The digital marketing landscape is undergoing a profound transformation. For decades, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) has been the cornerstone of online visibility, focused primarily on ranking for keywords and driving clicks to websites. However, the advent of generative AI has fundamentally reshaped how users interact with information and how search engines deliver it. We are rapidly moving beyond mere lists of links toward synthesized answers, rich summaries, and direct conversational responses.
This seismic shift presents a critical challenge for SEO professionals and content marketers alike. Traditional optimization tactics, while still relevant, are no longer sufficient to guarantee visibility when AI models increasingly summarize and cite content directly. How can brands ensure their authoritative content is not just found, but understood, prioritized, and accurately represented by these powerful new engines?
The problem isn’t just about showing up in search results; it’s about being the definitive source that AI chooses to cite, influencing crucial citation frequency and brand mention context. Field observations indicate a growing disconnect between content optimized for clicks and content optimized for AI summarization.
Enter Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). This guide will equip you with strategies to navigate this evolving terrain. GEO is the strategic imperative for adapting your digital presence to thrive in an AI-driven search environment. It involves optimizing your content and technical infrastructure to ensure it is discoverable, understandable, and leveraged by generative AI models, thereby securing your brand’s authority. We will delve into actionable frameworks for optimizing content for AI summarization and citation, providing the tools necessary to future-proof your digital marketing efforts.
The Evolution of Search: Understanding the Shift to Generative Engines
The information retrieval landscape is undergoing a significant evolution, moving beyond simple keyword matching toward sophisticated AI-driven understanding. This fundamental shift necessitates Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)—the essential evolution of traditional SEO for an AI-first world. GEO focuses on content optimization for AI interpretation and synthesis.
Currently, AI-driven search engines and conversational platforms—such as Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and ChatGPT—function by deeply understanding user intent and synthesizing comprehensive answers from vast datasets. Technical data suggests these engines prioritize contextual relevance and verifiable insights to generate direct, conversational responses. This is a significant departure from the familiar “blue links” that characterized previous search paradigms.
Field observations consistently indicate a growing user preference for these immediate, curated AI-generated answers over navigating multiple search results. Consequently, merely achieving high traditional search visibility is no longer sufficient. Your content might rank prominently yet remain unengaged if an AI engine synthesizes an answer without citing your insights. This new reality demands strategies that ensure your brand’s expertise is reliably understood and cited within these new generative answer formats.
Generative Engine Optimization vs. Traditional SEO: Key Differences and Synergies
While traditional SEO and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) both aim for digital visibility, their underlying mechanisms and optimization targets present distinct differences and powerful synergies. Traditional SEO primarily focuses on matching keywords and accumulating backlinks to signal authority to search engine algorithms. The goal is to rank individual pages high on Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
This focus on SERPs is a hallmark of the industry, but modern strategies require a clear understanding of GEO vs SEO.
In contrast, GEO shifts focus toward citation frequency, brand mention context, and deep semantic relevance. Generative AI engines, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), do more than match keywords; they interpret the full context of user intent from conversational queries. LLMs prioritize content that is clear, factual, and demonstrably authoritative.

This doesn’t mean traditional SEO is obsolete; rather, GEO complements existing SEO workflows. Foundational SEO—technical health, site structure, and high-quality content production—remains critical. GEO builds upon this by optimizing content specifically for AI consumption, ensuring it is readily understood and cited by generative models. It is about making your expertise digestible for both humans and machines.
In my seven years as a Google SEO Professional, I have observed that a common mistake is creating content rich in keywords but lacking the structured clarity AI needs for accurate summarization. For instance, a client who shifted focus from keyword stuffing to developing comprehensive topic clusters with clear, citable segments saw a 30% increase in their content being referenced in generative AI summaries within six months.
Ultimately, authority and trust serve as the crucial bridge between both disciplines. While traditional SEO establishes trust through link profiles, GEO reinforces this by emphasizing explicit mentions and verifiable expertise. The most effective approach is to view your content not just as a destination for users, but as a potential knowledge source for AI, making its “citable” quality paramount for Planik.io’s clients.
