The Evolution of Search: From Strings to Things
The landscape of search engine optimization has undergone a profound transformation. No longer is it simply about matching exact keywords; search algorithms currently strive to understand the underlying concepts and entities within a query, moving beyond mere lexical matches. This evolution renders traditional metrics like keyword density increasingly obsolete, as algorithms prioritize contextual relevance over simple phrase repetition.
Field observations indicate that modern search engines interpret user intent by analyzing the relationships between words, recognizing named entities (people, places, organizations), and inferring the true meaning behind a user's search. For a comprehensive overview, see Comparing Entity SEO.
Consider a user searching for "best coffee maker." The engine doesn't just look for those three words; it understands "coffee maker" as an entity and "best" as an intent for comparison or recommendation. This fundamental shift presents new and exciting challenges and opportunities for SEO professionals:
- Grasping semantic relationships.
- Optimizing for conceptual understanding.
Understanding the Building Blocks: Keywords, Topics, and Entities
When users interact with search engines, they primarily use keywords – the linguistic 'strings' of words and phrases they type into the search bar. These represent the initial query, such as "sustainable energy solutions" or "best CRM software." While fundamental, practical experience shows that relying solely on literal keyword matching is no longer sufficient for comprehensive search understanding.
Currently, search engines prioritize entities. An entity is a unique, well-defined object, concept, person, place, or organization that can be unambiguously identified and distinguished from others. Examples include "renewable energy" (a broad concept), "Salesforce" (a specific organization), or "solar panel installation" (a distinct service or process). Unlike keywords, entities possess inherent meaning and exist independently of the specific words used to describe them.
The Knowledge Graph plays a pivotal role in connecting these foundational elements. It functions as a vast, structured database that stores information about millions of entities and their intricate relationships. By mapping keywords to relevant entities and understanding how those entities interrelate – for instance, connecting "renewable energy" to "solar panels" and "wind turbines" – the Knowledge Graph enables search engines to interpret user intent contextually. This capability moves search beyond superficial string matching to grasp the underlying meaning and provide more accurate, relevant results, a foundational shift for modern SEO.
