices.
Why does Google recommend JSON-LD?
Google recommends JSON-LD because it is easy to implement and maintain. Unlike other formats, it is separate from the HTML body, reducing the risk of breaking code during site updates.
Where should I place JSON-LD code?
It is best practice to place JSON-LD scripts within the <head> section of your HTML, although search engines can also process it if placed in the <body>.
How do I validate my JSON-LD markup?
You can validate your markup using the Google Rich Results Test to check eligibility and the Schema Markup Validator to identify syntax or structural errors.