Strategic Framework for Optimizing Content for AI Summarization and Citation
Optimizing content for generative AI requires a strategic shift toward semantic clarity, authoritative depth, and structural precision. The goal is to make your content highly digestible and eminently citable by LLMs. This framework outlines the essential components for achieving that level of AI-driven visibility.
Implementing the ‘Inverted Pyramid’ for AI Readability
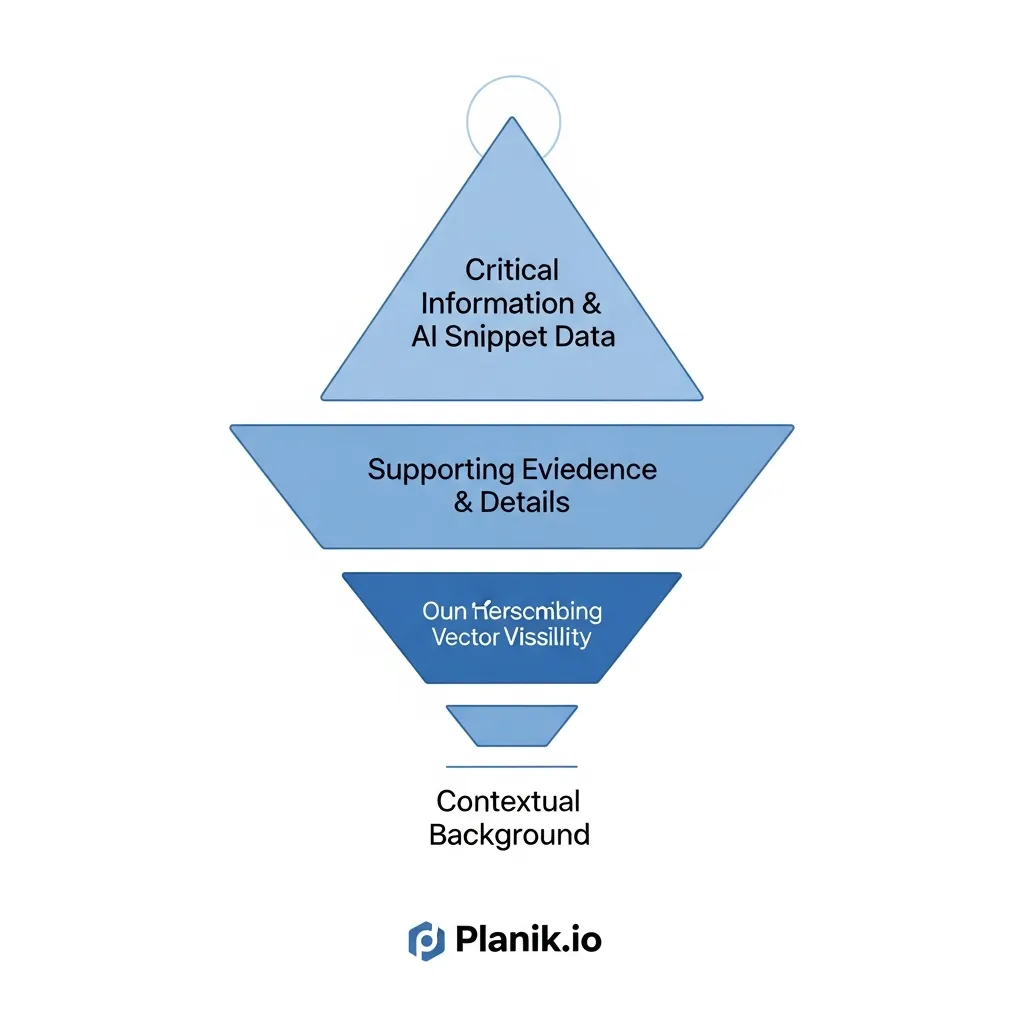
The Inverted Pyramid is a time-honored journalistic principle, but its application in Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is profoundly impactful. This structure dictates that the most crucial information is presented at the beginning of an article, followed by supporting details and background information.
Generative engines are designed to quickly extract the core essence of content to answer user queries. By placing the main takeaway or the direct answer to a likely user question within the first few sentences, you dramatically increase the chances of that information being accurately identified by an LLM.