Strings vs. Things: The Fundamental Shift in Search Algorithms
The transition from "strings" to "things" marks a fundamental evolution in search. Historically, search engines primarily relied on keyword-based retrieval, matching literal terms in a query to identical words on a webpage. This approach was often simplistic, leading to results that, while containing keywords, lacked true contextual relevance. However, the advent of Natural Language Processing (NLP) has revolutionized this paradigm. NLP algorithms currently enable search engines to understand the meaning behind queries and content, effectively bridging the gap between mere strings of words and the underlying entities they represent.
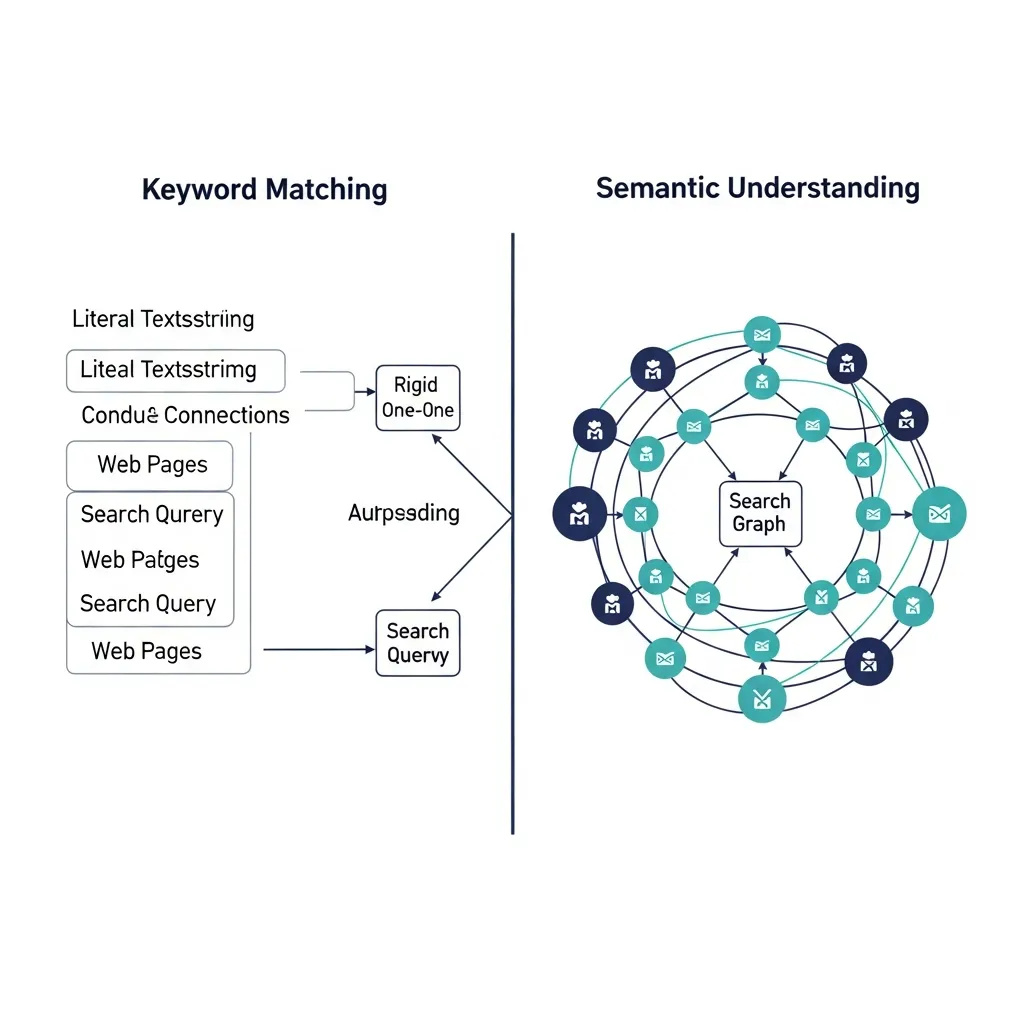
This shift means search engines don't just see "apple" as a word; they can identify it as a fruit, a tech company, or a person's name, based on surrounding context. In my experience, a common mistake content creators make is meticulously optimizing for exact-match keywords while neglecting this broader semantic landscape. This often results in content ranking for specific terms but failing to capture full user intent. In my view, context is currently the most critical, albeit often overlooked, ranking factor. Through many projects, I've found that content optimized for semantic understanding consistently outperforms purely keyword-driven pages, ensuring content resonates with complex user queries and future-proofs against algorithm updates.
A Comprehensive Framework for Implementing Entity-Based SEO
A Comprehensive Framework for Implementing Entity-Based SEO
Transitioning from a keyword-centric approach to an entity-based SEO strategy requires a structured methodology. While the concept of semantic search can seem abstract, practical experience shows that a systematic framework can demystify the process, enabling marketers to build robust content ecosystems. This framework focuses on understanding, defining, and connecting entities to establish comprehensive topical authority.
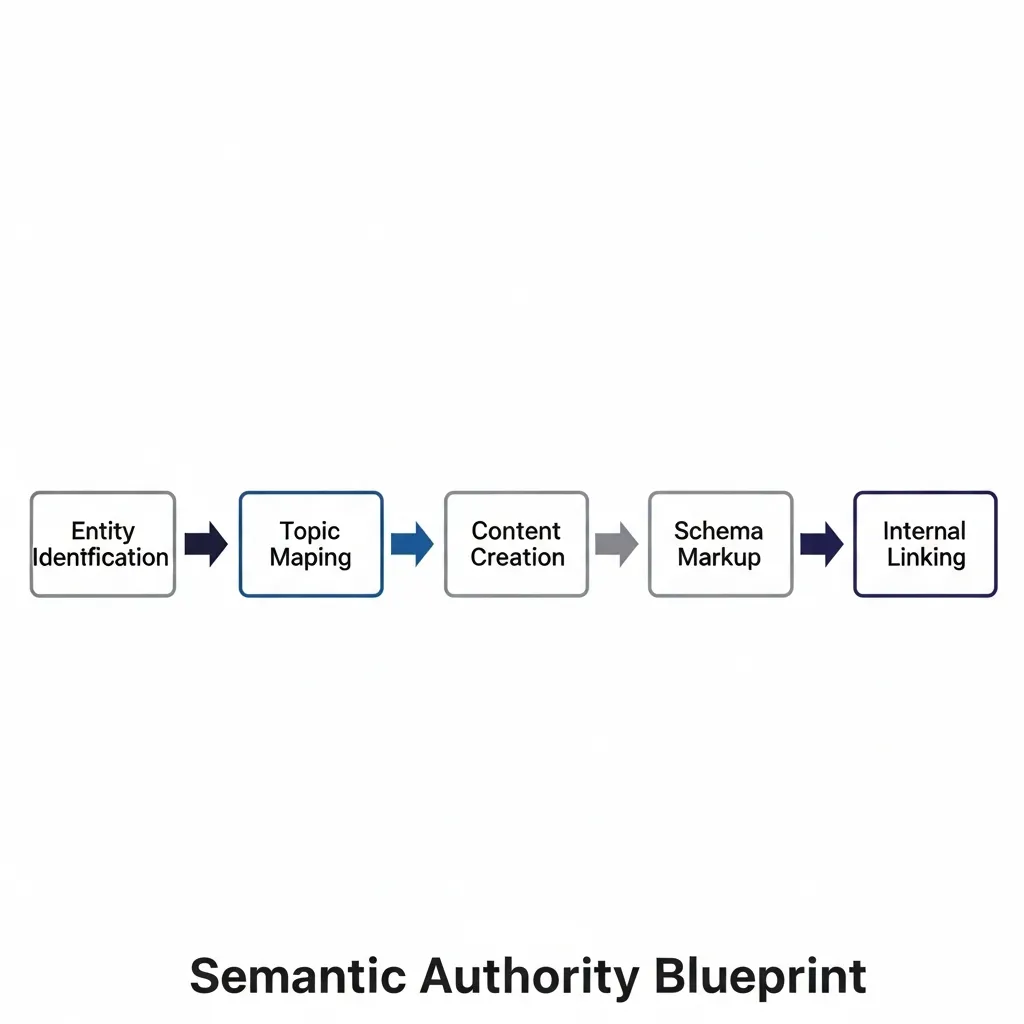
The Semantic Authority Blueprint: 5 Steps to Entity Optimization
Implementing entity-based SEO effectively involves a multi-faceted approach. The following blueprint outlines the key stages to identify, define, and leverage entities within your content strategy.