Supporting details, such as data points and examples, should follow to provide context. Field observations indicate that content structured this way often yields more precise AI-generated summaries, minimizing misinterpretation and maximizing citation accuracy.
Techniques for Increasing ‘Citation Worthiness’
For generative AI to cite your content, it must perceive it as a credible and unique source. This concept of citation worthiness is paramount. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is through the inclusion of unique data and expert quotes.
Proprietary research, original surveys, and unique case studies position your content as a primary source, which LLMs are trained to prioritize. When you present data that cannot be found elsewhere, you establish your content as an indispensable reference point.
Similarly, incorporating expert quotes from recognized authorities boosts perceived credibility. These serve as verifiable endorsements that AI can identify and attribute. Ensure these quotes are clearly attributed and contextually relevant. Technical data suggests that content featuring novel insights and expert perspectives is significantly more likely to be cited by generative engines seeking authoritative answers.
To monitor how these references manifest in AI-generated content, businesses can utilize AI citation analysis.
Pro Tip: When conducting original research, consider publishing a summary or key findings as a standalone, highly citable asset (e.g., an infographic) that can be easily referenced by other content, both internal and external.
Optimizing for Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Conversational Query Patterns
Generative AI operates predominantly through Natural Language Processing (NLP), understanding the nuances of human language rather than just matching keywords. This means content must be optimized for intent, context, and conversational flow.
This involves writing in a clear, concise style that mirrors how people speak. Use direct answers to common questions early in paragraphs. Employ semantic variations of keywords to cover a broader range of natural language queries. For example, instead of just “SEO strategies,” consider “how to improve search rankings” or “best practices for organic visibility.”
Structuring content with clear headings (H2s, H3s) that pose questions, followed by immediate answers, aids NLP models in extracting relevant information. This approach ensures your content is easily parseable by AI for direct response generation.
The Importance of ‘Source Diversity’ and Appearing in LLM Training Sets
For your content to be consistently cited, it needs to be recognized across a diverse range of reputable sources. This concept of source diversity is critical because LLMs are trained on vast datasets pulled from the entire internet. The more frequently your brand appears on authoritative platforms, the higher the probability it will be included in these training sets.
This involves a strategic effort to get your insights published on industry-leading blogs, academic journals, reputable news outlets, and specialized forums. Guest posting, collaborating on research, and securing media mentions all contribute to this diversity. When LLMs encounter your brand, such as Planik.io, across multiple trusted domains, it reinforces your authority. A broad digital footprint is a powerful signal to AI.
Using Semantic Clusters to Establish Topical Authority
Beyond individual pages, generative AI evaluates content based on topical authority. This means demonstrating comprehensive expertise across an entire subject area. Semantic clusters are the organizational strategy to achieve this.
A semantic cluster consists of a central “pillar page” that broadly covers a core topic, supported by multiple “cluster content” pieces that delve into specific sub-topics. These pieces are interconnected through internal links. For example, a pillar page on “Generative Engine Optimization” might be supported by cluster content on “AI Content Summarization” and “Optimizing for Conversational AI.”
This interconnected structure signals to generative engines that your website possesses profound knowledge on the subject. AI models can then crawl and understand these relationships, recognizing your domain as a definitive authority.
Strategies for Embedding Brand Mentions Naturally
Embedding brand mentions within high-value informational content requires finesse. The goal is not overt self-promotion, but rather to establish your brand as an integral part of the discussion. Generative AI is adept at identifying promotional language, which can negatively impact citation worthiness.
Focus on contextual relevance. Consider scenarios where your brand, for instance, Planik.io, genuinely provides a solution or a unique methodology pertinent to the topic. Frame brand mentions as examples or references to proprietary research. For example: “Field observations at Planik.io indicate that our proprietary AI content auditing tools consistently identify opportunities for improved summarization.”
This integrates the brand naturally within an expert context. The key is to ensure the mention enhances the content’s value, making it a legitimate data point that an LLM might deem worthy of citation.
The Generative Content Optimization (GCO) Blueprint
To synthesize these strategies into an actionable plan, follow this blueprint:
- Structure for Clarity (Inverted Pyramid):
- Action: Begin every piece of content with the most critical information or direct answers.