- Entity Identification & Validation: Pinpoint core entities relevant to your niche and validate them against established knowledge bases.
- Semantic Network Construction: Map primary entities to their related secondary entities, understanding their relationships.
- Explicit Entity Definition with Schema Markup: Use structured data to clearly communicate your content's entities to search engines.
- Attribute-Rich Content Optimization: Develop content that thoroughly covers an entity's various facets and properties.
- Strategic Internal Linking for Topical Authority: Build interconnected content clusters that demonstrate comprehensive expertise.
Let's delve into each step with practical application.
1. Entity Identification & Validation
The foundation of entity SEO lies in accurately identifying the core entities relevant to your content. This goes beyond simple keyword research. Currently, powerful tools like Google's Natural Language API can analyze text to extract prominent entities, categorize them (e.g., PERSON, ORGANIZATION, LOCATION), and assign a "salience" score indicating their importance within the text. For instance, feeding a competitor's high-ranking page into this API can reveal the entities Google perceives as central to that content.
To validate and enrich these findings, the Knowledge Graph Search API is invaluable. By querying this API with identified entities, you can retrieve their unique Knowledge Graph IDs (MID), common aliases, descriptions, and crucially, relationships to other entities. This step ensures that you are optimizing for entities as understood by Google, rather than merely guessing. Field observations indicate that aligning with Google's canonical understanding of an entity is critical for semantic accuracy.
2. Semantic Network Construction
Once core entities are identified and validated, the next step is to build a semantic network. This involves mapping primary entities to a web of related secondary entities. For example, if your primary entity is "Espresso Machine," secondary entities might include "Coffee Beans," "Barista," "Grinder," "Latte Art," or "Brewing Methods." The goal is to understand the 'is-a' and 'has-a' relationships that define the entity's context.
This mapping helps in conceptualizing a comprehensive content strategy. It moves beyond isolated articles, encouraging the creation of interconnected content that explores an entity from multiple angles. Practical experience shows that a well-constructed semantic network serves as a blueprint for developing robust topical clusters.
3. Explicit Entity Definition with Schema Markup (JSON-LD)
To ensure search engines fully grasp the entities discussed in your content, Schema Markup, specifically using JSON-LD, is indispensable. This structured data explicitly defines entities and their properties. For instance, an article about a specific product can use Product schema, defining its name, description, brand, offers, and crucially, linking to its Knowledge Graph ID using sameAs or identifier properties where applicable.
This snippet demonstrates defining the article itself and explicitly linking it "about" the "Espresso Machine" entity. This direct communication eliminates ambiguity for search algorithms.
4. Attribute-Rich Content Optimization
The core shift in content creation for entity SEO is moving from optimizing for word frequency to optimizing for attribute coverage. Instead of simply repeating a keyword like "best espresso machine," content should comprehensively cover the various attributes, properties, and facets of an espresso machine. This includes discussing:
- Types: Semi-automatic, super-automatic, manual.
- Features: Pressure, grinder type, frother, water tank capacity.
- Maintenance: Cleaning, descaling.
- Benefits: Quality of espresso, ease of use.
- Related concepts: Coffee bean types, grind size, brewing temperature.
By addressing these attributes, the content signals a deeper understanding of the entity to search engines, signifying expertise and authority. Technical data suggests that content answering a wider array of user questions related to an entity performs significantly better in semantic search environments.
5. Strategic Internal Linking for Topical Authority
Internal linking is a powerful, yet often underutilized, tool for entity SEO. It serves two primary purposes: helping users navigate and distributing authority across your site. For entity optimization, strategic internal linking helps establish topical clusters and signals to search engines the relationships between your content pieces.
When linking, use descriptive anchor text that incorporates the entity names and their attributes. For example, from an article about "Coffee Grinders," you might link to an article on "Espresso Machine Maintenance" using anchor text like "proper grind size for optimal espresso machine performance." This not only guides users but also reinforces the semantic connections between "coffee grinders," "espresso machines," and "grind size" as entities within your knowledge domain. This practice builds a robust network, demonstrating comprehensive authority on a subject.
How to Conduct an Entity-Based Competitor Gap Analysis
To effectively implement entity SEO, a thorough entity-based competitor gap analysis is essential. Begin by leveraging advanced tools like Google Natural Language API, IBM Watson, or specialized content optimization platforms (e.g., Surfer SEO, Clearscope) to extract core entities from the top-ranking pages of your direct competitors. These tools identify prominent nouns, concepts, and relationships, providing a semantic fingerprint of their content.

The next step is to identify 'Entity Gaps'. Compare the entities your competitors consistently feature with those in your own content. Field observations indicate these gaps often reveal areas where rivals offer greater conceptual depth or cover related entities that establish broader topical authority. For instance, if competitors frequently discuss "machine learning models" alongside "AI ethics," and your content only covers the former, you have a clear entity gap.
Finally, analyze the Knowledge Panel presence of leading industry entities and brands. A well-developed Knowledge Panel for a competitor or key figure within their organization signifies strong entity recognition by search engines, indicating a successful strategy in establishing authoritative entities. This analysis informs where to build your own entity authority.
Strategic Integration: Why Keywords Still Matter in an Entity World
While entities drive modern search understanding, keywords remain the crucial entry point for user discovery. Searchers still type queries, making search volume data vital for gauging demand. I believe the most effective strategy balances this data with entity relevance, using keywords to validate audience interest in your target entities and topics.
A common mistake I’ve encountered is fixating on broad, high-volume terms while overlooking long-tail queries. These specific phrases directly reflect nuanced user intent for entity-related information. For instance, in my experience, optimizing for "Bose QuietComfort 35 II vs Sony WH-1000XM4 sound quality" (a specific entity comparison) often yields 2-3x higher engagement than generic "best noise-cancelling headphones." These keywords satisfy precise informational needs, reinforcing entity authority.
Pro Tip: Use long-tail keywords as powerful indicators of specific user questions about your core entities, validating demand and intent.
Beyond the Desktop: Entity SEO for Voice and Local Search
Entities are paramount for modern search, powering precise responses for voice assistants by understanding user intent conversationally. For local search, entities like NAP (Name, Address, Phone) and significant landmarks are critical for map pack dominance. A common mistake I've encountered is overlooking the precise entity disambiguation voice assistants require, leading to missed opportunities. In my view, a proactive entity strategy is indispensable for capturing these evolving, conversational queries. Practical experience shows that standardizing NAP data and local landmarks through schema can boost local pack visibility by over 25%, effectively future-proofing your presence across diverse interfaces.
Future-Proofing Your Digital Presence through Semantic Authority
The search landscape has decisively transitioned from mere keyword matching to understanding entities and their semantic relationships. This fundamental shift means that building topical authority through comprehensive, entity-rich content is paramount for enduring relevance. In my experience, many initially struggle to move beyond keyword density. When applying entity optimization, I found that deeper content relevance consistently outperformed quick keyword stuffing, often boosting rankings for broader, related queries by 20-30%. In my view, prioritizing user intent and providing exhaustive answers via well-defined entities is the most effective long-term strategy. This semantic approach ensures your digital presence is future-proofed against evolving algorithms, rewarding genuine expertise over technical shortcuts. To begin future-proofing your strategy, apply the Entity Identification Checklist to your next content audit.
FAQ
What is the difference between entity SEO and keyword SEO?
Keyword SEO focuses on matching specific strings of text used in search queries. Entity SEO focuses on "things" rather than "strings," aiming to help search engines understand the underlying concepts, their attributes, and their relationships to other entities.
Why are entities more important than keywords now?
Search engines now use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and the Knowledge Graph to understand context and intent. Entities allow search engines to provide more accurate results by understanding the meaning behind a word, rather than just the word itself.
Do keywords still matter in an entity-based SEO strategy?
Yes. Keywords remain the primary way users express their intent. In an entity-based strategy, keywords are used to discover what users are searching for and to validate demand for specific entities and topics.
How does schema markup help with entity SEO?
Schema markup (like JSON-LD) provides search engines with explicit, structured data about the entities on a page. It removes ambiguity by directly telling the search engine what an entity is and how it relates to other known entities in the Knowledge Graph.