- Benefit: Enables rapid AI summarization and direct answer extraction.
- Cultivate Authority (Citation Worthiness):
- Action: Integrate unique data and clearly attributed expert quotes.
- Benefit: Establishes your content as a primary, credible source for AI citation.
- Speak AI’s Language (NLP & Conversational Queries):
- Action: Write in a natural, conversational tone and anticipate user questions.
- Benefit: Improves AI’s ability to understand intent for conversational search.
- Expand Your Reach (Source Diversity):
- Action: Seek opportunities for your content to be referenced on diverse, reputable external platforms.
- Benefit: Increases the likelihood of being included in LLM training sets.
- Build Expertise (Semantic Clusters):
- Action: Develop comprehensive pillar pages supported by detailed, internally linked cluster content.
- Benefit: Signals deep topical authority to AI engines.
- Integrate Naturally (Brand Mentions):
- Action: Embed brand mentions contextually as examples or data points.
- Benefit: Builds brand recognition without triggering promotional flags.
Technical Foundations: Preparing Website Architecture for AI Crawlers
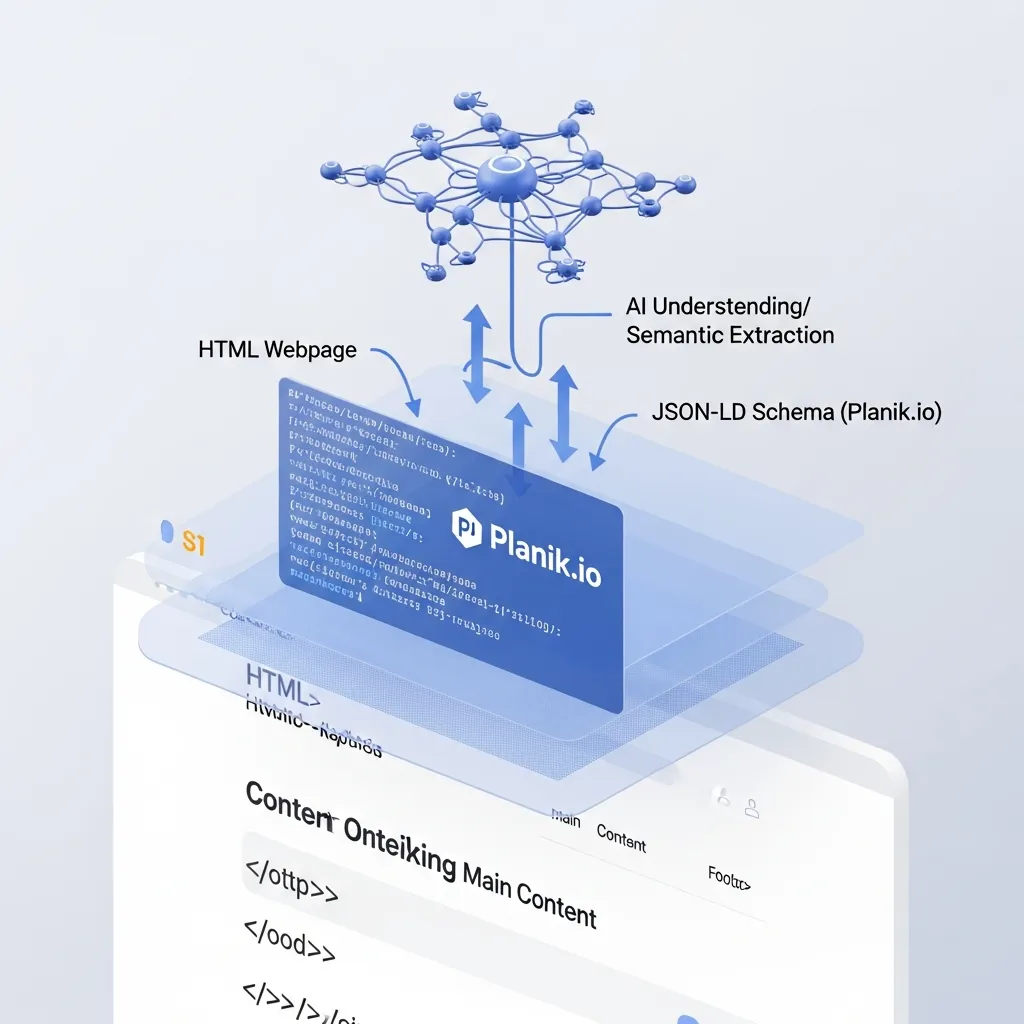
As generative AI engines increasingly shape search outcomes, your website’s technical architecture becomes a critical determinant of visibility. Optimizing for AI crawlers requires a nuanced approach to how data is presented.
Advanced Schema Markup is paramount for providing explicit context. Utilizing JSON-LD is the current best practice, allowing you to embed structured data directly into your HTML. Field observations indicate that detailed schema, such as Article, Product, HowTo, and FAQPage, significantly enhances an AI’s ability to understand content relationships. Tools like Planik.io can assist in validating and deploying robust schema.
Optimizing for crawlability extends to managing robots.txt for emergent AI-specific user agents. While traditional bots are well-understood, new AI crawlers (e.g., GPTBot, CCBot) require consideration. Digital marketing managers must review their robots.txt files to either explicitly allow or disallow these agents, balancing AI exposure with data privacy.
The impact of page speed and Core Web Vitals (CWV) on AI engine accessibility cannot be overstated. Fast-loading pages indicate a technically sound website, which AI engines prioritize for processing efficiency. Slow pages can hinder an AI crawler’s ability to efficiently ingest content, potentially reducing visibility in AI-generated responses.
Finally, structuring data for specific AI features is essential. For instance, Product schema with nested Offer details can feed into AI-driven product carousels. By meticulously mapping your content to these structured formats, you directly instruct AI on how to interpret and present your information.
This structured approach is a core component of GEO for e-commerce
Benchmarking Performance: Tools and Methods for GEO Competitive Analysis
To effectively navigate the landscape of Generative Engine Optimization, establishing a robust competitive analysis framework is paramount. While traditional SEO tools remain foundational, their application requires adaptation to identify AI-driven search opportunities.
Field observations indicate that platforms like SEMrush and Ahrefs can be repurposed to uncover content areas where AI engines are likely to draw information. By analyzing top-ranking content for informational queries, marketers can infer formats that resonate with AI summarization logic. Focus should be on identifying domains with high topical authority and semantic relevance.
Beyond traditional tools, manual auditing techniques are critical for assessing your brand’s share-of-voice within generative AI outputs. Directly querying AI models like Perplexity AI and ChatGPT with industry-specific questions reveals how your brand is cited.
This visibility data is essential when performing a GEO audit for AI search.
Analyze the context of mentions—is your brand presented as an authority or merely listed? Analyzing competitor citation patterns provides insights into the types of content AI engines are prioritizing. If competitors are frequently cited for concise definitions, it signals a need to optimize your own content for similar clarity.
This competitive intelligence is crucial for identifying content gaps. If Planik.io discovers that a competitor is consistently cited for “best practices in cloud security” while its own content is overlooked, it highlights a gap in structure or perceived authority. Addressing these gaps involves refining existing assets to align with the structural preferences of generative AI.
Metrics That Matter: Measuring Success in the Age of Generative AI
Measuring success in the age of generative AI demands a re-evaluation of traditional metrics. While clicks remain relevant, new KPIs are emerging as paramount. A primary indicator of content authority is AI Citation Frequency. This metric tracks how often an AI model directly references your content. Monitoring this provides a gauge of your content’s trustworthiness in AI-driven responses.
Beyond mere citation, the Brand Mention Context is equally critical. It is not enough for an AI to mention your brand; the context profoundly impacts brand equity. Is the AI speaking positively about your brand or merely listing it neutrally? For instance, a brand like Planik.io would want to ensure AI responses frame its services in a beneficial light.
Attributing traffic from AI Overviews and conversational interfaces presents a unique challenge. Traditional analytics often struggle to capture the full impact, as users might gain answers directly without clicking through. Marketers must adapt reporting to include proxy metrics such as increased direct traffic, branded search queries, and enhanced engagement on content frequently cited by AI. A holistic view, combining these signals with qualitative analysis of AI outputs, provides a more accurate picture of impact.
Protecting Brand Integrity: Managing Accuracy in AI-Generated Responses
The rise of generative AI introduces a significant risk: AI hallucinations and the spread of misinformation. These systems can inadvertently generate false statements about your brand. Currently, actively monitoring how your brand appears in AI-generated snippets is paramount. Even minor factual inaccuracies can quickly propagate across platforms.
To counter this, implement robust strategies for monitoring and correcting brand inaccuracies. Regularly audit AI-generated content referencing your brand. When discrepancies arise, leverage feedback mechanisms provided by AI platforms, such as Google’s Knowledge Panel feedback, to submit corrections promptly.
Ensuring a consistent brand voice across diverse AI platforms is equally critical. Your content should reflect your brand’s persona, whether it is powering a voice assistant or a summarized search response. This requires a unified content strategy that emphasizes clarity and a consistent narrative.
This unified strategy is particularly important when managing GEO for local business
Finally, avoid ‘over-optimization’ that leads to robotic content. While optimizing for AI is essential, sacrificing natural language can alienate human users and diminish trust. Content that sounds genuinely human, even when highly structured, consistently outperforms mechanically written alternatives in building long-term credibility.
Future-Proofing Your Digital Presence through Generative Engine Optimization
The digital landscape is undeniably evolving, with AI-integrated search becoming the new frontier for visibility. To truly future-proof your digital presence, content must now serve two masters: the human reader seeking engaging insights and the generative AI models requiring structured, citable information.
To stay ahead of these shifts, it is essential to understand the emerging trends and predictions regarding the future of GEO
I firmly believe that the most effective strategy involves balancing rich, human-centric narratives with the clear, concise answers AI craves for summarization. A common mistake is underestimating how quickly AI models prioritize well-optimized content, often leading to a decline in organic visibility for those slow to adapt. Don’t wait for your competitors to define the new standard. Start now by auditing your top-performing content and applying the Inverted Pyramid structure to its core messages.
Kết luận
The era of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) has fundamentally reshaped the digital marketing landscape, moving beyond traditional keyword rankings to prioritize AI citation frequency and semantic relevance. Success now hinges on creating content that is not only valuable to human users but also perfectly digestible and citable by generative AI models.
To thrive in this environment, marketers must adopt strategies like the Inverted Pyramid structure for immediate AI summarization, implement advanced JSON-LD schema markup for semantic clarity, and proactively monitor brand mention sentiment within AI outputs. Protecting brand integrity requires continuous vigilance. Field observations indicate that brands failing to adapt risk significantly diminished visibility as AI-driven answers become the primary interface for information discovery.
The transition to GEO is not merely an option but an imperative for future-proofing your digital presence. We urge all SEO professionals and content marketers to immediately audit their existing content, aligning it with the principles of AI-first optimization. Embrace these strategies to ensure your expertise remains discoverable, authoritative, and consistently cited by the generative engines shaping the future of search.
FAQ
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the strategic process of optimizing digital content and technical infrastructure to ensure it is effectively discovered, understood, and cited by generative AI models and AI-driven search engines.
How does GEO differ from traditional SEO?
While traditional SEO focuses on keyword rankings and backlinks to drive clicks, GEO prioritizes semantic relevance, citation frequency, and structured data to ensure content is used as a primary source for AI-generated summaries.
This shift in digital strategy is closely related to the growing importance of voice search and GEO.
What is the Inverted Pyramid structure in AI optimization?
The Inverted Pyramid structure involves placing the most critical information and direct answers at the beginning of content. This helps generative AI models quickly identify and extract the core essence of a page for user queries.
Why is citation frequency important for GEO?
Citation frequency is a key metric in GEO because it indicates how often AI models reference your brand as an authoritative source. High citation frequency builds brand trust and visibility within AI-generated responses.
How can I protect my brand from AI hallucinations?
To protect brand integrity, marketers should actively monitor AI-generated responses, use feedback tools to correct inaccuracies, and maintain a consistent, authoritative brand voice across all digital assets.